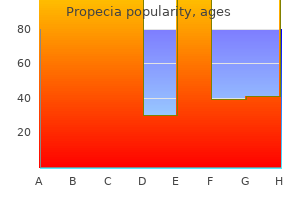
Propecia
"Order propecia 5 mg without prescription, hair loss chemo".
By: Q. Brant, M.S., Ph.D.
Co-Director, University of Missouri–Kansas City School of Medicine
This score has been available since the early 1990s and is the most widely recognized hair loss in toddlers propecia 5 mg line, used hair loss in men 3 button 1 mg propecia with mastercard, and validated score hair loss yeast infection buy propecia on line amex. These scores are not as simple as the Duke treadmill score but lend themselves to easy clinical application. To determine risk group, total points for the appropriate choice for each clinical and exercise test variable. If there is no appropriate choice for a particular variable, score points as zero for that variable. Estrogen status positive includes women who are premenopausal, receiving hormone replacement therapy, or with intact ovaries under age 50. Evaluation of pretest and exercise test scores to assess all-cause mortality in unselected patients presenting for exercise testing with symptoms of suspected coronary artery disease. It incorporates most of the important prognostic exercise test variables, as well as other important clinical variables. The originally published nomogram is more difficult to apply in routine clinical settings, but it is available in a more user-friendly, free, online software application (see Fig. None of these has been validated outside the derivation institution or compared to other scores (e. The score equation is: Score ranges of greater than 100, 0 to 100, −1 to −100, and less than −100 yielded mean survival at 10 years of 98%, 97%, 89%, and 62%, respectively. An integrated scoring model using these four parameters demonstrated a stepwise increase in risk as the number of abnormal parameters increased. As the number of these three abnormal treadmill variables increased, the risk of mortality increased regardless of the scan interpretation. A patient with a normal scan but two or three variables that were abnormal had the same all-cause mortality risk as a patient with a severely abnormal scan but two or three variables that were normal. In the original guidelines, exercise testing carried class I indications before hospital discharge (submaximal, 4 to 7 days), 14 to 21 days after discharge (symptom limited if not performed before discharge), and 3 to 6 weeks after discharge (symptom limited if predischarge submaximal exercise performed). In this setting the exercise test was found to be safe, with a reported mortality rate of 0. This subset of patients is likely to be a small percentage of the total postinfarction group. In addition, it is highly likely that many of these patients will undergo stress imaging rather than a simple exercise test. Preoperative Evaluation in Noncardiac Surgery Published guidelines for the preoperative evaluation of patients undergoing noncardiac surgery indicate a 36 limited role for simple exercise testing in this process (see Chapter 11). In most if not all patients who are candidates for stress imaging, this will be done with (or with the potential to convert to) pharmacologic stress. Exercise time is not generally chosen because of the influence of exercise training on the peripheral musculature with serial testing. Less prominent are applications that pertain to certain nonatherosclerotic conditions. In each case, exercise imaging, especially with echocardiography, provides important information for evaluation of these conditions. Exercise testing also has a role in patients with valvular heart disease who want to participate in 39 competitive athletic activity. Frequently, exercise testing is combined with echocardiography to assess structural and physiologic responses. This is the preferred approach in evaluating patients with mitral stenosis and disparate clinical and resting echocardiographic data, such as severe stenosis without symptoms or symptoms with mild to moderate stenosis. In patients with chronic severe mitral or aortic regurgitation, the diagnostic role of exercise testing is limited to the evaluation of functional capacity in patients with equivocal symptoms. Aortic Stenosis It is universally agreed that exercise testing is absolutely contraindicated in patients with symptomatic 38,40 severe valvular aortic stenosis. However, for asymptomatic patients, exercise testing has found a role in two specific scenarios (see Chapter 68). Patients with more moderate stenosis but suspected symptoms might also be considered. Customary practice is to defer aortic valve replacement until symptoms develop (see Chapter 67).
Rupture is often of abrupt onset hair loss in men 2a purchase cheap propecia on line, causes chest pain hair loss 12 months postpartum purchase propecia visa, and creates continuous arteriovenous shunting and acute volume loading of both right and left heart chambers hair loss in men 2 syndrome generic propecia 1 mg with mastercard, which promptly results in heart failure. An additional complication is infective endocarditis, which may originate either on the edges of the aneurysm or on those areas in the right side of the heart that are traumatized by the jet-like stream of blood flowing through the fistula. The presence of this anomaly should be suspected in a patient with a combination of chest pain of sudden onset; resting or exertional dyspnea; bounding pulses; and a loud, superficial, continuous murmur accentuated in diastole when the fistula opens into the right ventricle, as well as a thrill along the right or left lower sternal border. This may demonstrate generalized cardiomegaly and usually heart failure after the fistula develops. Studies based on 2D and pulsed Doppler echocardiography may detect the walls of the aneurysm and disturbed flow within the aneurysm or at the site of perforation. This reveals a left-to-right shunt at the ventricular or, less commonly, the atrial level; the diagnosis may be established definitively by retrograde thoracic aortography. Management Options and Outcomes Preoperative medical management consists of measures to relieve cardiac failure and to treat coexistent arrhythmias or endocarditis, when present. At operation the aneurysm is closed and amputated, and the aortic wall is reunited with the heart, either by direct suture or with a prosthesis. All efforts should be made to preserve the aortic valve in children because patch closure of the defect combined with prosthetic valve replacement greatly increases the risk of operation in small patients. Vascular Rings and Compression Morphology The term vascular ring is used for those aortic arch or pulmonary artery malformations that exhibit an abnormal relation with the esophagus and trachea, often causing dysphagia and/or respiratory symptoms. The most common vascular ring is produced by a double aortic arch in which both the right and left fourth embryonic aortic arches persist (eFig. In the most common type of double aortic arch, there is a left ligamentum arteriosum or occasionally a ductus arteriosus. Although both arches may be patent at the time of diagnosis, invariably the left arch distal to the left subclavian artery is atretic and is connected to the descending aorta by a fibrous remnant that completes the ring. In the setting where both arches are patent, the right arch is typically larger than the left. This usually occurs as an isolated lesion, with the respiratory symptoms being caused by tracheal compression and frequently associated laryngomalacia, usually in the neonate and young infant. A right aortic arch with a left ductus or ligamentum arteriosum connecting the left pulmonary artery and the upper part of the descending aorta is the next most frequent vascular ring seen. Although all cases with this lesion have a vascular ring, not all cases are symptomatic. Indeed, those patients who are symptomatic usually have an associated diverticulum of Kommerell. This is a large outpouching at the distal takeoff of the left subclavian artery from the descending aorta. It is the combination of the diverticulum and the ring that causes the airway compression. Other cases without a diverticulum of Kommerell have a loose vascular ring, made up of the aberrant left subclavian artery and a left ligamentum. Anomalous origin of a right subclavian artery is one of the most common abnormalities of the aortic arch. Although the aberrant right subclavian artery runs posterior to the esophagus, it does not form a vascular ring unless there is an associated right-sided ductus or ligamentum to complete the ring. During adulthood about 5% of patients with an aberrant right subclavian artery (and a left ductus) develop symptoms (usually dysphagia rather than respiratory symptoms) owing to rigidity of the aberrant vessel. In this setting there may be either an ascending left and descending right aorta or an ascending right and descending left aorta. The retroesophageal component of the descending aorta causes esophageal, and sometimes tracheal, compression, in conjunction with the left- or right-sided ligamentum. This is usually made up of the left pulmonary artery arising from the right pulmonary artery, which runs posterior to the trachea but anterior to the esophagus. This is usually seen in isolation and can be associated with significant hypoplasia of the tracheobronchial tree, which is the predominant cause of the airway symptoms. Clinical Features The symptoms produced by vascular rings depend on the tightness of anatomic compression of the trachea and esophagus and consist principally of respiratory difficulties, including stridor and dysphagia. Although most patients with a true ring and some airway compression present early in life, others present later with dysphagia and still others escape diagnosis forever. If there is evidence of a right aortic arch in a symptomatic patient, a vascular ring should be suspected. Prominent posterior indentation of the esophagus is observed in many of the common vascular ring arrangements, although the pulmonary artery vascular sling produces an anterior indentation.
The cardioplegia adminis- tration cannula is placed into the three-way stopcock and arranged so that cardioplegia can be administered into the arterial catheter hair loss cure news 2012 purchase generic propecia canada. As all of the arteries are controlled by snug- gers except the innominate artery hair loss men best order for propecia, the cardioplegia can infuse only the ascending aorta and thereby the coronary arteries hair loss using wen order cheapest propecia and propecia. Once this cardioplegia is administered, the snuggers on the innominate artery can be appropriately rearranged and the stopcock can be moved back for institution of regional perfu- sion. Once the neoaortic arch is constructed, the surgeon may elect to use the Sano shunt or to perform the systemic-to–pulmonary artery shunt, as the proximal anastomosis is already com- pleted. If the shunt option is elected, the neoaorta must be cannulated, and systemic perfusion is continued through this 20 Norwood Operation/Damus-Stansel-Kaye 301 route (not shown). The graft can then be measured regional perfusion can be converted to full systemic arterial and implanted into the isolated pulmonary artery. Generally, the proximal anastomosis is artery has been performed to place the main pulmonary performed first, after a small ventricular incision is made artery toward the right of the ascending neoaorta, so that the inferior to the pulmonary artery annulus to avoid injury to shunt can be placed as centrally as possible into pulmonary the pulmonary valve. This graft is This same clipped shunt can be used later to establish extra- measured very carefully to ensure that one or two ribs are corporeal membrane oxygenation if necessary. Ideally the exter- assessed and will guide the next phase of surgical nal ribs will stent the graft within the wall of the ventricle improvements. The pulmonary artery was connected end-to-side into the aorta and a conduit from the right ventricle to the pul- monary artery was placed to complete the repair. In this manner, the aortic valve, which still arises from the right ventricle, remains closed by the aortic pressure, which is greater than the right ventricular pressure. Historically, this procedure has been useful in patients who are undergoing staged conversion from an atrial baffle procedure to sys- temic correction, because dense adhesions after multiple operations may prohibit coronary transfer and arterial switch. Others have used this approach for patients with the Taussig-Bing anomaly, with good results. The disadvan- tages of this operation involve the fate of the aortic valve, which is situated over the right ventricle in a static, closed position and is subject to leaking and clot formation. Another obvious disadvantage is the need for periodic con- duit changes as the child grows. This principle is now used to treat patients undergoing a univentricular repair whose anatomic details involve the aorta arising from an outflow chamber that is connected to the functionally single ven- tricle through a bulboventricular foramen that can also be referred to as a ventricular septal defect. The bulboventric- ular foramen can become obstructive and has the same physiologic effect as subaortic stenosis. Other surgeons prefer to use the Damus-Stansel-Kaye prin- ciple to bypass the obstructed foramen and allow unob- monary artery and aorta is performed. In: Mavroudis C, artery is transected close to the bifurcation, and the distal Backer C, editors. It is characterized by an Operative epicardial findings are characterized by a visible abnormal, direct, paravalvular, endothelialized communica- bulge along the anterolateral aspect of the aorta, which tion between the ascending aorta and the left ventricle. Most represents the fibromuscular tunnel wall that lies in direct cases arise upstream of the right coronary sinus, above the histologic continuity with the aorta. The posterior wall sinotubular junction; origin from the left coronary sinus is contains the true aortic wall, with the inferomedial aspect or rare. Patients present with symptoms of congestive heart the floor of the tunnel involving the muscle of the right failure in the first year of life owing to the physiologic ventricular outflow tract. Standard aorto- bicaval cardiopulmonary bypass is used with mild cooling, left ventricular venting, and a combination of antegrade and retrograde cardioplegia. The topical anatomy and echo- cardiographic findings will determine whether to use one or two patches for the repair. Type I defects can usually be approached through a transverse aortotomy with pericardial patch closure of the defect, usually above or downstream of the right coronary sinus of Valsalva. The coronary artery is usually not involved, but special care is taken not to constrict the orifice with the suture technique used to close the tunnel. Those patients with extracardiac or intracardiac aneurysmal dilatation will require two patches for repair. The tunnel is depicted as being above the right coronary sinus and above or downstream of the right coronary orifice. After aortobicaval cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegic arrest (antegrade and retrograde techniques) are established, the aorta is subtotally or totally transected to maximally dis- play the anatomy (Fig. Care must be taken to confirm both pathways, the tunnel and the coronary artery course.
Generic propecia 1 mg amex. Hair Fall and Homeopathic Cure with 20 Real Time Cases.