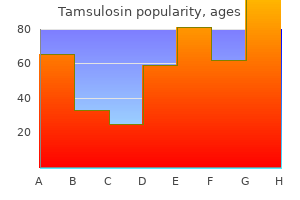
Tamsulosin
"Purchase tamsulosin with paypal, prostate cancer quotes".
By: D. Garik, M.A.S., M.D.
Deputy Director, UCSF School of Medicine
In a large observational European series prostate size buy tamsulosin 0.4 mg free shipping, risk factors for sudden death and appropriate implantable cardioverter- defibrillator therapy included nonsustained ventricular tachycardia prostate health vitamins generic 0.2 mg tamsulosin visa, left ventricular ejection fraction less 20 than 45% at presentation prostate cancer lung metastasis tamsulosin 0.4mg on-line, male sex, and lamin A or C non–missense mutations. Routine imaging for evaluation of left ventricular function is appropriate in all patients with Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy and the associated disorders. Patients with left ventricular dysfunction should benefit from pharmacologic therapy, but data on this issue are limited. Female carriers of X-linked recessive Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy develop conduction disease, and electrocardiographic monitoring on a routine basis is appropriate. Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophies Genetics The limb-girdle muscular dystrophies are a group of disorders with a limb-shoulder and pelvic girdle 21 distribution of weakness, but with otherwise heterogeneous inheritance and genetic cause. Autosomal recessive (subtypes 2A to 2W), dominant (subtypes 1A to 1H), and sporadic patterns of inheritance have been observed. Genes involved include those encoding dystrophin-associated glycoproteins, sarcomeric proteins, sarcolemma proteins, nuclear membrane proteins, and cellular enzymes. An autosomal dominant limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (subtype 1B) with a high prevalence of arrhythmias and a late dilated cardiomyopathy is caused by mutations encoding lamin A/C, as in Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. An autosomal recessive or sporadic limb-girdle muscular dystrophy associated with a progressive dilated cardiomyopathy is caused by mutations affecting the function of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex, including sarcoglycan and fukutin-related proteins (subtypes 2C to 2F and 2I, respectively). The sarcoglycans complex with dystrophin-associated glycoproteins to counteract mechanical stress associated with contraction. Fukutin-related proteins affect glycosylation of a dystrophin-associated glycoprotein. An autosomal recessive limb-girdle muscular dystrophy associated with a variable onset of a dilated cardiomyopathy is caused by a mutation in a sarcolemmal repair protein termed dysferlin (subtype 2B). Other more recently discovered and rarer subtypes of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy are variably associated with cardiac or arrhythmia abnormalities in limited reports. Clinical Presentation The onset of muscle weakness is variable but usually occurs before age 30. The recessive disorders tend to cause earlier and more severe weakness than the dominant disorders. Patients commonly present with complaints of difficulty with walking or running secondary to pelvic girdle involvement. As the disease progresses, involvement of the shoulder muscles and then more distal muscles occurs, with sparing of facial involvement. Cardiovascular Manifestations As with many of the features of the limb-girdle muscular dystrophies, heterogeneity in the presence and degree of cardiac involvement is usual. The limb-girdle muscular dystrophies types 2C to 2F, termed sarcoglycanopathies, manifest with a dilated cardiomyopathy. Cardiac abnormalities are detected in a majority of patients typically a decade after skeletal muscle symptoms occur. Cardiomyopathy is most common in the subtype 2E and least common in the subtype 2D. A severe cardiomyopathy, including presentation with heart failure in childhood, can occur. Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2I, caused by mutations in fukutin-related proteins, is associated with a dilated cardiomyopathy. The age at disease onset and severity of skeletal muscle involvement are variable, with symptoms emerging in some patients during childhood but more typically developing after the age of 20 years. Approximately one half of patients with limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2I exhibit cardiac involvement (Fig. Cardiac findings include regional wall motion abnormalities or a dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure. Conduction disease does not occur separate from the structural cardiac involvement. Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2B, termed a dysferlinopathy, has been associated with increased myocardial fibrosis on cardiac magnetic resonance imaging and variably with a dilated cardiomyopathy.
This can be done either with a coronary artery punch descending thoracic aorta is immediately posterior to the left or freestyle with a #11 blade prostate cancer and back pain buy tamsulosin without a prescription. The anastomosis is almost always close to the proximal branch of the right pulmonary artery prostate cancer awareness color buy tamsulosin with mastercard. The patient is then the left pulmonary artery from the right pulmonary artery has warmed and weaned from cardiopulmonary bypass; the ster- been partially transected prostate ultrasound biopsy procedure cheap 0.2mg tamsulosin otc. A cuff of left pulmonary artery is notomy incision is closed in the usual fashion. The technique of slide tracheoplasty is illus- nary artery sling will have tracheal stenosis secondary to trated in Figure 4. This operation is performed through a complete tracheal rings, as shown in Figure 4. In contrast, the inset shown in the mid- the trachea may be opened without the need for intubation of portion of this child’s trachea demonstrates complete tra- the bronchus through the operative field. This nosis extends up to the cricoid cartilage, we have used a col- forms a complete cartilaginous tracheal ring, which compro- lar incision in the neck at the top of the sternotomy incision mises the tracheal lumen. The stenosis secondary to com- to adequately visualize the cervical portion of the trachea. If plete tracheal rings can sometimes be severe—as small as the patient has an associated pulmonary artery sling or intra- 2 mm in diameter. Techniques for the care of infants with cardiac anomaly that requires correction, these procedures complete tracheal rings have evolved over the past 30 years. In many cases, we pass a small needle through the anterior trachea to identify and carefully assess the precise midportion of the trachea. Once the midportion of the trachea has been identi- fied, the trachea is transected at this site, as illustrated in Figure 4. The first is an incision in the anterior aspect of the infe- rior portion of the transected trachea. The incision is performed with a #11 blade and continues until the carina has been reached or the tracheal rings have ended and there is normal membranous trachea posteriorly. The anastomosis can then be per- formed with either interrupted sutures, as shown in Figure 4. The trachea is now half of its previous length, but the internal luminal diameter has been increased by a factor of four. Following the anasto- mosis, bronchoscopy is performed to aspirate secretions and to ensure that the stenosis has been resolved. This operation is facilitated by fully mobilizing the trachea, taking care to avoid the recurrent laryngeal nerves in the neck. The heart is allowed to beat in normal sinus rhythm throughout the pro- For approximately 15 years, pericardial tracheoplasty was cedure. The anterior side of the trachea is dissected through- our procedure of choice, but we no longer use it. An incision is should be familiar with this operation, however, as it may be then made in the anterior trachea, extending from the begin- useful in some cases. The pericardial patch is then sutured in place, as which occurs in 10–15 % of patients with complete tracheal illustrated in Figure 4. For pericardial tracheoplasty, cardiopulmonary bypass operation effectively opens the tracheal lumen. An autologous pericardial cheal tube is used as a stent for the patch and must be left in patch that is as long as the length of the tracheal stenosis is place for 1–2 weeks postoperatively. We did not treat a significant problem following the operation, but it can be these pericardial patches with glutaraldehyde, but rather pre- partially avoided by tacking the pericardium to surrounding served them in a sterile saline solution while the trachea was vascular structures such as the ascending aorta and innomi- prepared. The patient is placed on cardiopulmonary bypass nate artery at the time of closure. The sec- For the patient with a short segment of tracheal stenosis, it is tion of tracheal stenosis is sharply resected. The end-to-end possible to mobilize the trachea and perform an end-to-end anastomosis is then performed by mobilizing the superior anastomosis, as illustrated in Figure 4. The tra- less than 30 % of the total tracheal length (usually less than cheal lumen is then evaluated again with fiberoptic bron- five complete tracheal rings). These patients can be formed with a median sternotomy approach and the use of weaned and extubated rather quickly because of the rela- cardiopulmonary bypass.
General Care The general management of survivors of cardiac arrest is determined by the specific cause and the underlying pathophysiologic process prostate one a day discount 0.2 mg tamsulosin fast delivery. The indications for revascularization after cardiac arrest are limited to those who have a generally accepted indication for angioplasty or surgery prostate biopsy video tamsulosin 0.2 mg low cost, including a documented ischemic mechanism of the cardiac arrest mens health no gym workout order tamsulosin online from canada. Moreover, in an uncontrolled observation comparing cardiac arrest survivors who had ever received beta blockers after the index event with those who had not, a significant improvement in long-term outcome with beta-blocker therapy was noted. Indications for implantable cardioverter-defibrillators based on evidence and judgment. Guideline classifications and levels of evidence are derived from an amalgamation of narrative and tabular statements in two 165,166 recent guidelines documents, with variations in the documents adjudicated by the authors. Indications for implantable cardioverter-defibrillators based on evidence and judgment. Four antiarrhythmic strategies, which are not mutually exclusive, can be considered for patients at high risk for cardiac arrest: implantable defibrillators, antiarrhythmic drugs, catheter ablation, and antiarrhythmic surgery. The mainstay of therapy for the highest-risk patients is the implantable defibrillator. The choice of a therapy, or combinations of therapies, is based on estimation of risk determined by evaluation of the individual patient by various risk-profiling techniques, coupled with available efficacy and safety data. Methods to Estimate Risk for Sudden Cardiac Death General Medical and Cardiovascular Risk Markers The presence and severity of acquired medical disorders (e. The model demonstrated large, nonlinear gradients of risk, with the major impact in the highest one or two deciles. This magnitude of risk is not sufficient to justify certain interventions, and further risk stratification is needed to identify even higher-risk subgroups at sufficient risk to merit advanced therapies. The potential importance of proper timing and combining of risk markers has been explored. Ambulatory Monitoring Ambulatory monitoring remains useful for profiling the risk for development of life-threatening sustained arrhythmias in individuals with certain forms of structural or electrophysiologic disease who are considered to be at high risk (see Chapter 35). Technological advances facilitate very-long-term monitoring and allow identification of episodic arrhythmias as causes of relevant symptoms, such as near- syncope and syncope. For the evaluation of precipitating ventricular arrhythmias, most previous studies had demonstrated limitations because an average of less than 50% of cardiac arrest survivors had inducible ventricular arrhythmias. For patients without prior cardiac arrest who have symptomatic arrhythmias or who are considered to be at potentially high risk, programmed stimulation is still used, although to a more limited extent. Although it has been suggested that induction of nonsustained ventricular rhythms may indicate risk, it is generally considered nonspecific in the absence of structural heart disease or when an aggressive protocol is used. The reliability of noninducibility to 172 predict absence of risk is also questioned. It had evolved as the preferred method of management despite concerns about the sensitivity and specificity of the various pacing protocols and the extent to which myocardial status at the time of the programmed electrical stimulation study reflects that present at the clinical cardiac arrest. Nonetheless, as mentioned, most studies have demonstrated limitations based on observations that a relatively small fraction of cardiac arrest survivors (an average of <50% on the basis of multiple studies) had inducible arrhythmias. Surgical Intervention Strategies The previously popular antiarrhythmic surgical techniques now have limited applications. With rare exceptions, catheter ablation techniques are not used for the treatment of higher-risk ventricular tachyarrhythmias or for definitive therapy in patients at risk for progression of the arrhythmic substrate. The outcome demonstrated a 59% reduction in the relative risk for total mortality (54% cumulative) and a 19% reduction in the absolute risk of dying at 2 years of follow-up. The problem that affects all long-term strategies for cardiac arrest survivors, however, is the lack of a reliable concurrent natural history denominator against which to compare the effects of interventions, because of ethical concerns about withholding therapy in a placebo- controlled study model for patients at high risk of dying, in conjunction with the confounding influence of specific cardiovascular therapies that may also improve survival. Because it is a retrospective analysis and underpowered, the observation calls for confirmation. Since a placebo-controlled trial cannot be done on ethical grounds, this would require a rigidly designed and executed postimplant surveillance study. All the major trials for both primary and secondary indications were published during an interval of 10 years between late 1996 and early 2005.
Discount 0.2mg tamsulosin with mastercard. Resistance Band Glute Stretch - OL Healthy Living Quick Tip.