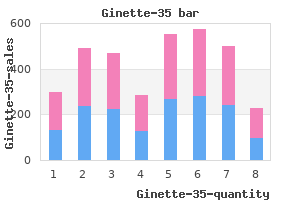
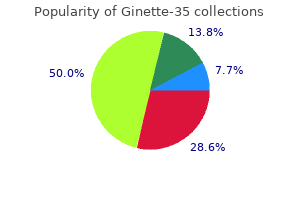
Ginette-35
"Generic 2mg ginette-35 mastercard, menopause hot flashes relief".
By: N. Kayor, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Professor, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health
Phase 2 Goals: Improve balance of the lower extremity womens health your best body meal plan purchase generic ginette-35 from india, increase quadriceps strength women's health center frost street buy ginette-35 2 mg line, and restore good knee function obama women's health issues 2mg ginette-35 visa. Treatment, add ● Balance and coordination training with grad- ual increase of difficulty and loading on the patellofemoral joint. In order to try to mainly train the knee joint stabilizers I suggest that these exercises should be performed in a standing position with a slightly flexed knee joint. Balance training on a balance board can initially be performed standing on one leg with addition of electrical stimulation of VMO to facilitate a proper balance between VMO and VL (Figure 9. When good muscle con- trol is achieved the patient can continue the balance exercise standing on one leg without electrical muscle stimulation (Figure 9. Stretching of lateral muscle structures, the tensor fascia lata and thereby compression forces within the and the iliotibial band. Single-leg standing balance board training with addition of electrical stimulation of VMO. Balance board training standing on two legs on two balance boards. Conservative Treatment of Athletes with Anterior Knee Pain 161 Figure 9. Stepping-down with addition of electrical stimulation of VMO. Squatting with addition of electrical stimulation of VMO. Walking, jogging, and should be performed during terminal knee different types of jumping exercises are recom- extension, approximately between 30° and 0° mended during this phase. However, proceed- of knee flexion, and open kinetic chain ing to a higher knee loading activity or exercise between approximately 90° and 40° of knee should only be allowed if there is no knee pain flexion. Isokinetic training should preferably and no swelling. Goal ● It is recommended to give the patient individual Return to previous physical activity level. Conservative Treatment of Athletes with Anterior Knee Pain 163 References of the vasti in patellofemoral pain syndrome. Altered vastii recruitment when people with etry: Applications and limitations. Sports Med 1989; 8: patellofemoral pain syndrome complete a postural 101–116. Therapeutic stretch on the flexibility of the hamstring muscles. Cowan, SM, KL Bennell, PW Hodges, KM Crossley, Sports Med 1989; 8(4): 841–860. BenGal, S, J Lowe, G Mann, A Finsterbush, and ment of the vasti in untrained postural tasks can be Y Matan. The role of the knee brace in the prevention restored by physical therapy. J Orthop Res 2003, 21(3): of anterior knee pain syndrome. Evaluation and treat- Analysis of outcome measures for persons with ment of anterior knee pain using eccentric exercise. The influence of foot and treatment of chondromalacia patellae. Bockrath, K, C Wooden, T Worrel, CD Ingersoll, and 27. Effects of patella taping on patella position lacia patellae in athletes. Vastus lar tracking in lateral patellar compression syndrome. The function of the vastus medialis smerter: diagnostikk og behandling. Fairbank, J, P Pynsent, J van Poortvliet, and H Phillips.
A 45-year-old Asian man who is currently serving in the United States Marine Corps comes to the emer- gency department because of fever womens health 33511 buy ginette-35 2mg with mastercard, which has persisted for 8 days menstruation 1700s buy ginette-35 with a mastercard. He reports returning from the Middle East 2 days ago women's health clinic elko nv buy ginette-35 with mastercard. He states that, before his departure, several other marines had become ill and that some of them were so ill that they had to be transported to a hospital off the base. His symptoms also include headache, muscle aches, diarrhea with blood, and a rash on his extremities. On the basis of World Health Organization (WHO) data, which of the following findings would NOT support the diagnosis of acute hemorrhagic fever? Severe illness and no predisposing factors for hemorrhagic manifes- tations D. Hemorrhagic rash Key Concept/Objective: To understand the diagnosis and presentation of hemorrhagic fever viruses Initial symptoms of the acute hemorrhagic fever virus syndrome may include fever, headache, myalgia, rash, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, arthralgias, myal- gias, and malaise. Illness caused by Ebola virus, Marburg virus, Rift Valley fever virus, yellow fever virus, Omsk hemorrhagic fever virus, and Kyasanur Forest disease virus has an abrupt onset, whereas Lassa fever and the diseases caused by Machupo, Junin, Guarinito, and Sabia viruses have a more insidious onset. Initial signs may include fever, tachyp- nea, relative bradycardia, hypotension (which may progress to circulatory shock), con- junctival injection, pharyngitis, and lymphadenopathy. Hemorrhagic symptoms, when they occur, develop later in the course of illness and include petechiae, purpura, bleed- ing into mucous membranes and conjunctiva, hematuria, hematemesis, and melena. Hepatic involvement is common, and renal involvement is proportional to cardiovas- cular compromise. Clinical diagnostic criteria based on WHO surveillance standards for acute hemorrhagic fever syndrome include temperature greater than 101° F (38. A 90-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with his 87-year-old wife, who is his primary caregiver. The patient has fallen once at home, and his appetite has diminished recently. He returns in 3 months after having fallen two more times. Which of the following interventions is NOT consistent with the general principles of geriatric assessment? Addressing the falls to prevent injury from subsequent falls C. Monitoring results of dietary recommendations to assess improve- ment in intake D. Always placing the physician in charge of the geriatric assessment team because he is most qualified to direct patient care E. Questioning the patient about issues related to sexuality Key Concept/Objective: To understand the fundamental principles of geriatric assessment General features of geriatric assessment include the following: (1) an interdisciplinary team approach to patient care; (2) a focus on prevention, including the prevention of decline (maintaining functional status); and (3) a feedback loop to promote adherence to recommendations by other health care providers, patients, and caregivers, as well as to promote patient self-efficacy or confidence in the ability to perform specific activi- ties. This patient will benefit from seeing members of an interdisciplinary team, with team leadership rotating, depending on the major concern for the patient at any par- ticular time. Addressing sexuality in this age group represents another form of preventive care that may require special inter- vention. Any intervention, such as a dietary modification, needs to be monitored for success or failure so that further adjustments can be made. An 85-year-old man is admitted to a geriatric acute care unit from home for treatment of nausea and vomiting related to a urinary tract infection. Which of the following statements does NOT accurately characterize the benefits of a geriatric acute care unit over a general inpatient ward? The geriatric acute care unit provides a specially prepared environment B. Patients who receive care in a geriatric acute care unit have improved functional status 3 months after discharge, compared with those in a general inpatient ward C. The geriatric acute care unit provides patient-centered care that emphasizes independence D. There is an increased likelihood that patients receiving care in a geriatric acute care unit will be able to return home upon discharge E. The geriatric acute care unit provides intensive review of medical care to minimize the adverse effects of medications Key Concept/Objective: To understand the benefits of specialized geriatric inpatient care Geriatric acute care units were designed to improve functional outcomes for older patients. The programs comprise four key elements: (1) a specially prepared environ- ment (e.
Buy 2mg ginette-35 free shipping. Women's Health: Knowledge is Power.
Were you to take a drug for a month or so it would be fairly safe but were you to take it for 5 years it would not be breast cancer 5k columbia sc buy ginette-35 2mg on line. In the same way women's health magazine uk back issues buy ginette-35 2 mg lowest price, the medical field is very eager to learn about people who meditate for a lifetime menopause 60 years ginette-35 2mg overnight delivery. That might include people who have problems, what the nature of those problems are, how they get problems and what they do to be rid of them. I’d like to know how you came to practice with Master Chia, whether there was any health problem that brought you into it or whether it was simply because you were interested in it. S: I hurt my back about 6 years ago and ever since then have a hard job sitting, let alone lying down. I couldn’t sleep through a whole night, my neck especially would hurt me. Ever since I came to practice with Master Chia, in fact, immediately upon trying this, the pain abated. As though to prove the point, about 2 or 3 weeks ago I became a little slipshod about my practice. There are formulae you have to do — exercises might be a better term — and I was pressed for time and began to find excuses. I cut down the number of repetitions that were called for in each of the meditations and sure enough, my neck began to hurt again and my back has begun to hurt gain, too. I don’t really know, it may be a purely circumstantial thing. There may be other factors involved in this case, but it would seem over the years that I tried various things and had no help. It is more than - 136 - Chapter XIII coincidence that when I tried Master Chia’s practice it did seem to help. I had the usual orthopedic treatments with hot soaks and analgesics and muscle relaxants, which had me walking around in a stupor. I went to a chiropractor with very transitory results, but with some arrest of pain. Then I went to an acupuncturist, who didn’t help at all. This practice seems to have done something, seriously. S: They said that there was severe muscle spasm — espe- cially of the upper back, involving the neck and the area that was subscapular. They also found a portion of my lower back in which the distance between the vertebrae was narrowed. It looked as though I’d have a chronic condition mainly because of some pulled or torn muscle attachments. For almost two weeks after I fell, I couldn’t lift my head. No inkling of a mes- sage (that I wanted to lift my head) would come through. In fact, when I tried to get up, just after I fell, I couldn’t. When I pushed myself over onto my side my head just flopped over. Gradually, after two weeks strength came back into my neck muscles, but there was still an assortment of clicking and crunching noises and pains. My head was tilted to one side and one shoulder was con- tracted and higher than the other for months. The insurance people, in fact, agreed that the whole area was in spasm. Young: What did Master Chia suggest you do to cure this condition? S: He first asked me to relax the area between and around my eyes. All kinds of heat and flowing sensations came on on their own. There were various pre- scribed exercises designed to open up various energy routes. For example, the six healing sounds I found most relaxing.
He has no symptoms and has never been vaccinated for rabies women's health vernon nj purchase ginette-35 2 mg. He is treated with prompt postexposure prophylaxis breast cancer tattoo design discount ginette-35 line, consist- ing of thorough washing of the bite wound and irrigation of the site with povidine-iodine solution menstrual headaches symptoms safe 2mg ginette-35. He is given human rabies immunoglobulin and rabies vaccine and is monitored closely. Which of the following statements regarding the infectivity of rabies virus is false? A bite on the face is associated with a 60% chance of disease B. A bite on the arm is associated with a 75% chance of disease C. A bite on the leg is associated with a 3% to 10% chance of disease D. A bite on the hand is associated with a 15% to 40% chance of disease Key Concept/Objective: To understand the relationship between site of infection and risk of disease Rabies virus is of the family Rhabdoviridae, genus Lyssavirus. However, in the United States, canine rabies has been sharply limited, and therefore, wildlife rabies has increased in importance; 90% of all reported cases of animal rabies now occur in wildlife, particularly wild car- nivores and bats. The infectivity of rabies virus varies with the site and mode of trans- mission. A bite on the face presents a 60% chance of disease; a bite on the hand or arm reduces the chance of disease to between 15% and 40%, and a bite on the leg presents only a 3% to 10% chance of disease. The risk of disease from a bite is almost 50 times greater than the risk from scratches by a rabid animal. The virus can be inhaled; inhala- tion of virus can cause rabies in laboratory workers exposed to viral aerosols and in explorers of bat-infested caves. Which of the following causes of mosquito-transmitted meningoencephalitis has a rodent vertebrate host? Murray Valley encephalitis virus 7 INFECTIOUS DISEASE 95 C. West Nile virus Key Concept/Objective: To know the vertebrate host of various viruses that cause meningoencephalitis Viral encephalitis is caused by a number of arboviruses belonging to the families Flaviviridae, Togaviridae, Bunyaviridae, and Reoviridae; other zoonotic viruses can also cause viral encephalitis. Almost all viruses that cause encephalitis are transmitted by either mosquitoes or ticks. Of those transmitted by mosquitoes, the majority have a bird vertebrate host. The exceptions are the encephalitides caused by Bunyaviridae, which include La Crosse encephalitis; California encephalitis; some viruses of the Togaviridae family, including Venezuelan equine encephalitis; and some cases of Western equine encephalitis. Louis encephalitis, West Nile encephalitis, and Murray Valley encephalitis are all transmitted by mosquitoes that have birds as their vertebrate host. A 42-year-old man presents to your clinic with complaints of fever, rigors, headache, and backache. The onset of symptoms was sudden and began 5 days ago. He reports that he recently traveled to Brazil for a 2-month vacation on the Amazon and that symptoms began 1 week after he returned. He reports that the symptoms subsided somewhat approximately 2 days ago but that he again feels ill. In addition to fever, rigors, headache, and backache, his symptoms now include nausea, vomiting, and decreased urine output. He has no other significant medical history or family history, and he takes no medications. On physical examination, the patient appears ill, restless, and flushed. Vital signs are as follows: temperature, 104 F° (40° C); blood pressure, 97/74 mm Hg; respiratory rate, 19 breaths/min; heart rate, 69 beats/min. HEENT examination is significant for flushing, swollen lips, and red tongue. The cardiovascular examination is normal, and no gallop or murmurs are heard.