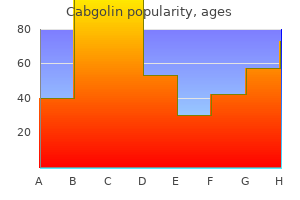
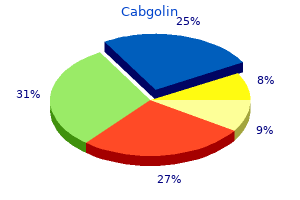
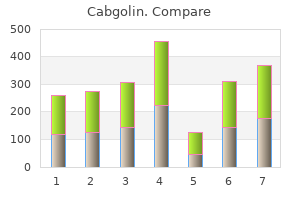
Cabgolin
"Discount 0.5mg cabgolin fast delivery, treatment leukemia".
By: X. Tempeck, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley School of Medicine
In the patient with back pain and fever medications erectile dysfunction purchase generic cabgolin canada, spinal epidural abscess must be strongly considered medicine lodge treaty cheap cabgolin 0.5mg free shipping. The spinal canal has both an anterior and a posterior epidural space containing fat and small vessels everlast my medicine order cabgolin 0.5mg on line. The spinal epidural space can become infected by a) spread of infection from osteomyelitis or disk-space infection; b) spinal surgery or epidural catheter placement; c) hematogenous spread from skin or urinary tract infection or intravenous drug abuse. Symptoms and signs include a) low back pain and fever; b) radicular pain accompanied by lower motor neuron deficits; c) signs of cord compression in later stages (Babinski reflex, hyperreflexia, loss of motor function, bladder dysfunction). Within 24 hours of onset, irreversible paraplegia may occur; d) localized spinous process tenderness in posterior epidural abscesses. If methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is suspected, vancomycin coverage is also required. In posterior epidural abscesses, severe localized tenderness over the infected area is encountered. However, in anterior epidural abscesses (a rarer event), infection is deep seated, and tenderness cannot be elicited. Magnetic resonance imaging scan with contrast showing a Staphylococcus aureus epidural abscess. These guidelines reduced the delay in diagnosis of spinal epidural abscess by over 70%. Gram-negative aerobes are the second most frequent cause, followed by aerobic streptococci, S. Mycobacterium tuberculosis is another important cause, most commonly associated with tuberculous infection of the thoracic vertebra. Community-acquired bacterial meningitis: risk stratification for adverse clinical outcome and effect of antibiotic timing. Epidemiology, diagnosis, and antimicrobial treatment of acute bacterial meningitis. The diagnostic accuracy of Kernig’s sign, Brudzinski’s sign, and nuchal rigidity in adults with suspected meningitis. Long-term valacyclovir suppressive treatment after herpes simplex virus type 2 meningitis: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Evidence of human herpesvirus 6 infection in 4 immunocompetent patients with encephalitis. Herpes simplex encephalitis in Sweden, 1990-2001: incidence, morbidity, and mortality. Dexamethasone for the treatment of tuberculous meningitis in adolescents and adults. The poor prognosis of central nervous system cryptococcosis among nonimmunosuppressed patients: a call for better disease recognition and evaluation of adjuncts to antifungal therapy. Consensus document on controversial issues for the treatment of infections of the central nervous system: bacterial brain abscesses. Efficacy and safety of cefotaxime in combination with metronidazole for empirical treatment of brain abscess in clinical practice: a retrospective study of 66 consecutive cases. A review of brain abscess surgical treatment–78 years: aspiration versus excision. Prospective evaluation of a clinical decision guideline to diagnose spinal epidural abscess in patients who present to the emergency department with spine pain. If antibiotic prophylaxis is to be administered, when should the antibiotic be given? When bacterial endocarditis is suspected, what are the skin lesions that should be searched for, and how often are they seen? How should blood samples for culture be drawn if the clinician suspects bacterial endocarditis? Are bacteriostatic antibiotics effective in the treatment of bacterial endocarditis?
Pattens and Clogs (Yellow Toadflax). Cabgolin.
- What is Yellow Toadflax?
- Digestive problems, urinary problems, reducing swelling, use as a diuretic ("water pill"), hemorrhoids, wounds, skin rashes, or other conditions.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Yellow Toadflax.
- How does Yellow Toadflax work?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96111
Patients with blunt medicine 223 purchase cabgolin pills in toronto, multiple-organ trauma have a shorter duration of mechanical ventilation symptoms magnesium deficiency buy cabgolin in united states online, fewer episodes of nosocomial pneumonia [22] symptoms 3 days after embryo transfer buy cabgolin with a visa, and a significant reduction in hospital costs [23] when the tracheostomy is performed within 1 week of their injuries. Similar benefits have been reported in patients with head trauma and poor Glasgow Coma Score [24], acute spine trauma [25], and thermal injury [26] if a tracheostomy is performed within a week after the injury. Also, patients with facial injuries may require early tracheostomy to allow or facilitate facial fracture surgery, fixation, and immobilization. When time is short, the patient is uncooperative, anatomy is distorted, and the aforementioned requirements are not met, then tracheostomy can be very hazardous. Emergency tracheostomy comprises significant risks to nearby neurovascular structures, particularly in small children in whom the trachea is small and not well defined. The risk of complications from emergency tracheostomy is two to five times higher than for elective tracheostomy [27,28]. Nonetheless, there are occasional indications for emergency tracheostomy [29], including transected trachea; anterior neck trauma with crushed larynx [30]; severe facial trauma; acute laryngeal obstruction or near-impending obstruction; and pediatric (younger than 12 years) patients requiring an emergency surgical airway in whom a cricothyrotomy is generally not advised. In emergency situations, when there is inadequate time or personnel to perform an emergency tracheostomy, a cricothyrotomy may be a more efficient and expedient manner to provide an airway. Cricothyrotomy Although initially condemned because of a high rate of complications, cricothyrotomy may have some potential advantages over tracheostomy. These include technical simplicity; speed of performance; low complication rate [31]; suitability as a bedside procedure; usefulness for isolation of the airway for median sternotomy and radical neck dissection [32]; lack of need to hyperextend the neck; and formation of a smaller scar. Also, because cricothyrotomy results in less encroachment on the mediastinum, there is less chance of esophageal injury and virtually no chance of pneumothorax or tracheal arterial fistula [33]. Despite these considerations, many authorities currently recommend that cricothyrotomy be used as an elective long-term method of airway access only in highly selected patients [34]. Use of cricothyrotomy in the emergency setting, particularly for managing trauma, is not controversial [35–37]. Emergency cricothyrotomy is useful because it requires a small number of instruments and less training than tracheostomy, and can be performed quickly as indicated as a means of controlling the airway in an emergency when oral or nasotracheal intubation is nonsuccessful or contraindicated. The cricothyroid membrane is higher in the neck than the tracheal rings and therefore closer to the surface and more accessible. In emergency situations, translaryngeal intubations fail because of massive oral or nasal hemorrhage or regurgitation; structural deformities of the upper airway; muscle spasm and clenched teeth; and obstruction by foreign body through the upper airway [35]. Cricothyrotomy finds its greatest use in trauma management, axial or suspected cervical spine injury, alone or in combination with severe facial trauma, where nasotracheal and orotracheal intubation is both difficult and hazardous. Use and Contraindications Cricothyrotomy should not be used to manage airway obstruction that occurred immediately after endotracheal extubation because the obstruction may be found below the larynx [36]; likewise, with primary laryngeal trauma or diseases such as a tumor or an infection, cricothyrotomy may prove to be useless. It is contraindicated in infants and children younger than 10 to 12 years under all circumstances because stenosis and even transection are possible [36]. In this age group, percutaneous needle catheter transtracheal ventilation may be a temporizing procedure until the tracheostomy can be performed. Anatomy the cricothyroid space is no larger than 7 to 9 mm in its vertical dimension, smaller than the outside diameter of most tracheostomy tubes (outside diameter 10 mm). The cricothyroid artery runs across the midline in the upper portion, and the membrane is vertically in the midline. The cricothyroid membrane is approximately 2 to 3 cm below the laryngeal prominence and can be identified as an indentation immediately below the thyroid cartilage. This major complication occurs at the tracheostomy or cricothyrotomy site, but not at the cuff site [38]. Necrosis of cartilage due to iatrogenic injury to the cricoid cartilage or pressure from the tube on the cartilage may play a role [37]. Possible reasons that subglottic stenoses may occur more commonly with cricothyrotomy than with tracheostomy are as follows: the larynx is the narrowest part of the laryngotracheal airway; subglottic tissues, especially in children, are intolerant of contact; and division of the cricothyroid membrane and cricoid cartilage destroy the only complete rings supporting the airway. Furthermore, the range of tube sizes is limited because of the rigidity of the surrounding structures (cricoid and thyroid cartilages), and the curvature of the tracheostomy tube at this level may obstruct the airway because of posterior membrane impingement [39]. Prior laryngotracheal injury, as with prolonged translaryngeal intubation, is a major risk factor for the development of subglottic stenosis after cricothyrotomy [31]. The association of cricothyrotomy with these possible complications leads most authorities to consider replacing a cricothyrotomy within 48 to 72 hours with a standard tracheostomy procedure.
Inadequate Banding Many times symptoms enlarged spleen order cabgolin cheap, the tightness of the band is limited by the hemodynamic response of the patient treatment resistant schizophrenia order discount cabgolin on-line. To limit the pulmonary blood flow in these patients treatment junctional rhythm generic 0.5mg cabgolin fast delivery, ligation of the pulmonary artery or a Damus-Kaye-Stansel anastomosis and shunt procedure may be required (see Chapter 30). Early Reoperation to Adjust Band It is not uncommon to leave the operating room with a suitable band, only to have the patient develop signs that the band is too tight or too loose in the early postoperative period. Placing the Band Too Proximally If the band is placed too proximally, the sinotubular ridge of the pulmonic valve will be distorted. To adequately relieve the gradient during the debanding procedure, the sinus portion(s) of the pulmonary root often needs to be patched. This is especially problematic when an arterial switch or Damus-Kaye-Stansel procedure is planned at the second stage. Band Migration the band should be sewn to the adventitia of the proximal aspect of the main pulmonary artery. This precaution prevents the band from migrating distally, narrowing the pulmonary artery at its bifurcation and obstructing the right, left, or both branches. After the optimal band constriction has been achieved, it is secured and the pericardium is approximated with multiple interrupted sutures. A punch is taken from the center of this disc, whose diameter is roughly the size of a shunt appropriate for the baby by weight. A transverse, partial pulmonary arteriotomy is made halfway between the pulmonary root and the bifurcation, and through this partial incision, the backwall of the Gore-Tex “washer” is sewn using a running Prolene. As this is continued anteriorly, the Gore-Tex is included in between the two edges of the cut pulmonary artery. This technique has the advantage of (1) a controlled source of pulmonary blood flow and (2) eliminating the possibility of either band migration or pulmonary valve damage. This device is capable of repeated narrowing and releasing of the pulmonary artery at the bedside, avoiding reoperation. Because of its elliptic shape, there usually is no need for reconstruction of the pulmonary artery when the device is removed. It may be necessary to reconstruct the pulmonary artery to eliminate any gradient across the band site. When a Silastic band has been in place for a short time, simple removal of the band often results in no gradient. If a pressure gradient or obvious deformity is noted at the band site, the pulmonary artery is repaired with the patient on cardiopulmonary bypass. An appropriately sized patch of glutaraldehyde-treated autologous pericardium or Gore-Tex is then sewn onto the defect with a continuous 5-0 or 6-0 Prolene suture. Persistence of the Gradient Inadequate enlargement of the main pulmonary artery may be responsible for persistence of the gradient across the site of the band. Alternatively, the portion of the main pulmonary artery involved in the banding can be resected and an end-to- end anastomosis performed between the proximal main pulmonary artery and the confluence of the right and left pulmonary arteries. Pulmonary Valve Insufficiency When the band has caused distortion of the sinotubular ridge, patching anteriorly into one sinus only often causes valvular insufficiency. If the patient will not tolerate pulmonary valve incompetence, the pulmonary artery can be transected and all three sinuses patched as described for supravalvular aortic stenosis (see Chapter 24). Incorporation of the Band into the Pulmonary Artery With the passage of time, the band may burrow through the wall of the pulmonary artery to become subendothelial. The band can be divided anteriorly but left in situ and the pulmonary artery enlarged with a patch angioplasty. Occasionally, the band may migrate distally to the pulmonary artery bifurcation and cause distortion of its branches. The incision on the pulmonary artery is then extended distally onto the left or both the left and right pulmonary artery branches as needed. Sizing the Patch the pericardial patch should be wide enough, particularly at its distal end, to prevent a residual gradient. The ascending aorta gives rise to right and left arches that encircle the trachea and esophagus and rejoin to form the descending thoracic aorta.
The most common side effects are nausea symptoms in early pregnancy purchase cabgolin 0.5mg without a prescription, vomiting medicine administration buy 0.5 mg cabgolin, and anorexia treatment whooping cough buy 0.5mg cabgolin overnight delivery, and neurologic effects such as dizziness, paresthesias, tremor, ataxia, and confusion. Monitoring for clinical or laboratory signs of agranulocytosis has been recommended, particularly during the first 12 weeks of therapy. Because 40% of tocainide elimination is renal, urine acidification theoretically increases tocainide excretion, but is not recommended because of enhanced systemic toxicity. Mexiletine Mexiletine is structurally similar to lidocaine and undergoes extensive metabolism in the liver to largely inactive compounds [48,49]. Patients with chronic liver disease, such as hepatic cirrhosis, undergo a marked reduction in the hepatic metabolism of mexiletine [50]. Mexiletine is generally well tolerated, with little effect on hemodynamics, even in patients with congestive heart failure [51]. Mexiletine shares much of the side-effect profile of lidocaine, including cross-reactivity in allergic individuals. Seizures have been reported to occur in the absence of cardiovascular abnormalities, and the prolonged duration of seizures compared with lidocaine overdose may be due to mexiletine’s longer elimination half-life of 5. A urine drug immunoassay was reported as positive for amphetamines in the setting of a mexiletine overdose, likely from cross-reactivity due to structural similarity of these compounds [52]. This phenomenon effectively results in two distinct populations of patients having very different clearance rates. Amiodarone can double the serum concentration of flecainide when the two drugs are concomitantly administered; the flecainide dose should be reduced by 50% when these drugs are coadministered. Flecainide has a very narrow therapeutic index and can be toxic even at therapeutic concentrations [53]. Furthermore, flecainide possesses considerable negative inotropic effects that limit its usefulness in the setting of congestive heart failure. Serious cardiac effects that can occur include severe bradycardia, high-grade conduction blocks, and ventricular arrhythmias. For overdose patients, both hypertonic sodium bicarbonate and sodium lactate have been reported to be effective [56]. Hypertonic sodium bicarbonate or sodium lactate should be considered for patients with evidence of disturbed ventricular conduction. In one report, a patient who developed refractory ventricular fibrillation because of a flecainide overdose was successfully resuscitated after a 300-mg amiodarone bolus was given [53]. Propafenone Propafenone is used for selected patients with atrial fibrillation and for refractory ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation. Administering propafenone with food may significantly increase bioavailability among extensive metabolizers by diminishing first-pass drug extraction [58]. Propafenone administration may increase digoxin concentrations between 35% and 85% because of impairment of nonrenal digoxin clearance. Coadministration of propafenone with warfarin may result in a 25% increase in prothrombin time from unknown mechanisms. Transvenous cardiac pacing was successful in a case with severe bradycardia due to a high-grade conduction block [61]. Amiodarone is generally considered the most effective antiarrhythmic agent for treatment and prophylaxis of most types of arrhythmia [64]. After oral administration, amiodarone widely distributes into body tissues where drug concentration generally exceeds that of the plasma. It is highly lipophilic, highly bound to plasma proteins, and has an extremely long (average, 53 days) elimination half-life [66]. The major metabolite, desethylamiodarone, accumulates in plasma and tissues and has electrophysiologic properties that are similar to the parent compound [67]. Many side effects are dose dependent, but therapeutic drug monitoring is of little benefit, except to determine compliance. Evidence suggests a limited correlation between drug level and antiarrhythmic effects [68], and serious noncardiac toxicity seems to be more likely at levels above 2. Pulmonary fibrosis is an important and potentially life-threatening side effect of long-term therapy [70]. Pulmonary toxicity is somewhat dose dependant; its prevalence ranges from 5% to 15% in patients who take at least 500 mg per day, but is 0.
Cheap cabgolin online mastercard. "Do I Have An Anxiety Disorder?" Signs Symptoms Etc. - Psychotherapy Crash Course.