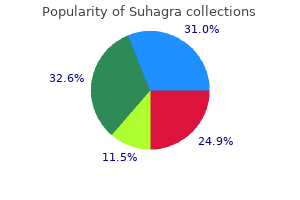
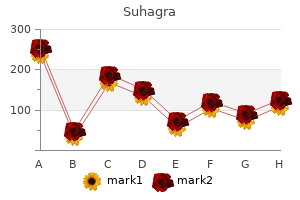
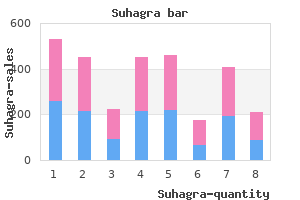
Suhagra
"Order suhagra from india, impotence 36".
By: Y. Urkrass, M.A., Ph.D.
Program Director, University of Massachusetts Medical School
It describes the final menstrual cycle erectile dysfunction doctor nyc order generic suhagra line, but is commonly used to describe the time in a woman’s life after that point erectile dysfunction unable to ejaculate suhagra 100 mg visa. It is ch ar act er iz ed in the years leading up to the menopause by irregular menstrual cycles outcome erectile dysfunction without treatment cheap suhagra 100mg with amex. Women often complain of night sweats, another form of hot flushes, wh ich must be different iat ed from a disease process or ot h er causes. At ages younger than 30 years, autoimmune diseases or karyotypic abnormalities should be considered. Sympt oms include irregular menses due t o anovulat or y cycles, vasomo- tor symptoms such as hot flushes, and decreased estrogen and androgen levels. The decreased est radiol concent rat ions lead t o vaginal at rophy, bone loss, and vasomotor symptoms. While most clinicians agree that hormone- replacement therapy is currently the best treatment for the vasomotor symptoms and to prevent osteoporosis, scient ific dat a raises concerns about the risks of this therapy. The Women’s Health Initiative Study of continuous estrogen– progestin treatment reported a small but significant increased risk of breast cancer, heart dis- ease, pulmonary embolism, and st roke. Women on hormone- replacement therapy had fewer fractures and a lower incidence of colon cancer. Short-term hormone-replacement therapy (5 years or less) is indicated for vaso- motor symptoms, and should be used for as short a duration as possible in the smallest dose. For women wh o cannot or ch oose not t o t ake est rogen, clonidine, or gabapent in may h elp wit h the vasomotor symptoms. Another class of pharmaceuticals that may be helpful to relieve the hot flushes is the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. A selective est rogen recept or modulat or, such as raloxifene, is helpful in prevent ing bone loss, but does not alter the hot flushes. Weight-bearing exercise, calcium and vitamin D supplement at ion, and est rogen replacement are import ant cornerst ones in main- taining bone mass. Other diseases that are important to consider in the perimenopausal woman include hypot hyroidism, diabet es mellitus, hypert ension, and breast cancer. Women in t his st age of life may also experience depression, whet her spont aneous in it s onset or situational due to grief or midlife adjustments. The practitioner should advocat e aerobic exercise at least t hree t imes a week, again, wit h weight -bearing exercise being advant ageous for t he prevent ion of ost eoporosis. Alcohol abuse may be seen in up t o 10% of post menopausal women, and requires clinical suspicion t o est ablish the diagnosis. The next step is to individualize patients based on stage and risk factors into the treatment of these women (Table 30– 1). W hich of t he following t est s is also likely t o reveal an abnormal fin d in g? O varian failure due t o follicular at resia is the reason for oligo-ovulat ion in the perimenopausal years. During perimenopause (or climacteric), follicular at resia occurs from hypoest rogenemia, as do t he vasomot or changes t hat lead to hot flushes. There is nothing dysfunctional occurring in this scenario, as it is a common occurrence in a perimenopausal pat ient. There is no pathol- ogy related to the ovaries; however, this patient will most likely be amenor- rheic due to the lack of stimulation to the ovaries by the gonadotropins. T h i s p a t i e n t m o s t l i k e l y h a s p o l yc ys t i c o va r i a n s yn d r o m e ( P C O S ). Because of this, they are often prescribed pro- gest er on e alon e or com bin at ion or al con t r acep t ive pills t o in du ce vagin al bleeding and to prevent endometrial hyperplasia. Ovarian failure is the most likely etiology in this woman with probable Turner syndrome (45,X). She most likely has decreased est rogen levels as well, wh ich predisposes h er t o complicat ions such as ost eoporosis lat er in life. This pat ient’s symptoms result from a chromosomal abnormality and not a hypo- thalamic or pituitary dysfunction. Excessive exercise may lead to hypothalamic dysfunction, but many times simple weight gain will lead to it s rest orat ion of funct ion. The “female athlete t riad” of eat ing disorder, amenorrhea, and osteoporosis is associated with hypothalamic dys- fu n ct ion an d h yp oest r ogen em ia.
Syndromes
- A tube thru the nose into the stomach to empty the stomach (gastric lavage)
- Look for sunscreens that block both UVA and UVB light.
- Ultrasound to locate the blockage of urine and find out how well the bladder empties
- Irritability
- Improving blood oxygen levels
- Drowsiness
- Premature atrial contractions (PAC)
- Sjogren syndrome
- Suddenly changing behavior, especially calmness after a period of anxiety
The husband reveals on the telephone that his wife has not slept since the baby was born and is making bizarre comments about the health of the baby natural treatment erectile dysfunction exercise buy suhagra with amex. Her psychiatric liaison worker has left a written care plan in her obstetric notes erectile dysfunction caused by stroke purchase cheap suhagra on-line. She gives a history of postnatal depression that involved several months of in-patient care following her previous delivery erectile dysfunction due to old age buy suhagra 100 mg. Initially there was some minor abdominal pain, but this has settled and there is no uterine activity. The uterus is nontender and the baby is well grown but appears to be lying transversely. There are no contractions and the condi- tion of both the mother and the baby is stable. An ultrasound scan confirms that the baby’s abdominal circumfer- ence is on the tenth centile of the growth chart and the liquor volume is less than expected. Answer [ ] A Candida albicans B Chlamydia trachomatis C Escherichia coli D Gardnerella vaginalis E Gonococcus F Group B streptococcus 45 03:11:03 06 46 G Listeria monocytogenes H Parvovirus B19 I Rubella J Streptococcus faecalis K Toxoplasma gondii The clinical scenarios that follow relate to women with infectious diseases in pregnancy. The community midwife refers her to hospital for an ultrasound scan, which shows polyhydramnios and fetal hydrops. On examination she is flushed, has a tachycardia of 100 bpm, and has a tem- perature of 38°C. Speculum examination reveals a florid ectropion with contact bleeding on taking swabs. On speculum examination there is a thick, white discharge adherent to the vaginal walls. Several children in her class have ‘slapped cheek syndrome’ at the start of term and when she comes to hospital for her routine anomaly scan her baby is found to be hydropic. Answer [ ] 46 03:11:03 06 47 Curriculum Module 4 Management of Labour and Delivery Syllabus You will be expected to have the knowledge, understanding, and judge- ment to be capable of initial management of intrapartum problems in a hospital and in a community setting. You will need to demonstrate appropriate knowledge of regional anaesthesia, analgesia, and operative delivery including caesarean section. This part of the exam will be much easier if you have worked on a labour ward since you were a medical student. In the last pregnancy she had a very slow first stage of labour and got stuck at 9 cm dilatation. The baby was in the occipito-posterior position, but there was no evidence of cephalo-pelvic disproportion. Which of these factors increases the chances of rupture of the uterine scar during labour? A primigravid woman whose baby is in the occipito-posterior position at the start of labour B. A woman with an otherwise uncomplicated pregnancy who has had a successful external cephalic version E. The woman refuses to give consent for the operation and the midwife looking after her thinks that she may be confused on account of her high temperature. Use the Mental Health Act to justify proceeding with caesarean delivery Answer [ ] 4. Halfway through the first stage of labour the patient has become increasingly distressed and is complaining of severe abdominal pain. The pain continues between contractions, which are occurring every 3 minutes and the midwife has noticed that the uterus is tender and hard on palpation. The inexperienced student midwife hands you a selection of drugs to choose from to try and stop the uterine bleeding. Which of the following pregnant women does not need a cannula when she is admitted? A woman who had a forceps delivery for fetal distress in her previous pregnancy E.
Factors that decrease risk of colorectal carcinoma: • Diet: Increased fbre erectile dysfunction treatment nyc buy suhagra 100mg with visa, fruits doctor for erectile dysfunction in gurgaon order suhagra 100 mg overnight delivery, vegetable erectile dysfunction doctor melbourne generic 100mg suhagra fast delivery, garlic, milk. Any patient over 40 years of age presenting with new large bowel symptoms should be investigated. Alarming symptoms are change in bowel habit, rectal bleeding, anorexia and weight loss, faecal incontinence, tenesmus and passing mucus per rectum. Remember the following: • Colorectal carcinoma is common in the Western world, less among Asians. Palliative: • Surgical resection of the primary tumour is appropriate for some patients with metastases to treat obstruction, bleeding or pain. Syptoms of anaemia: tiredness, weakness, dizziness, giddiness, breathlessness, palpitation, fatigue. Presentation of a Case: • This patient has generalized lymphadenopathy involving cervical, supraclavicular, axillary and inguinal lymph nodes which are of variable size and shape, rubbery in consistency, discrete, non-tender, free from underlying structure and overlying skin. My differential diagnoses are (mention according the age of the patient): If the patient is young or child: • Lymphoma (usually Hodgkin’s disease). It usually occurs in adolescence and young adults (20 to 35 years of age), also after 45 years of age (50 to 70 years, two peaks of incidence). Chest X-ray (shows bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy and widening of mediastinal shadow). Ultrasonography of whole abdomen (to see para-aortic lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly). A: It is a malignant cell of B-cell origin, characterized by: • Large cell with paired mirror image nuclei that resembles ‘Owl’s eye’ appearance. X: Bulky disease (a widening of the mediastinum by more than 1/3rd or the presence of a nodal mass. E: Involvement of a single extranodal site that is contiguous or proximal to the known nodal site. Staging is done for selection of therapy (radiotherapy or chemotherapy) and also helpful for prognosis. A: If no relapse after 5 years of withdrawal of treatment, it is called cure or disease-free. Skin involvement (T-cell lymphoma) presents as Mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome. A: 2 types or grades (depending on the rate at which the cells are dividing): Low grade shows the following characteristics: • Low cell proliferation rate. A:It is a circle of lymphatic tissue in posterior part of oropharynx and nasopharynx, which includes adenoids and tonsils (pharyngeal, tubal, palatine, lingual tonsil). Radiotherapy is also indicated for residual localized site of bulk disease after chemotherapy, for spinal cord and other compression syndrome. Transformation to high grade is associated with poor prognosis, occurs in 3% per annum. In high-grade lymphoma: 75% respond to initial therapy and 50% are disease free for 5 years. Relapse is associated with a poor response to further chemotherapy (,10% 5-year survival), but in patients under 65 years, bone marrow transplantation improves survival. Prognosis High cure rate Low cure rate (low-grade tumours are incurable) mebooksfree. Presentation of a Case (Elderly or Middle Aged): • Present as described in generalized lymphadenopathy. A: Common in the elderly, M:F 5 2:1, involving B lymphocyte, after 45 years (usually 60 to 70 years). A:It is a neoplastic disorder of lymphocyte that usually involves B-lymphocytes and rarely T-lymphocytes (5%). Another staging (Rai staging): • Stage 0: Lymphocytosis, no lymphadenopathy, no hepatosplenomegaly, no anaemia or no thrombocytopenia. A: Treatment depends on stage: • Stage A: No treatment, unless progression occurs. Symptomatic: • For anaemia and thrombocytopenia: Prednisolone and blood transfusion. If refractory or recurrent, splenectomy may be done (also indicated for hypersplenism).
Clue for the diagnosis of different types of goitre: • Diffuse and soft goitre fda approved erectile dysfunction drugs cheap suhagra 100mg, with exophthalmos: Suggestive of Graves disease erectile dysfunction zyrtec generic suhagra 100 mg. A: Because it is hard erectile dysfunction remedies pump purchase 100mg suhagra fast delivery, irregular surface and margin, fxed with the underlying structure. Usually, thyroid malignancy is associ- ated with euthyroidism, occasionally hyperthyroidism. Treatment and prognosis: • Total thyroidectomy followed by high dose (100 mCi) radioiodine therapy (to ablate remaining thyroid tissue and metastatic site). If raises, indicates recurrence or metastasis (normally, thyroglobulin is undetectable). Treatment: • Total thyroidectomy with removal of affected lymph nodes and thyroxine therapy. Large foot Widely apart teeth with prognathism Prognathism (side view) (front view) Presentation of a Case (General Examination): Case No. A: Because of the enlargement of peripheral (acral) parts of body (acro means periphery or limbs and megaly means big). A: Yes, if excess growth hormone starts in adolescence and persists in adult life, the two conditions may be present together. A: As follows: • Progressive increase in body size (may be history of change in size of rings, shoes, hats). The patient complains of sudden severe headache and loss of consciousness (require immediate neurosurgical intervention). Radiology: • Skull X-ray: It shows enlarged sella turcica, erosion of clinoid process, enlarged skull, mandible and sinuses. Surgery: • Trans-sphenoidal removal of pituitary tumour (high success rate, rapid reduction of growth hormone and low incidence of hypopituitarism). External irradiation by linear accelerator is given, when the tumour persists after surgery, to stop the tumour growth and to lower growth hormone levels. However, growth hormone level falls very slowly over many years (previously implantation of Yttrium was used). But it is less potent in lowering growth hormone and recurs after withdrawal of drug. Drugs: • Dopamine antagonist group of drugs: - Antipsychotic (phenothiazine, butyrophenones). Clinical features of hyperprolactinaemia: • Galactorrhoea, hypogonadism (commonest symptoms). Remember the following points: • If serum prolactin is high, repeat measurement is indicated to reconfrm. It is also done in macroadenoma, though complete removal may not be possible with risk of pituitary damage. In such case, dopamine agonist therapy (usually bromocriptine) should be started, if there are symptoms. There is truncal obesity with relatively lean and thin limbs (lemon on a match stick appearance). Plethoric moon face with Hirsutism and plethoric Buffalo hump—left arrow, stria on arm moon face supraclavicular fat right arrow, hirsutism mebooksfree. A: Striae are pink or purple coloured in the skin of abdomen and other parts of body. A: It is defned as constellation of symptoms and signs characterized by prolonged glucocorticoid excess due to any cause. A: Cortisol excess due to other illness without involvement of pituitary adrenal axis is called Pseudo- Cushing’s syndrome. There is increased urinary excretion of steroid, absent diurnal variation of cortisol and failure of suppression by dexamethasone. All the features of Cushing’s syndrome revert to normal after removal of the cause (features in favour of Cushing’s syndrome are bruise, myopathy and hypertension, all of which are usually absent in Pseudo- Cushing’s syndrome). Remember, if there is history of alcohol intake, advice the patient to stop taking alcohol. In Cushing’s syndrome due to adrenal cause: • In adrenal adenoma: Clinical features of glucocorticoid excess are present, but androgenic effect like hirsutism and virilization are absent and there is no pigmentation.
Buy suhagra overnight. Erectile Dysfunction: Treatment for ED.