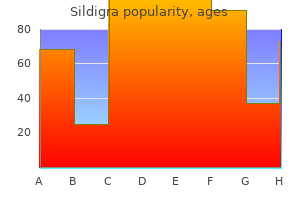
Sildigra
"Buy sildigra 100mg lowest price, erectile dysfunction kamagra".
By: S. Derek, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, University of Utah School of Medicine
Recommendation Patients with migraine and tension-type headache tend to develop psychological states such as anxiety and depression as a level of symptom erectile dysfunction beta blockers buy 120 mg sildigra with amex, and these psychological states are associated with chronicity of headache erectile dysfunction due to medication cheapest sildigra. In addition erectile dysfunction quetiapine discount sildigra uk, psychiatric disorders such as mood disturbances (major depression) and anxiety disorder (including panic disorder) are common comorbidities. Paying attention to the coexistence of these psychological states and psychiatric disorders is clinically important. Grade B Background and Objective Psychological factors such as anxiety and depression have been known to be closely associated with the onset and progression of migraine and tension-type headache. In addition, many studies have reported various psychiatric disorders that tend to be coexist with primary headaches, such as mood disturbances (such as major depression, dysthymia, and bipolar disorder), drug addiction, anxiety disorders (panic disorder, phobia, generalized anxiety disorder), somatoform disorder (such as somatization disorder, and pain disorder). Especially, the involvement of abnormal serotonin metabolism in the relationship between migraine and panic disorder or major depression has gained attention. The objective of this section is to collect available literature and present the knowledge concerning the relationship between primary headaches and depression or anxiety. Comment and Evidence For migraine, large epidemiological surveys have been conducted actively. The annual prevalence of major depression among migraine patients has been reported to be approximately 8. Many studies so far have demonstrated an association of migraine with major depression, panic disorder, and phobia, but no signifcant relationship with obsessive compulsive disorder and substance abuse. Psychiatric comorbidities in migraine patients in headache centers also showed similar high association9)-11) as in epidemiological studies. The prevalence of psychiatric comorbidities in migraine patients is especially high in migraine with aura, chronic migraine, and migraine with medication overuse. The association with psychological states including psychosocial stress and anxiety/depression has been found, and psychiatric comorbidities including mood disturbances (such as depression), anxiety disorders (such as panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, and obsessive-compulsive disorder), and somatoform disorders have also been reported9)10)13) as in migraine. However, the evaluation methods for psychological states or psychiatric disorders are not standardized. While the high association has been attributed to the involvement of serotonin, a consensus is yet to be arrived. The Italian Collaborative Group for the Study of Psychopathological Factors in Primary Headaches. Recommendation Occupational health physicians and brain health check-up physicians should participate actively in providing headache medical care for workers and health check-up receivers with headaches. Grade A Background and Objective The objective of this section is to search for literature on the frequency and status of persons with primary headaches in the workplace and brain health check-up setting to examine the roles of occupational health physicians and brain health check-up physicians in providing medical care for headache. Comment and Evidence Migraine has been reported to cause reduction in working hours and socio-economic loss. Brain health check-up fndings of those who had migraine revealed cerebral aneurysm (1. Occupational health physicians and brain health check-up physicians should identify serious secondary headaches and promptly refer the afected workers and health check-up receivers to appropriate medical facilities, organize headache educational activities in the workplace to detect persons with primary headaches that cause disability in daily living, and guide these persons to receive appropriate medical care. Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Grants-in-aid for Medical Research on Mental Health “Research Related to the Development of Diagnostic and Treatment Guidelines for Chronic Headache”, Summary and Co investigator’s Study Reports for 2003. Recommendation In addition to primary headaches such as migraine and tension-type headache, headaches encountered in schools also include headache as one form of psychosomatic pain. In schools, school nurses look after children who complain of headache, but school physicians are also sometimes consulted regarding headaches. Terefore, school physicians should possess correct knowledge on primary headaches (especially migraine). Headaches may be related to the circumstances surrounding the children, such as stress with teachers and classmates in school or problems at home. Terefore, understanding the background of the children and the mental issues during the developmental process is sometimes necessary. Grade A Background and Objective Among the complaints of children at school, headache is one of the most common symptoms. Although headache can be a symptom of acute diseases such as upper respiratory tract infection, primary headaches represented by migraine and tension-type headache are also frequently encountered in school settings. While the teacher in charge of the class is usually the frst to deal with headache, the actual care is provided by the school nurse. The school physician provides health consultation for school children and students, and is also consulted about headache through the school nurse during health check-ups and other situations. In students who refuse to go to school or enter classroom, headache is a common reason.
Lactation the American Academy of Paediatrics classifies nitrofurantoin as compatible with breastfeeding (18) impotence vacuum pump buy generic sildigra online. Other than in these women impotence effects on relationships order discount sildigra on line, if nitrofurantoin is strongly indicated breastfeeding may continue (21) erectile dysfunction 30 years old buy 25mg sildigra fast delivery. Issued by the manufacturer state: (Macrodantin®) “Caution should be exercised while breastfeeding an infant known or suspected to have any erythrocyte enzyme deficiency as nitrofurantoin is detected in trace amounts in breast milk. Nitrofurantoin is contraindicated in infants under three months as well as pregnant women at term (in labour and delivery) because of the theoretical possibilities of haemolytic anaemia in the fetus” (51). There are over 25,000 published cases of amoxicillin use during pregnancy, no increased risks of spontaneous miscarriage, overall congenital malformation, intrauterine death or neonatal complications were identified in these analyses (52). Amoxicillin was associated in two studies with an increase in facial clefts (37, 53). However, it is worth noting that in one of these study’s the absolute risk for cleft lip/ palate increased from the baseline risk of 1-2 per 1,000 live births to 2-4 per 1,000 live births. This was a doubling of relative risk but quite a modest increase in absolute terms compared with the overall baseline risk of malformations at birth of about 30 per 1,000 (54). Most studies have not suggested an increase in malformations associated with this drug (12). Limited information indicates that single maternal doses of amoxicillin 1 gram produce low levels in milk that are not expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. Limited information indicates that single maternal doses of penicillin G of 4 million units intramuscularly produce low levels in milk that are not expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. Limited information indicates that single maternal doses of penicillin V of 1320 mg produce low levels in milk that are not expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. In summary: Penicillin derivatives are the antibiotics of choice during breastfeeding (21). Because tazobactam is a penicillin derivative, it is also ® probably safe in pregnancy and Reprotox states that “Based on experimental animal data, tazobactam therapy is not expected to increase the risk of congenital anomalies” (12). No fetal harm in animals was observed when the piperacillin-tazobactam combination was used at doses close to those used in humans (6). Lactmed says that the use of piperacillin tazobactum combination is acceptable during breastfeeding (22). Although no information is available on the use of piperacillin and tazobactam during breastfeeding, limited information indicates that maternal doses of piperacillin produce low levels in milk that are not expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. Owing to the high sodium content of this antibiotic, high doses may lead to hypernatraemia (7). Issued by the manufacturer state: (Tazocin®): “Piperacillin is excreted in low concentrations in human milk; tazobactam concentrations in human milk have not been studied. Women who are breastfeeding should be treated only if the expected benefit outweighs the possible risks to the woman and child” (23). Schaefer et al states “despite its toxicity, quinine belongs to the drugs of choice when dealing with chloroquine-resistant malaria tropica in pregnancy. Quinine containing analgesics and excessive or regular consumption of quinine containing drinks should be avoided during pregnancy (21). Treatment with quinine has been reported to increase insulin secretion and prescribers should be vigilant for the associated risk of maternal hypoglycaemia (57). A small risk cannot be excluded, but a high risk of congenital anomalies in the children of women treated with low therapeutic doses (300-500 mg/d) of quinine during pregnancy is unlikely (13). Lactation the American Academy of Paediatrics classifies quinine as compatible with breastfeeding (18). Due to the low levels of quinine in breast milk, amounts ingested by the infant are small and would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. However, quinine should not be used in mothers with an infant who is glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficient (22). With malaria prophylaxis, the exposure for the infant may continue for considerably longer than with acute therapy. General recommendations are therefore more difficult and so limitation of breastfeeding should be decided on a case by case evaluation in consultation with a specialist. However, quinine is among the drugs for which there is most experience and it doesn’t have substantial indications of potential for damage via the mother’s milk (21).
However erectile dysfunction medications causing purchase generic sildigra, because there is no published experience with linezolid during breastfeeding erectile dysfunction yoga exercises buy sildigra with american express, an alternate drug may be preferred erectile dysfunction caffeine order sildigra mastercard, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant (22). Issued by the manufacturer state: (Zyvox®) “Animal data suggest that linezolid and its metabolites may pass into breast milk and, accordingly, breastfeeding should be discontinued prior to and throughout administration” (23). Although the limited pregnancy experience does not allow a full assessment of the embryo fetal risk, another carbapenem antibiotic is considered safe to use during the perinatal period (i. Lactation Although no information is available on the use of meropenem during breastfeeding, beta lactams are generally not expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants (44). Until more human data is available, infants should be monitored for the most common adverse effects observed in adult patients – headache, constipation, diarrhoea, anaemia, vomiting and rash (6). Consistent with its molecular weight (about 384 Daltons) meropenem is excreted into breast milk (6). A case report in 2012 of a woman treated with meropenem 3g per day for 7 days starting 6 days postpartum, found that the theoretical maximum infant dose was 97 mcg/kg/day, which equates to 0. Issued by the manufacturer state: (Meronem®): “It is unknown whether meropenem is excreted in human milk. A decision must be made whether to discontinue breastfeeding or to discontinue/abstain from meropenem therapy taking into account the benefit of therapy for the woman”(23). Although these analyses include different studies, the conclusions are the same the risk of congenital anomalies does not appear to be increased among the infants of women who use vaginal metronidazole in the first trimester of pregnancy. Some of the available reports have arrived at conflicting conclusions as to the safety of metronidazole in pregnancy, however, most of the published evidence suggests that metronidazole use during pregnancy does not represent a significant risk of adverse pregnancy outcome and structural defects to the fetus. However, they state that “a short course or low dose regimen of maternal metronidazole can be commenced without interruption of normal breastfeeding routine”. Schaefer et al states that when necessary, metronidazole may be used during breastfeeding. With intravenous treatment spread over several days, the administration should be, whenever possible, in the evening after the last feed in order to limit the exposure during the nightly breastfeeding break (21). With maternal intravenous and oral therapy, breastfed infants receive metronidazole in doses that are less than those used to treat infections in infants, although the active metabolite adds to the total infant exposure (22). Plasma levels of the drug and metabolite are measurable, but less than maternal plasma levels. Case reports of candida infections and diarrhoea have been reported, and a comparative trial suggested that oral and rectal colonisation with Candida might be more common in infants exposed to metronidazole (22). Issued by the manufacturer state: (Flagyl®): “Metronidazole should only be used during pregnancy or lactation following careful evaluation and only if considered essential by the physician. The drug crosses the placenta and is excreted in breast milk in which concentrations equal those in serum. If a single oral dose of metronidazole is used for trichomoniasis, the American Academy of Paediatrics recommends discontinuing breastfeeding for 12-24 hours to allow excretion of the drug (18), though other authors state that weaning or interruption of breastfeeding no longer seems justifiable based on the available experience (21). Nitrofurantoin increased the incidence of congenital anomalies in mice at high exposure levels. An increase in malformations in human pregnancy has not been established, although an association of nitrosatable drugs with craniosynostosis was proposed. Haemolytic anaemia and increased jaundice have been reported in neonates (13, 49). Therapeutic doses of nitrofurantoin during pregnancy are unlikely to pose a substantial teratogenic risk, but the data are insufficient to state that there is no risk (12). Due to the theoretical risk of haemolysis in neonates, nitrofurantoin is usually avoided after week 36 and where delivery is imminent. Issued by the manufacturer state: (Quinine sulphate tablets Actavis®): “Quinine sulphate is excreted into breast milk, but no problems in humans have been reported. However, quinine sulphate should not be given to nursing mothers unless the benefit outweighs the risk” (55). No adverse effects of ciprofloxacin use during human pregnancy have been documented (12) the use of ciprofloxacin during human gestation does not appear to be associated with an increased risk of major congenital malformations (6).
Buy sildigra 50mg with amex. NEW Erectile Dysfunction Treatment That Lasts - Agenixs Chicago.
National and regional streptococcal reference laboratories are lacking in many parts of the world and attention needs to be given to establish such laboratories and to assure quality control erectile dysfunction vegan cheap sildigra 25mg free shipping. Patients with rheumatic valvular disease need timely referral for operative intervention when clinical or echocardiographic criteria are met erectile dysfunction caused by high blood pressure medication buy sildigra 100 mg line. Primary prevention of rheumatic fever consists of the effective treatment of group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis erectile dysfunction vitamin buy sildigra from india, with the goal of preventing the first attack of rheumatic fever. While it is not always feasible to implement broad-based primary prevention programs in most developing countries, a provision for the prompt diagnosis and effective therapy of streptococcal pharyngitis should be integrated into the existing healthcare facilities. Secondary prevention of rheumatic fever is defined as regular administration of antibiotics (usually benzathine penicillin G given intramuscularly) to patients with a previous history of rheu matic fever/rheumatic heart disease in order to prevent group A streptococcal pharyngitis and a recurrence of acute rheumatic fever. Establishment of registries of known patients has proven effective in reducing morbidity and mortality. Infective endocarditis remains a major threat for individuals with chronic rheumatic valvular disease and also for patients with prosthetic valves. Individuals with rheumatic valvular disease should be given prophylaxis for dental procedures and for surgery of infected or contaminated areas. It is important to include such programs in national health development plans, and to implement them through the existing national infrastructure of ministries of health and of education without requiring a new administrative framework or health care delivery infrastructure. This can result in the targeting of high risk indi viduals and populations to make more effective use of often lim ited financial and human resources. Basic research studies are also needed to further elucidate the pathogenesis mechanisms responsible for the development of the disease process and for development of a cost-effective vaccine. Produced in collaboration with the Ethiopia Public Health Training Initiative, the Carter Center, the Ethiopia Ministry of Health, and the Ethiopia Ministry of Education. Important Guidelines for Printing and Photocopying Limited permission is granted free of charge to print or photocopy all pages of this publication for educational, not-for-profit use by health care workers, students or faculty. All copies must retain all author credits and copyright notices included in the original document. Under no circumstances is it permissible to sell or distribute on a commercial basis, or to claim authorship of, copies of material reproduced from this publication. Except as expressly provided above, no part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or by any information storage and retrieval system, without written permission of the author or authors. This material is intended for educational use only by practicing health care workers or students and faculty in a health care field. In North America it has been a corner stone of surgical training for more than a century. In Ethiopia this course started to be given as integral part of the surgical curricula of medical students not for more than 10 years. The ethical issue and effectiveness of surgical training by using real patient has raised the concept of essential surgical course. It was found that trainees who didn’t take this course have a problem in handling basic surgical problems. The department of surgery, University of Gondar, was involved in in-service training of health officers who have started practicing in the health centers. The inclusion of this course in the health officer curriculum was the main reason which initiates the preparation of this practical manual. In this manual we intended to highlight the practical and management skill for health officer students. The management skill was attempted to be addressed through a short theoretical introduction and case scenarios. The case scenarios are meant to elicit discussion and to revise the subject matter in that specific chapter. The role of the instructor should be very brief and limited only to demonstration of a specific procedure. Finally the authors would like to express their willingness to accept any comment or suggestion both from students and instructors. We would like to acknowledge the Dean’s office, College of Medicine and Health Science, University of Gondar. The Health Officer as care giver and often team leader should aim to give, or arrange for the delivery of care that he or she would want for himself or her family. This includes: o Being available when the patient needs care o Delivery of services in a safe, clean, calm and private place o Full disclosure to the patient and family of the aims of treatment and the risks of both treatment and diseases. Clean wounds: traumatic, non-infected wound no break in sterility technique, as occurring during elective hernia repair.