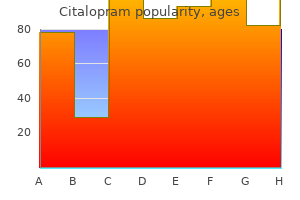
Citalopram
"Discount citalopram 10mg free shipping, kapous treatment".
By: X. Ramirez, MD
Co-Director, University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
The major ligaments of the ankle joint include the deltoid treatment lupus cheap citalopram 20 mg with visa, anterior talofibular medicine ball abs buy 10mg citalopram with amex, calcaneofibular medicine cards generic citalopram 10 mg on-line, and posterior talofibular ligaments, which provide the majority of strength to the ankle joint (Fig. The deltoid ligament is exceptionally strong and is not so subject to strain as the anterior talofibular ligament. The triangular-shaped deltoid ligament is made up of a number of smaller separate ligaments including the anterior tibiotalar ligament, tibiocalcaneal ligament, posterior tibiotalar ligament, and tibionavicular ligament (Fig. A deep layer attaches below to the medial body of the talus, with the superficial fibers attaching to the medial talus, the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus, and the navicular tuberosity (Fig. A,B: the anatomy of the deltoid ligament and its relationship with the other ligaments of the medial ankle. The triangular-shaped deltoid ligament is made up of a number of smaller separate ligaments, including the anterior tibiotalar ligament, tibiocalcaneal ligament, posterior tibiotalar ligament, and tibionavicular ligament. Medial view of one osteoarticular dissection showing the components of the superficial layer of the deltoid ligament, especially the tibiospring ligament (major component). Also known as the medial ligament of talocrural joint, the deltoid ligament is susceptible to strain at the joint line or avulsion at its origin or insertion. The deltoid ligament is frequently injured from eversion injuries to the ankle that occur when tripping when wearing high heels, landing hard on uneven surfaces, and during dancing, soccer, and American football (Fig. The pain of deltoid ligament damage is localized to the medial ankle and is made worse with plantar flexion and eversion of the ankle joint. Activity, especially involving weight bearing, plantar flexion, and eversion of the ankle will exacerbate the pain. Local heat and decreased activity as well as elevation of the affected ankle may provide a modicum of relief. Sleep disturbance is common in patients suffering from trauma to the deltoid ligament of the ankle. Coexistent fracture, bursitis, tendinitis, arthritis, or internal derangement of the ankle may confuse the clinical picture after trauma to the knee joint making clinical diagnosis difficult. The deltoid ligament is frequently injured by eversion injuries that occur when tripping when wearing high heels, landing hard on uneven surfaces, and during dancing, soccer, and American football. Plain radiographs are indicated in all patients who present with deltoid ligament pain, especially after ankle trauma (Fig. An external stress rotation mortise view will aid in identification of disruption of the deltoid ligament (Fig. Based on the patient’s clinical presentation, additional testing may be indicated, including complete blood cell count, sedimentation rate, and antinuclear antibody testing. Magnetic resonance imaging, computerized tomography, and/or ultrasound imaging of 1066 the ankle are indicated if internal derangement or occult mass or tumor is suspected as well as to confirm the diagnosis of suspected deltoid ligament injury (Figs. Bone scan may be useful to identify occult stress fractures involving the joint, especially if trauma has occurred. Swelling and ecchymosis are frequently identified on physical examination following deltoid ligament injury. Radiograph demonstrating a fracture dislocation of the ankle with complete disruption of the deltoid ligament. Does medial tenderness predict deep deltoid ligament incompetence in supination-external rotation type ankle fractures? Longitudinal image along the medial joint line demonstrates tears of the superficial (talocalcaneal) and tibionavicular fibers of the deltoid ligament (arrows). Does medial tenderness predict deep deltoid ligament incompetence in supination-external rotation type ankle fractures? A high-frequency linear ultrasound transducer is placed in the longitudinal position with the superior aspect of the transducer placed just over the center of the medial malleolus and rotated toward the Achilles tendon (Fig. A survey scan is taken which demonstrates the triangular-shaped deltoid ligament nestled between the medial malleolus and talus (Fig. After the deltoid ligament is identified, the ligament is evaluated for fluid accumulation, strain, tears, and rupture (Figs. Color Doppler may aid in identification of neovascularization of the deltoid ligament following injury (Fig. Correct longitudinal position for the ultrasound transducer for ultrasound evaluation of the deltoid ligament. Note the superior aspect of the ultrasound transducer is slightly rotated toward the Achilles tendon.
A single back-titration by 100 mg was allowed at the end of the titration period for patients experiencing signifcant adverse Seizure freedom rate events medications 44 175 purchase citalopram cheap. The primary ef- 4 fcacy variable symptoms quiz purchase genuine citalopram on line, median percentage reduction in seizure frequency from baseline to maintenance treatment xeroderma pigmentosum purchase citalopram 40 mg mastercard, was 10% in the placebo group and 3 26%, 39% and 40% in the lacosamide 200, 400 and 600 mg/day groups, respectively. Reductions in seizure frequency over place- 2 bo were signifcant for the 400 mg/day (28. Although there was a 1 statistical trend favouring the 200 mg/day group, the median per- centage reduction in seizure frequency per 28 days over placebo 0 did not reach statistical signifcance (14. A signif- Placebo 200 mg 400 mg 600 mg cantly greater proportion of patients experienced a 50% or great- Percentage of patients seizure free er decrease in seizure frequency during the maintenance period Figure 37. Most of these reports refer to children with fo- proportion of patients in the 400 mg/day arm meeting predefned cal seizures, who may respond better to lacosamide than children seizure-related exit criteria by day 112, compared with the historical with mixed or generalized seizure types [60]. Among the 284 patients in the 400 mg/ favourable responses do not appear to be necessarily restricted to day group , 82 (28. One report suggested that seizure associated with Meier analysis predicting a 30% exit rate (95% confdence interval Lennox–Gastaut syndrome may be aggravated by lacosamide [61], 24. Tese results provide evidence that lacosamide is efca- in some patients with this syndrome [52,62]. Primary reasons for discontinuation were However, further studies are needed to better characterize its thera- lack of efcacy (26%) and adverse events (11%). Adverse efects most commonly reported were dizziness, Adverse effects nausea, headache, falls, vomiting, diplopia and nasopharyngitis, which are similar to those reported in short-term double-blind tri- Most common adverse events reported in als. Overall, data were consistent with persistence of clinical beneft controlled trials in a sizeable proportion of patients. Adverse events observed during the lacosamide clinical develop- In a survey of patients with uncontrolled focal seizures ment programme seem to be consistent with its proposed mech- followed-up at a single centre, 35 of 160 lacosamide-treated pa- anism of action. Of importance, the incidence of somnolence became seizure-free on lacosamide monotherapy afer withdrawing was relatively low in lacosamide trials [17,72]. La- the lacosamide-treated groups (all dosages combined) and great- cosamide was discontinued in 24 patients (15%) for lack of efcacy er than placebo: dizziness (31% versus 8%), headache (13% ver- and in 12 (7. A >50% reduction in seizures frequency was reported in es of 200, 400 and 600 mg/day, compared with 8% among patients 57% of the patients at 12 months, and the seizure freedom rate was randomized to placebo [17]. A prospective curred with an incidence of >10% in the lacosamide 600 mg/day open-label study from Spain reported preliminary experience with group only [46]. Overall discontinuation rates due to adverse events the drug in 130 children and adolescents aged less than 16 years emerging during treatment were 8%, 17% and 29% in the groups as- (range 6 months to 16 years) with refractory focal or symptomatic signed to lacosamide doses of 200, 400 and 600 mg/day, compared generalized epilepsies [52]. The initial dose was 1–2 mg/kg/day in with 5% among patients randomized to placebo [46]. Afer analysis of tolerability data in relation to type of co-medication, a 3 months, 62% of patients had a >50% reduction in seizure frequen- dose-dependency of discontinuations due to adverse events was cy and 14% had their seizures completely controlled. The meta-analysis suggested that adverse events associat- tural heart disease or severe cardiac disease [25,75]. Severe hypersensensitivity re- evaluated in a small retrospective study in a naturalistic setting actions have also been rarely reported [24,77], including one case of in which patients on adjunctive therapy underwent assessments acute liver failure secondary to levetiracetam in combination with of executive functions, verbal memory and subjective ratings of lacosamide documented by liver biopsy [78]. The results of both subjective and objective measures in this study Tere is insufcient information on human exposure during preg- suggested that the cognitive side-efect profle of lacosamide is com- nancy. Of note for patients with phenylketonuria, the oral solution con- Tese results require confrmation in a formal prospective study. Patients In epilepsy patients, the incidence of reported treatment-emer- tolerated the intravenous formulation just as well as the oral for- gent frst-degree atrioventricular block as an adverse event is un- mulation, and no serious adverse events were reported [79]. Lacosamide displays potent antinociceptive efects in equivalent intravenous dose (200–800 mg/day range) over progres- animal models for infammatory pain. The investigational anticonvulsant la- sively shorter infusion durations (30, 15 and 10 min) for 2–5 days. Most commonly reported adverse events were headache (7%), diz- Mol Pharmacol 2008; 73: 157–169. One patient, who was also taking a be- causes failure of carbamazepine, but not of lacosamide, in blocking high-frequen- cy fring via diferential efects on persistent Na+ currents. Epilepsia 2012; 53: ta-blocker, had a serious adverse event (bradycardia) on day 2 of 1959–1967.
Aplasia of the optic nerve the particular auto-fluorescence property of optic disc and disk in treatment 1-3 generic citalopram 20mg without a prescription. Arch Ophthalm ol Several reports have described the association of retini- 1941 medications images order citalopram cheap,26:61 treatment 4 lung cancer purchase citalopram 40 mg with mastercard. Z Zclllorsch clasticum is another disease in which optic disc drusen M ikrosk Anat 1968;84:1-8. Br of hyaline material inside and outside the cells of the capil I O phthalm ol 1978;62:7-15. Other histologic features include concentric laminations Arch O phthalm ol 1970;84:572-8. Agenesis o f the septum lucidum with m alform ation of electroretinographic findings. Optic nerve hypoplasia with good visual and ncuroradiologic abnorm alities associated with septo-optic dys acuity. H ypothalam ic-pituitary function in esis in a patient with blepharophim osis syndrom e. Puberty in the syndrom e of syndrom e and m ultiple pituitary horm one deficiency. Visual im pairm ent and ocular abnorm alities in students at the Alabama School for the Blind. Trans Am O phthalm ol Soc fetal alcohol syndrome: clinical and anim al m odel studies. Clinical and electroretinographic found in Tajimi Eye Health Care Project participants, Jpn J findings in fetal alcohol syndrom e. Septo-optic dysplasia associated with dren of m others with type I diabetes incllitus. Carbamazepine, epilepsy, and optic with dysm orphic features, bilateral optic pathway aplasia and norm al nerve hypoplasia. Iris colobom a with iris m utations associated with isolated congenital pituitary hypoplasia heterochrom ia: a com m on association. Genetic m apping of a sia and com bined pituitary horm one deficiency in a Japanese patient. Novel m utation in detected in patients w ith a variety of optic-ncrvc m alform ations. Hcterotopic adipose m icrophthalm ia, retinal dysplasia and defective retinal ganglion cell tissue and sm ooth muscle in the optic disc: association with isolated axon guidance. Selection o f surgical technique for retinal detach Implications of missed diagnosis in the peri-operative period. M orning glory syndrom e: unusual congenital optic disk trum of hybrid disc anom alies in a single eye. Pseudodoubling of the E ntartung dcs Sehnerven m il bcsondcrer Bctciligung der optic disc: a colour Doppler im aging study. Pituitary stalk anom alies coarctation of the aorta and cardiac defects, and eye duplication in association with moya moya disease and bilateral abnorm alities. Torres M, Gom ez-Pardo E, Gruss P Pax2 contributes to inner ear traction-rhcgm atogcnous retinal detachm ent in the m orning glory patterning and optic nerve trajectory. M orning glory disc expansion and contraction m utations of РЛХ2 and inclusion of anom aly in neurofibrom atosis type 2. Arch O phthalm ol 1999;117: Chiari 1 m alform ation as part o f renal-colobom a syndrom e. O cular m alform ations, moy- apoptosis in fetal kidneys o f Pax2(lN cu) + / - m utant mice. M orning glory disk anom aly—m ore than meets the prenatal detection and clinical spectrum in a large family. Renal colobom a syn oidal colobom a, and congenital constrictive m alform ations of the drom e. R edefining papillorenal ol the optic disc associated with m oyam oya disease: case report). A case of peripapillary m idline cranial defects and abnorm al carotid circulation: an asso staphyloma.

Electromyography and nerve conduction velocity testing are useful in helping in the differentiation of golfer’s elbow from cervical radiculopathy and other nerve entrapment syndromes walmart 9 medications discount citalopram 10mg. Plain radiographs symptoms food poisoning order generic citalopram, ultrasound imaging medicine 5658 discount citalopram 10 mg without a prescription, and magnetic resonance imaging are indicated in all patients who are thought to be suffering from golfer’s elbow in order to confirm the diagnosis as well as to rule out occult bony pathology involving the medial epicondyle and elbow joint and to identify occult fractures, masses, or tumors that may be responsible for the patient’s symptomatology (Fig. Based on the patient’s clinical presentation, additional testing may be indicated, including complete blood count, uric acid, sedimentation rate, and antinuclear antibody testing. The ultrasound-guided injection technique described below serves as both a diagnostic and therapeutic maneuver as ultrasound imaging can clearly delineate pathology of the flexor musculotendinous units at their insertion on the medial epicondyle. Common flexor tendon maintains a fuzzy fibrillar pattern (arrowheads) with a small hypoechoic focus (large arrow). B: Anteroposterior radiograph of the elbow also shows the calcification (arrow), which is not contiguous with the underlying bone. With the patient in the above position, the medial epicondyle is identified and the point of maximal tenderness is then isolated by careful palpation. A high-frequency linear ultrasound 357 transducer is then placed in a longitudinal over the medial epicondyle at the point of maximal tenderness (Fig. The oval egg-shaped hyperechoic curve of the medial epicondyle and the overlying common flexor tendon insertions attaching to the medial epicondyle are then identified (Fig. The trochlea will be seen as a hyperechoic line gently sloping away from the medial epicondyle towards the ulna. The area of flexor tendinous insertions on the medial epicondyle are identified and evaluated for tears which will appear as hyperechoic areas within the substance of the tendon. The ultrasound transducer is then slowly moved proximally so that the gentle hyperechoic slope of the medial epicondyle and the overlying common flexor tendon insertions are at the bottom of the ultrasound image to fully assess the site of origin (Fig. The common flexor tendon is then evaluated in both the longitudinal and transverse planes for thickening, tendinopathy, and tears (Figs. Proper longitudinal position for the linear high-frequency ultrasound transducer to perform ultrasound-guided injection for golfer’s elbow. Longitudinal ultrasound image demononstrating the oval egg-shaped hyperechoic curve of the medial epicondyle and the overlying common flexor tendon insertions attaching to the medial epicondyle. The trochlea is seen as a hyperechoic line gently sloping away from the medial epicondyle towards the ulna. The ultrasound transducer is then slowly moved proximally so that the oval egg-shaped medial 358 epicondyle and the overlying common flexor tendon insertions are at the bottom of the ultrasound image to fully assess its origin. Ultrasound long-axis (A) and short-axis (B) views of the medial elbow demonstrate thickening and hypoechogenicity of the common flexor tendon origin (arrow). Sonogram longitudinal to the common flexor tendons show abnormal hypoechoic thickening. The anterior bundle finds its origin on the underside of the medial condyle and inserts on the sublime tubercle of the ulnar coronoid process (Fig. This ligament is often damaged from excessive valgus stress on the elbow joint in conjunction with the common flexor tendon apparatus. Ultrasound imaging is also useful in assessment of the adequacy of surgical repair of the ulnar collateral ligament of the elbow. Longitudinal ultrasound image showing the anterior bundle of the ulnar collateral ligament (known as the medial collateral ligament) of the elbow where it lies deep to the common flexor tendon. The anterior bundle finds its origin on the underside of the medial condyle and inserts on the sublime tubercle of the ulnar coronoid process. A: Ultrasound longitudinal to anterior bundle of ulnar collateral ligament shows abnormal thickening and hypoechogenicity (arrowheads). With valgus stress, the joint space between the trochlea of the humerus and ulna (arrow) did not widen, excluding full-thickness tear. Dynamic scanning with flexion, extension, and valgus stress views will be helpful in further elucidating the cause of the patient’s functional disability and pain. It should be remembered that golfer’s elbow and abnormalities of the ulnar collateral ligament can coexist with other abnormalities of the elbow.
Order citalopram 10mg without prescription. Extreme benzo withdrawal trial.