Panmycin
"Buy panmycin with mastercard, antibiotics and xanax side effects".
By: U. Tuwas, M.A.S., M.D.
Co-Director, Idaho College of Osteopathic Medicine
The systolic pressure indicates vasoconstriction alongwith stroke volume and rigidity of the main vessels virus journal 500 mg panmycin with visa. The pulse pressure antimicrobial lotion purchase discount panmycin online, which is systolic pressure minus diastolic pressure antibiotic resistance journal panmycin 500mg on line, indicates the stroke volume of the heart and cardiac output. If the patient is not hyperventilating in shock, he is probably suffering from central nervous system or respiratory system damage. Persistent hyperventilation is an ominous sign and indicates improper treatment of shock. This is performed with full aseptic precautions with the patient in head-down position. The head-down position is used to distend the vein and to prevent air being sucked in. The catheter tip is gradually pushed in to be positioned in the superior vena cava. An alternative route is the insertion of the catheter via the median basilic vein in the antecubital fossa. This catheter provides 3 types of information — (a) flow in the cardiovascular system; (b) sampling of blood from the pulmonary artery to give accurate measurements of blood gases in mixed venous blood and (c) filling pressure of both right and left sides of the heart can be measured. A known volume of a cold crystalloid solution is injected into the right atrium and by measuring the resulting temperature drop in the pulmonary artery is passed by a thermistor located at the end of the catheter. Computers specially designed to calculate cardiac output from thermodilution measurements are available. The pulmonary artery systolic and diastolic pressures can also be measured but with less accuracy. The pulmonary artery wedge pressure is a better indicator of circulating blood volume and left ventricular function. If the catheter is in a portion of the lung where inflation of the lung occludes the pulmonary capillaries the end of the Swan-Ganz catheter estimates the pressure in the alveoli rather than the pressure in the left atrium. So the end of the catheter is to be positioned where it is not compressed by the lungs. This catheter is used to differentiate between left and right ventricular failure, presence of pulmonary embolism and can also be used as a guide to therapy with fluids. Appropriate introducers, cannula and guide wire are used and the catheter is flushed with heparin saline where it is introduced into the right atrium. The normal pulmonary capillary wedge pressure is between 8 and 12 mm Hg or 11 and 16 cm H 0. The normal pulmonary artery pressure is2 about 25 mm Hg systolic and 10 mm Hg diastolic. This starts with establishment of a clear airway and maintaining adequate ventilation and oxygenation. Lowering of the head with support of the jaw to prevent airway obstruction and administration of oxygen are usually all that are needed. Lowering of the head will improve venous return preventing stasis of blood in the muscles of the leg and preventing oedema. In those patients where there is airway obstruction, intratracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation are required. Many patients in shock, particularly those who are suffering from traumatic or septic shock require intubation and positive-pressure ventilation. Abrupt increase in airway pressure expands the alveoli and displaces blood from the pulmonary vasculature into the left atrium and ventricle. But it must be remembered that positive-pressure ventilation is only applied when it is necessary otherwise it may compress the superior and inferior venae cavae and impair right atrial filling causing decrease in the right atrial stroke volume. This may be achieved by raising the footend of the bed and by compression bandage to tamponade external haemorrhage. Operation may be required to stop such bleeding as soon as some resuscitation has been achieved.
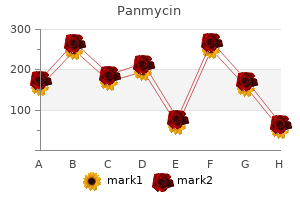
In case of the knee joint the quadriceps muscles waste first antibiotic for uti septra ds bactrim panmycin 500 mg fast delivery, similarly in case of hip the glutei waste first antibiotic prophylaxis dental generic panmycin 500mg with visa. The temperature of the diseased joint must be compared with that of the healthy joint treatment for dogs collapsing trachea discount 250mg panmycin overnight delivery. The teaching is that always feel the joint of the sound side first and then the diseased joint. The bones in the vicinity of the joint and the bony attachments of various ligaments are carefully palpated for tenderness, as the former will be tender in fracture and the latter will be tender in sprain. An enlarged bursa will be soft and cystic and will correspond with the anatomical position of the bursa. Occasionally a swelling at the joint may not be due to effusion but due to swelling like subcutaneous lipoma or cyst. It is always advisable to examine the sound side first so that the patient knows what is to be done with the affected joint and his fear and muscle spasm can be greatly eliminated. If so, when does the pain start and when does it disappear, (b) Is there any restriction of the movements? In certain diseases certain types of movements are restricted whereas the other movements remain normal, (c) Is there any protective muscular spasm? To demonstrate, a short sharp movement is made and the muscle will be seen to go into spasm. Muscular spasm is almost always associated with active stage of arthritis, (d) Is there any crepitus felt during movement of the joint? Limitation of movements in all directions is an important feature of acute arthritis. One thing must be borne in mind during examination of movements of different joints that a few joints e. This is due to the movements of the neighbouring joints, as for example in case of shoulder joint the movement of the scapula, acromioclavicular and sternoclavicular joints; in case of the hip such movements occur at the lumbar spine; in case of the ankle movements may occur at the subtaloid and midtarsal joints. In early cases of osteoarthritis fine crepitation may be missed by the palpating fingers. In case of the hip joint the external iliac group of lymph nodes are affected, whereas in case of the knee joint the inguinal group of lymph nodes are affected. The lungs and the cervical lymph nodes should be examined in case of suspected tuberculous arthritis. Signs of syphilitic stigmas should be looked for in case of syphilitic affection of the joint (See Fig. History of urethral discharge and examination of the smear obtained from prostatic massage will help to Fig. Search for septic foci in teeth, tonsils, air sinuses and even cervix uteri in case of acute arthitis, Fig. The jerk will be gradually losing and the ankle jerk will be lost earlier than the knee jerk. In the upper limb syringomyelia is the common lesion and this is diagnosed by dissociation of sensations (i. Examination of neighbouring joints is of immense importance in case of certain joints. This is referred pain due to common nerve supply of these two joints (femoral, obturator and sciatic nerves). Both the antero-posterior and the lateral views of the pathological joints are taken and may be compared with those of the sound side. In tuberculous arthritis appearance of sclerosis in the rarefied area is considered to be a definite sign of recovery. Increase in this space indicates effusion in the joint and denotes the first stage of arthritis. Diminution of this space indicates erosion of the articular cartilage and signifies the second stage of arthritis. Its negative result is more important as it excludes the presence of this disease. Biopsy of the lymph nodes may be done, though occasionally practiced, in suspected cases of tuberculous arthritis. Biopsy of the synovial membrane besides its diagnostic value possesses a therapeutic advantage in rheumatoid arthritis particularly when it affects a single joint.
Most commercial formulas are cow-milk–based with modifications to approximate breast milk infection from cat bite discount panmycin online mastercard. Specialty formulas (soy antimicrobial office supplies 500 mg panmycin with amex, lactose-free infection rate in hospitals purchase panmycin with paypal, premature, elemental) are modified to meet specific needs. Assessment based on acquisition of milestones occurring sequentially and at a specific rate Each skill area has a spectrum of normal and abnormal. Abnormal development in one area increases likelihood of abnormality in another—so need to do a careful assessment of all skills Developmental diagnosis—functional description/classification; does not specify an etiology Developmental delay—performance significantly below average, i. Exam questions typically describe an infant’s/child’s skills and ask for the corresponding age. Newborn Reflexes Gross Motor Visual Motor Language Social Adaptive Birth Symmetric Visually fixes on an Alerts to sound Regards face movements in supine object Head flat in prone 2 months Head in midline Follows past midline Smiles in response to touch Recognizes parent while held sitting and voice Raises head in prone Begins to lift chest 4 months Holds head steadily Reaches with both arms Laughs Likes to look around Supports on together Orients to voice forearms in prone Hands to midline Coos Rolls from prone to supine 6 months Sits with support Unilateral reach Babbles Recognizes that (tripod) Raking grasp someone is a stranger Feet in mouth in Transfers object supine 7 months Rolls from supine to prone May crawl Starts to sit without support 9 months Crawls well Immature pincer grasp “Mama,” “dada,” Plays gesture games Pulls to stand Holds bottle indiscriminately Explores environment Starting to cruise Throws object (not Understands “no” (crawling and overhand) Understands gestures cruising) 12 months May walk alone Mature pincer grasp 1-2 words other than “mama” Imitates actions (must by 18 months) Crayon marks and “dada” (used Comes when called Object permanence appropriately) Cooperates with (from 10 months) Follows 1-step command with dressing gesture 15 months Creeps up stairs Scribbles and builds 4-6 words Uses cup and spoon Walks backward towers of 2 blocks in Follows 1-step command (variable until 18 imitation without gesture months) 18 months Runs Scribbles spontaneously 15-25 words Imitates parents in Throws objects Builds tower of 3 blocks Knows 5 body parts tasks overhand while Plays in company of standing other children 24 months Walks up, and down Imitates stroke (up or 50 words Parallel play stairs one foot at a down) with pencil 2-word sentences time Builds tower of 7 blocks Follows 2-step commands Removes clothing Uses pronouns inappropriately 3 years Alternates feet going Copies a circle ≥250 words Group play up the stairs Undresses completely 3-word sentences Shares Pedals tricycle Dresses partially Plurals Takes turns Unbuttons All pronouns Knows full name, age Dries hands and gender 4 years Alternates feet going Copies a square Knows colors Plays cooperatively downstairs Buttons clothing Recites songs from memory Tells “tall tales” Hops and skips Dresses completely Asks questions Catches ball 5 years Skips alternating feet Copies triangle Prints first name Plays cooperative Jumps over lower Ties shoes Asks what a word means games obstacles Spreads with knife Answers all “wh-” questions Abides by rules Tells a story Likes to help in Plays pretend household tasks Knows alphabet Table 4-2. Developmental Milestones Clinical Recall A young boy is able to walk and build a tower with 7 blocks. He plays well alongside other children and can say “my toy” or “my turn,” with an inventory of about 50 words. While all babies receive hearing testing within the first month of life, that is for congenital sensorineural hearing loss. Over the first year of life, conductive hearing loss may occur from repeated ear infections. If there is a lack of development or regression of language skills with impaired social interaction, restricted activities and interests and stereotypic behaviors, consider autistic spectrum disorder. After a complete H and P with neurologic exam and development testing, the first step is to perform an autism screening questionnaire. If you feel the diagnosis is likely, the next step is to refer to a specialist in this area. When you find this, you must first look for a possible reason, and the child will need developmental therapy in ≥1 areas. The mother says that during the day he has no problems but is usually wet 6 of 7 mornings. No long- term laxative use Concomitant behavioral management Regular postprandial toilet-sitting High-fiber diet Familial support for behavior modification Group or individual psychotherapy Clinical Recall A concerned mother brings her 4-year-old son to the physician for evaluation of nocturnal enuresis. The baby is doing well, and physical examination, growth, and development are normal. The mother states that after the last set of immunizations the baby had a temperature of 39. What is your advice to this mother before administering the next set of immunizations? Unknown or uncertain immunization status When in doubt, the child should be considered to be disease-susceptible, and appropriate immunizations should be initiated without delay. To be counted, the vaccine(s) must be documented on a formal immunization record, regardless of country. Dose—No reduced dose or divided dose should be administered, including to babies born prematurely or at low birth weight (exception: first dose hepatitis B). Active immunization of people who recently received gamma globulin Live virus vaccine may have diminished immunogenicity when given shortly before or during the several months after receipt of immunoglobulin (Ig) so live vaccine is delayed (3–11 months). There is no causal relationship between hepatitis B vaccine administration and demyelinating neurologic disorders. There is no causal relationship between meningococcal vaccination and Guillain-Barré. Guidelines for administration are based on the physician’s assessment of illness and on specific vaccines the child is scheduled to receive. If fever or other problems suggest moderate or serious illness, the child should not be immunized until recovered. Influenza vaccine (and yellow fever) does contain egg protein and on rare occasions may induce a significant immediate hypersensitivity reaction. Give the vaccine and observe for 20-30 min, unless absolute evidence of previous severe reaction with egg or egg protein product. All children and adolescents who have not been immunized should begin the series during any visit to the physician. The rates of local reactions, fever, and other common systemic reactions are substantially lower with acellular pertussis vaccines than with whole-cell vaccine (but may still occur).
Straight X-ray of the abdomen particularly in sitting position may reveal gas under the diaphragm — a definite sign of rupture of a hollow viscus antibiotic resistance lancet buy panmycin 250 mg amex. Loss of psoas shadow may be helpful in the diagnosis of retroperitoneal effusion of blood antibiotics side effects buy panmycin 500 mg. Even in case of intraperitoneal haemorrhage one can find a bigger blurr gap between the air-fluid intestinal loops antibiotic that starts with r buy panmycin 250mg lowest price. Individual circulations are outlined by selective catheterization in case of hepatic, splenic, renal and superior mesenteric arteries. Particularly in delayed rupture of the spleen, the diagnosis is established much before and operation can be undertaken earlier which would otherwise have been postponed until actual rupture has taken place. First of all this test should only be ventured by those who are very much experienced in doing this test and secondly a negative result does not exclude intra-abdominal injury. Fluid should be sent for physical, chemical, microscopic and bacteriological examinations. After a few minutes this fluid is aspirated out and examined thoroughly to come to a diagnosis. Crush injuries may occur in run-over accidents or fall of heavy objects on the abdomen. Seat-belt injury is also included in this group in which during driving a car sudden break will cause the trunk and viscera to move forward with the abdominal wall and become decelerated against the seat-belt and compressed against the spinal column behind. There may be even detachment of the gut from the mesentery and contusion of the abdominal contents. In this type of injury the peritoneal cavity is exposed outside and peritonitis is almost inevitable. The intra-abdominal organ which may be injured by such injury depends on the site of this penetrating wound. As for example stab injury to the right upper quadrant of the abdomen may injure the liver. This often causes internal haemorrhage and/or peritonitis from injury to the hollow viscus. Internal haemorrhage produces certain general signs which are common for injury to any viscus inside the abdomen. In case of internal haemorrhage, increasing pallor, restlessness, small thready pulse, deep and sighing respiration (air-hunger), subnormal temperature and collapse are the general signs. Liver injury may occur as a result of a penetrating wound by stabbing or bullet injury. Right lobe is more commonly injured (5 : 1) than the left lobe as it is less mobile and large. Occasionally when the central part of liver is ruptured bleeding occurs into the large radicles of the biliary tree so that liquid blood is carried along the bile passages into the duodenum and there is haematemesis. Scanning with radioactive isotopes like colloidal gold or "Technetium may detect injury to the liver. Straight X-ray may show increased haziness around the liver region and the diaphragm becomes immobile. Fracture of lower ribs or transverse processes of first two lumbar vertebrae may become evident. This leads to catastrophic internal haemorrhage and becomes fatal within a few minutes. There are signs of initial shock when it may not be possible to state precisely which organ has been damaged. Gradually this initial shock is recovered and the signs of intra-abdominal bleeding caused by ruptured spleen will become evident. After moderate intra-abdominal haemorrhage, adequate clotting occurs to control the haemorrhage temporarily. Thus when the patient is first seen the general signs may not be that alarming, but the local signs become more important to come to a diagnosis. This sign may be demonstrated by elevating the foot of the bed for 15 minutes, by which time blood will accumulate below the left cupula of the diaphragm, (d) Presence of shifting dullness in the flanks is fairly common.