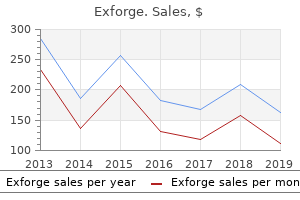
Exforge
"Generic 80mg exforge amex, blood pressure ratio".
By: V. Kayor, M.S., Ph.D.
Deputy Director, University of Missouri–Kansas City School of Medicine
Most trials specifically excluded patients with vascular dementia and clinically significant neurologic disease other than AD prehypertension prevalence 80mg exforge otc. Some trials did not specify such exclusion criteria or report the proportion of patients with such comorbid disease heart attack cover by sam tsui and chrissy costanza of atc discount exforge 80 mg otc. Most studies allowed patients to use other medications except for drugs with cholinomimetic effects or anticholinergic medications pulse pressure 12080 80mg exforge mastercard. Outcome measures Studies commonly included measures to assess symptom stabilization (e. Global change often was measured using scales such as the CGI-C, CIBIC-plus, or GDS; functional status was commonly assessed using measures such as the ADCS-ADL, DAD, Bristol ADL, and PDS. Changes in mood, behavior, and personality were assessed with measures such as the NPI or BEHAVE-AD. Some studies included other instruments that assessed quality of life or caregiver burden. Head-to-head comparisons We did not identify any randomized, double-blind, comparative trials. We did identify three open-label 27-29 27 head-to-head trials. One trial compared donepezil to galantamine over 52 weeks, one compared 28 29 donepezil to galantamine over 12 weeks, and one compared donepezil to rivastigmine over 12 weeks. These trials blinded only the rater to treatment allocation. Although open-label trials are subject to “fatal flaws” for internal validity, we review their results because they provide the only comparative evidence. Although these reviews do not make indirect comparisons among included ChEIs, the quantitative summary of placebo-controlled trials is useful for summarizing evidence for ChEIs in general. Galantamine One 52-week open-label trial compared donepezil 10 mg/day to galantamine 24 mg/day in 182 patients 27 with probable AD and MMSE scores between 9 and 18 at screening. On average, study participants were 73 years of age with a mean baseline MMSE score of 15. The primary study endpoint was based on function assessed by the Bristol ADL; cognitive outcome measures included the MMSE and ADAS-cog, behavioral disturbances were assessed with the NPI, and caregiver burden was measured using the SCGB scale. At endpoint no statistically significant differences were observed in functional abilities, cognitive symptoms, behavioral disturbances, or caregiver burden between the donepezil and galantamine treatment groups. One 12-week open-label trial compared flexible doses of donepezil 5-10mg/day (once daily) and 28 galantamine 8-24mg/day (twice daily) in 120 patients with probable or possible AD; as in the 52-week trial, only raters were blinded to treatment allocation. The mean age of study participants was 74 years with a mean baseline MMSE score of 21. On average, baseline MMSE scores for patients in this trial indicated less severe disease than in the 52-week trial. At baseline, patient demographics and disease characteristics were similar in both groups. The primary outcome measure was unblinded physician and caregiver satisfaction as measured on a scale specifically developed by the makers of donepezil for use in 29 another head-to-head trial (presumably this instrument had not been previously validated). Secondary outcome measures included cognition (ADAS-cog, MMSE) and disability (DAD). At 12 weeks, both physician and caregiver satisfaction ratings were significantly better for donepezil (P < 0. Furthermore, donepezil-treated patients demonstrated significantly more improvement on the ADAS-cog, MMSE, and DAD (P < 0. In contrast to the 52-week study that demonstrated no difference between donepezil and galantamine, this trial was funded by the makers of donepezil. Additionally, this trial demonstrated the worst reported galantamine response among all other clinical studies. Rivastigmine One 12-week open-label trial compared flexible doses (5-10 mg/day) of donepezil to flexible doses (6-12 mg/day) of rivastigmine in 111 patients with mild to moderate AD. With regard to baseline disease severity, patients in this trial most closely resembled the 12-week trial comparing donepezil to galantamine. Cognitive symptoms and disease severity were assessed with the ADAS-cog and MMSE, respectively.
Low Overall withdrawal blood pressure chart gender order discount exforge, overall adverse pregabalin events blood pressure 40 over 20 purchase 80mg exforge with amex, withdrawal due to adverse events arrhythmia dysrhythmia purchase exforge from india, and diarrhea: No significant difference Headache and nausea: Significantly greater with milnacipran Milnacipran vs. Low Overall withdrawal: No significant amitriptyline difference Insufficient Overall adverse events and withdrawal due to adverse events: No significant difference Pregabalin vs. Low Overall withdrawal: No significant amitriptyline difference Insufficient Overall adverse events and withdrawal due to adverse events: No significant difference Gabapentin, Insufficient No conclusions can be drawn about cyclobenzaprine, comparative harms because the citalopram, numbers of trials/patients were too few fluoxetine, controlled- to provide meaningful results in indirect release paroxetine comparisons vs. All Insufficient No evidence found Drugs for fibromyalgia 48 of 86 Final Original Report Drug Effectiveness Review Project Strength of Key question Comparison evidence Conclusion 3. Are there subgroups of patients based on demographics (age, racial or ethnic groups, and gender), socioeconomic status, other medications, or comorbidities for which any included drugs are more effective or associated with fewer harms? Amitriptyline, Low Age: Response to amitriptyline or cyclobenzaprine cyclobenzaprine did not differ based on age. Others Insufficient Sex: Efficacy findings (not specified) for cyclobenzaprine were not influenced by sex. However, effect of duloxetine on pain was no longer significant in males. Race: Race did not influence efficacy for cyclobenzaprine, but pain reduction with duloxetine was significant in white but not nonwhite patients based on a small sample size. Comorbidities: Compared with placebo, duloxetine, fluoxetine, controlled-release paroxetine, and pregabalin significantly improved fibromyalgia symptoms regardless of baseline depression. Controlled-release paroxetine and pregabalin significantly improved fibromyalgia symptoms regardless of baseline anxiety. Abbreviations: AE, adverse event; FIQ, Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire total score; HRQOL, health-related quality of life; PGII, Patient Global Impression of Improvement; PGIC, Patient Global Impression of Change. CONCLUSIONS We found eligible studies of treatment for fibromyalgia with amitriptyline, nortriptyline, citalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, cyclobenzaprine, pregabalin, gabapentin, milnacipran, and duloxetine. We found no eligible studies with the other included drugs and no eligible studies of included interventions when used as adjunctive therapy. Head-to-head trials were few, and provided low-strength evidence that short-term treatment with immediate-release paroxetine is superior to amitriptyline in reducing pain and sleep problems and provided low-strength evidence there are no significant differences between amitriptyline as compared to cyclobenzaprine and nortriptyline. Although there were some significant differences between drugs in overall adverse events, they did not produce any differences in withdrawals due to adverse events. Additionally, based on indirect comparison meta-analysis, we found low evidence that duloxetine was superior to milnacipran on outcomes of pain, sleep disturbance, depressed mood, and health-related quality of life. We found low evidence that both duloxetine and milnacipran were superior to pregabalin on improvement in depressed mood, whereas pregabalin was superior to milnacipran on improvement in sleep disturbance. Amitriptyline was similar to duloxetine, milnacipran, and pregabalin on outcomes of pain and fatigue with insufficient data on the other outcomes. Although there were some significant differences between duloxetine, milnacipran, and pregabalin in specific adverse events, they did not produce any differences in overall withdrawals, overall adverse events, and withdrawals due to adverse events. Amitriptyline was no different than duloxetine, milnacipran, and pregabalin in overall withdrawals with insufficient evidence to report on comparative overall adverse events and Drugs for fibromyalgia 49 of 86 Final Original Report Drug Effectiveness Review Project withdrawals due to adverse events. For the remaining drugs, there was only evidence of significant improvements in pain over placebo in 1 trial for gabapentin, 1 of 3 trials for cyclobenzaprine, and in 1 trial of fluoxetine. But, no conclusions can be drawn about comparative effectiveness or harms among these drugs because the numbers of trials/patients in placebo-controlled trials were too few to provide meaningful results in indirect comparisons. There was a small body of evidence suggesting that duloxetine was not effective on pain reduction in male, nonwhite, and older patients based on a small sample size that was underpowered to detect a difference. Compared with placebo, duloxetine, fluoxetine, controlled- release paroxetine, and pregabalin significantly improved fibromyalgia symptoms regardless of baseline depression but a significant milnacipran effect compared with placebo was only observed in nondepressed patients. Controlled-release paroxetine and pregabalin significantly improved fibromyalgia symptoms regardless of baseline anxiety. Drugs for fibromyalgia 50 of 86 Final Original Report Drug Effectiveness Review Project REFERENCES 1. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration.
The mean reductions in Social Phobia Inventory (SPIN) results were greater in the paroxetine group but did not reach statistical significance (46% compared with 31% prehypertension yahoo discount exforge on line, P=0 arrhythmia heart attack quality 80mg exforge. Three specific adverse events occurred significantly more frequently in paroxetine-treated patients: tremor (45% compared with 14% hypertension and kidney disease order exforge with visa, P=0. Second-generation antidepressants 97 of 190 Final Update 5 Report Drug Effectiveness Review Project Sertraline compared with placebo Three fair RCTs compared sertraline and placebo in the treatment of patients with depression and 317-319 co-occurring alcohol dependence. A 24-week study compared sertraline (50-150 mg/d) with placebo in recently detoxified 317 alcohol-dependent patients with current depressive symptoms. Response (> 50% decrease in MADRS score) was slightly higher in sertraline- than placebo-treated patients (44% compared with 39%). Both groups experienced significant improvements in HAM-D and MADRS scores during the study, but the two groups did not differ significantly. Relapse rates were higher in sertraline- than placebo-treated patients (31. Adverse event rates were similar for both treatment groups. The overall attrition rate was greater than 40 percent; however, there was not a significant difference in withdrawal between groups (sertraline, 45% compared with placebo, 44%). In this fair study, 82 currently depressed, actively drinking alcohol-dependent subjects were randomized to sertraline (50-200 mg/d) or placebo. There was no significant difference between groups in depression symptoms. However, in women, treatment with sertraline was associated with less depression at the end of treatment than those receiving placebo based on HAM-D scores (P=0. There was no difference between groups in time to first heavy drinking day (P=0. Sertraline-treated subjects had fewer drinks per drinking day compared to placebo-treated subjects; the difference was significant (P=0. Less drinking during the study was associated with improved depression outcomes. Serious adverse events occurred in four subjects: three treated with sertraline and one treated with placebo. Loss to follow-up was twice as high in the placebo group (33%) compared to the sertraline group (16%); however, details were not reported on withdrawals due to tolerability or lack of efficacy. This study randomized 328 patients with co-occurring MDD and alcohol dependence to sertraline (50-200 mg/d) or placebo for 10 weeks. After the run-in period, two groups of patients were randomized separately based on HAM-D scores: Group A scores were > 17 while Group B scores were < 16. Mean reduction in HAM-D scores did not differ significantly between all sertraline-treated (-10. There were significant differences in HAM- D response rates by group stratification. In Group A, sertraline led to significantly higher response rate than placebo (64% compared with 47%, P=0. However, in Group B, sertraline patients had a significantly lower response rate than placebo patients (58% compared with 77%, P=0. There were no significant differences between medication groups in the reduction in BDI score from baseline to endpoint nor within Group A or Group B. No significant differences were detected between medication groups in drinking measures. Overall, the incidence of adverse events was similar between medication groups; however, significantly more sertraline-treated patients discontinued due to adverse events than placebo-treated patients (P<0. Alzheimer’s disease/dementia Two randomized trials compared sertraline and placebo for patients with depression and 320, 321 comorbid Alzheimer’s disease. More patients treated with sertraline responded to treatment (full responders, 38%; partial responders, 46%) than did patients treated with placebo (full responders, 20%; partial responders, 15%) (P<0. A second fair 12-week trial which randomized 133 patients with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease and depression to either sertraline (100mg/d) or placebo did not replicate the above findings. Mood was assessed by the modified Alzheimer Disease Cooperative Study- Clinical Global Impression of Change index and the CSDD. At the end of week 12, CSDD scores and remission rates did not differ between sertraline and placebo (OR 2.
An indirect comparison rendered no differences in efficacy between abatacept and rituximab arteria jugularis externa exforge 80mg with amex. Data were insufficient to conduct other indirect comparisons blood pressure chart boy order generic exforge on-line. Credible or confidence intervals of most indirect comparisons arrhythmia practice test order exforge 80mg line, however, were wide leading to inconclusive results without statistical significance. Results of studies employing indirect comparisons, therefore, must be interpreted cautiously because clinically significant differences among targeted immune modulators cannot be ruled out with certainty. Table 7 summarizes studies that conducted indirect comparisons. Targeted immune modulators 36 of 195 Final Update 3 Report Drug Effectiveness Review Project Figure 2. Adjusted indirect comparisons of targeted immune modulators for American College of Rheumatology 50 response Favors second drug Favors first drug ABATACEPT abatacept-adalimumab 0. Adjusted indirect comparisons of etanercept including the TEMPO study for American College of Rheumatology 50 response Favors control drug Favors etanercept etanercept-abatacept 1. Characteristics and results of studies conducting indirect comparisons Author Primary Year Comparisons outcome Conclusion Rating Certolizumab pegol, adalimumab, Devine, et Similar efficacy among targeted 60 etanercept, golimumab, infliximab, ACR 50 Fair al. Adalimumab and infliximab are 56 Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab 20/50,70, Fair 2008 more efficacious than etanercept withdrawal No differences in efficacy between ACR Malottki, et Abatacept, adalimumab, etanercept, abatacept and rituximab in patients 61 20/50,70, Good al. Detailed assessment: Evidence on the general efficacy Multiple placebo-controlled randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses provided evidence 64-73 74-86 87-92 93-98 on the general efficacy of abatacept, adalimumab, anakinra, certolizumab pegol, 48,53,54,76,99-109 110-113 76,114-127 128-135 etanercept, golimumab, infliximab, rituximab, and 136-142 tocilizumab. Most of these studies were conducted in patients who had failed synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug treatment. In the following section, we have summarized evidence on the general efficacy of targeted immune modulators in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. This, however, does not provide evidence on the comparative efficacy and tolerability of targeted immune modulators. If we identified high quality meta-analyses, we reported the pooled estimates but did not describe the results of individual component studies, except when outcome measures of interest were reported (e. Table 8 summarizes studies included for general efficacy. Targeted immune modulators 39 of 195 Final Update 3 Report Drug Effectiveness Review Project Abatacept A well-conducted systematic review and meta-analysis of seven randomized controlled trials including 2908 patients treated with abatacept or placebo reported statistically significantly higher American College of Rheumatology 50 response rates for patients on abatacept (relative 64 risk, 2. The number needed to treat to achieve American College of Rheumatology 50 response was 5 (95% CI, 4 to 7). Patients treated with abatacept also showed statistically significant improvement in pain, physical function, and disease activity. Adalimumab Two well-conducted meta-analyses examined the efficacy of adalimumab in patients with 75,76 rheumatoid arthritis. Overall these studies included data on more than 2800 patients. Pooled results presented statistically significantly greater improvements of adalimumab- than placebo- treated patients on all outcome measures (American College of Rheumatology 20/50/70, DAS 28). The numbers needed to treat to achieve one additional responder on American College of 76 Rheumatology 20/50/70 were 5, 5, and 7, respectively. A placebo-controlled trial (n=47) 74 conducted in Asian patients reported similar findings. Anakinra 88 We identified one recent high-quality meta-analyses on the general efficacy of anakinra. Pooled results presented statistically significantly greater improvements of anakinra- than placebo-treated patients on all outcome measures (American College of Rheumatology 20/50/70, Health Assessment Questionnaire, and Patient Global Assessment). The numbers needed to treat to achieve one additional responder on American College of Rheumatology 20/50/70 were 8, 9, and 22, respectively. A placebo 143 controlled trial (n=54) conducted in Asian patients reported similar findings. Certolizumab pegol A good systematic review and meta-analysis of five randomized controlled trials including almost 2400 patients treated with certolizumab pegol or placebo reported statistically significantly higher American College of Rheumatology 50 response rates for patients on certolizumab pegol (relative risk, 2.