Meloxicam
"Buy meloxicam 7.5 mg line, arthritis finger joint pain".
By: P. Onatas, M.A., M.D.
Vice Chair, University of South Carolina School of Medicine
The elimination half-life of the drug is greater in women and is increased significantly in the elderly arthritis pain when pregnant generic meloxicam 7.5mg visa. In most cases rheumatoid arthritis knuckles purchase meloxicam 15 mg with mastercard, changes in renal function do not have a marked effect on the elimination of parent drugs rheumatoid arthritis rain buy meloxicam 7.5mg free shipping. Phenobarbital is excreted unchanged in the urine to a certain extent (20–30% in humans), and its elimination rate can be increased significantly by alkalinization of the urine. This is partly due to increased ionization at alkaline pH, since phenobarbital is a weak acid with a pK of 7. Factors Affecting Biodisposition The biodisposition of sedative-hypnotics can be influenced by several factors, particularly alterations in hepatic function resulting from disease or drug-induced increases or decreases in microsomal enzyme activities (see Chapter 4). In very old patients and in patients with severe liver disease, the elimination half-lives of these drugs are often increased significantly. The activity of hepatic microsomal drug-metabolizing enzymes may be increased in patients exposed to certain older sedative-hypnotics on a long-term basis (enzyme induction; see Chapter 4). Barbiturates (especially phenobarbital) and meprobamate are most likely to cause this effect, which may result in an increase in their hepatic metabolism as well as that of other drugs. Increased biotransformation of other pharmacologic agents as a result of enzyme induction by barbiturates is a potential mechanism underlying drug interactions (see Chapter 66). In contrast, benzodiazepines and the newer hypnotics do not change hepatic drug-metabolizing enzyme activity with continuous use. Multiple subunits of several of these classes have been characterized, eg, six different α, four β, and three γ. Binding of benzodiazepines and the newer hypnotic drugs such as zolpidem occurs at a single site between α and γ subunits, facilitating the process of chloride ion channel opening. The benzodiazepine antagonist flumazenil also binds at this site and can reverse the hypnotic effects of zolpidem. Strains of mice, in which a point mutation has been inserted converting histidine to arginine in the α1 subunit, show resistance to both the sedative and amnestic effects of benzodiazepines, but anxiolytic and muscle-relaxing effects are largely unchanged. Other mutation studies have led to suggestions that an α5 subtype is involved in at least some of the memory impairment caused by benzodiazepines. This multiplicity of sites of action of barbiturates may be the basis for their ability to induce full surgical anesthesia (see Chapter 25) and for their more pronounced central depressant effects (which result in their low margin of safety) compared with benzodiazepines and the newer hypnotics. In addition to the benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and the newer hypnotics (eg, zolpidem), many other drugs with central nervous system effects can modify the function of this important ionotropic receptor. These include alcohol and certain intravenous anesthetics (etomidate, propofol) in addition to thiopental. Central nervous system excitatory agents that act on the chloride channel include picrotoxin and bicuculline. Sedation—Benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and most older sedative-hypnotic drugs exert calming effects with concomitant reduction of anxiety at relatively low doses. In most cases, however, the anxiolytic actions of sedative- hypnotics are accompanied by some depressant effects on psychomotor and cognitive functions. In experimental animal models, benzodiazepines and older sedative-hypnotic drugs are able to disinhibit punishment-suppressed behavior. This disinhibition has been equated with antianxiety effects of sedative-hypnotics, and it is not a characteristic of all drugs that have sedative effects, eg, the tricyclic antidepressants and antihistamines. However, the disinhibition of previously suppressed behavior may be more related to behavioral disinhibitory effects of sedative-hypnotics, including euphoria, impaired judgment, and loss of self-control, which can occur at dosages in the range of those used for management of anxiety. The benzodiazepines also exert dose-dependent anterograde amnesic effects (inability to remember events occurring during the drug’s duration of action). The effects of sedative-hypnotics on the stages of sleep depend on several factors, including the specific drug, the dose, and the frequency of its administration. Despite possible reductions in slow-wave sleep, there are no reports of disturbances in the secretion of pituitary or adrenal hormones when either barbiturates or benzodiazepines are used as hypnotics. The use of sedative-hypnotics for more than 1–2 weeks leads to some tolerance to their effects on sleep patterns.
But arthritis foundation grants cheap 7.5mg meloxicam fast delivery, in practice signs of arthritis in your neck purchase meloxicam us, concentration of warfarin; enzyme inhibition by clinically important adverse drug–drug interactions become ciprofloxacin increases the concentration of likely with: theophylline arthritis pain early pregnancy buy meloxicam 15mg lowest price. Potentiation (to make more powerful) occurs when one Purgatives reduce the time spent in the small intestine and drug increases the action of another, i. Antimicrobials potentiate oral anti- sometimes one drug lacks the action concerned coagulants by reducing bacterial synthesis of vitamin K (benserazide plus levodopa), i. Carrier-mediated transporters con- metabolism trol processes such as bioavailability, passage into the • at receptor sites. Plainly, the mixing of solu- cells; quinidine, verapamil and ciclosporin inhibit this tions of salts can result in instability, which may or may transporter and increase the plasma concentration of di- not be visible in the solution, i. Probenecid inhibits cific sources of information are available in manufac- the organic anion renal transporter, which decreases the re- turers’ package inserts and formularies, issues of nal clearance of penicillin (usefully prolonging its effect) compatibility are complex and lie within the professional but also that of methotrexate (with danger of toxicity). Elu- competence of the hospital pharmacy, which should pre- cidation of the location and function of transport systems pare drug additions to infused solutions. In any situation will give the explanation for, and allow the prediction of, involving unfamiliar drugs their help and advice should many more drug–drug interactions. Antacids that for morphine overdose (opioid receptor), atropine for an- contain aluminium and magnesium form insoluble and ticholinesterase, i. Unwanted interactions include the loss of the antihyperten- Colestyramine interferes with the absorption of levothyr- siveeffectofb-blockerswithcommoncoldremediescontain- oxine, digoxin and some acidic drugs, e. Because of the As drugs are intended to relieve suffering, patients find variety of these factors, attempts to make a simple account it peculiarly offensive that they can also cause disease of the unwanted effects of drugs must be imperfect. Therefore, it is There is general agreement that drugs prescribed for dis- important to know how much disease drugs do cause ease are themselves the cause of a serious amount of disease and why they cause it, so that preventive measures can (adverse reactions), ranging from mere inconvenience to be taken. As there can be no hope of eliminating all adverse effects • Effects of prolonged administration: chronic of drugs, it is necessary to evaluate patterns of adverse reac- organ toxicity. It is for use of such knowledge can render avoidable what are at humans, in their desire to avoid suffering and death, present unavoidable reactions. In addition to this arbitrary division, which has claims on their time, must find time better to understand drugs, as well as understanding patients and their 1From: The remedy worse than the disease. Distin- peutic doses, and that are predictable and usually dose guishing between natural progression of a disease and drug- related. The der that are of importance in evaluating drug-induced majority of reactions develop soon after exposure. The term adverse ‘reaction’ Anaphylactic reactions (within minutes or hours) and is almost synonymous with adverse ‘effect’, except that hypersensitivity reactions (within weeks) may readily an ‘effect’ relates to the drug and a ‘reaction’ to the suggest an association, but delayed effects such as patient. Both terms should be distinguished from an carcinogenesis or tardive dyskinesia (after years or even adverse ‘event’, which is an adverse happening that oc- decades) present more difficulty. The relationship to what is already known about the in overdose2 and overdose can be absolute or relative; drug. This of course invites questions about consistency in the latter case an ordinary dose may be administered with the established pharmacology and toxicology of but may be toxic due to an underlying abnormality in the drug or related substances. Mutagenicity, carci- Degrees of conviction for attributing adverse reactions to drugs may be ascribed as3: nogenicity and teratogenicity (see Index) are special cases of toxicity. Examples are: vitamin deficiency or drugs; event ceases on stopping the drug; event returns opportunistic infection in patients whose normal bowel on restarting the drug (rarely advisable). Individuals vary greatly in their • Possible: time sequence is reasonable; event susceptibility to drugs, those at one extreme of the normal corresponds to what is known of the drug; uncertain distribution curve being intolerant of the drugs, those at the relationship to effect of stopping the drug; event could other, tolerant. AprincipleappreciatedbyParacelsus500 yearsago,whostatedthat‘All things are poisons and there is nothing that is harmless; the dose alone • Doubtful: event not meeting the above criteria. The physician, alchemist and philosopher is regarded as the founder of chemical therapeutics; he was the first to use carefully measured doses of mercury to treat syphilis. Administration of a placebo intensifies (or dimin- increased risk did become apparent after meta-analysis ishes) these symptoms. Similarly, minor and • A drug rarely induces an otherwise rare illness: this effect is possibly transient abnormalities in laboratory results, e. The effect could be detected by informal clinical observation or during any special post-registration surveillance and confirmed by Practicalities of detecting rare a case–control study (see p.
Meloxicam 15mg low cost. Gumball Machine Chooses Your Next Tattoo.
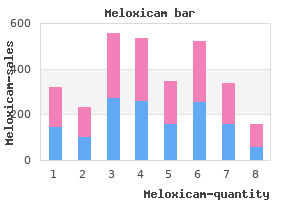
Primidone and phenobarbital serum concentra- tions as well as the presence of adverse drug effects should be monitored frequently in patients with liver or kidney disease taking primidone arthritis pain flare ups meloxicam 7.5 mg for sale. Primidone is significantly removed (~30% of total body amount) by hemodialysis arthritis of neck symptoms discount meloxicam 7.5 mg amex, and supplemental doses may need to be given after a dialysis session artritis ziekte order cheap meloxicam line. Because pheno- barbital is such a broad-based hepatic enzyme inducer, patients should be monitored closely for drug interactions whenever either of these agents is added to their therapeutic regimen. A brief list of the compounds whose metabolism and clearance are increased by concurrent phenobarbital treatment includes carbamazepine, lamotrigine, valproic acid, cyclosporin, nifedipine, diltiazem, verapamil, oral contraceptives, tricyclic antidepressants, quinidine, theophylline, and warfarin. Other anticonvulsants that decrease the metabolism and clearance of phenobarbital are felbamate and valproic acid. Phenytoin may also exhibit an interaction with phenobarbital where both agents change the metabolism and clearance of each other. The net result of this drug interaction is quite variable and can result in an increase, decrease, or no change in the steady-state concentration of both drugs. Primidone metabolism and clearance are increased by carbamazepine and pheny- toin treatment while valproic acid therapy decreases primidone metabolism and clearance. It allows individualized target serum concentrations to be chosen for a patient, and each pharmacokinetic parame- ter can be customized to reflect specific disease states and conditions present in the patient. Literature-based recommended dosing is a very commonly used method to pre- scribe initial doses of phenobarbital or primidone. Doses are based on those that com- monly produce steady-state concentrations in the lower end of the therapeutic range, although there is a wide variation in the actual concentrations for a specific patient. Pharmacokinetic Dosing Method The goal of initial dosing of phenobarbital or primidone is to compute the best dose possible for the patient given their set of disease states and conditions that influence phar- macokinetics of the drugs and the epileptic disorder being treated. In order to do this, pharmacokinetic parameters for the patient will be estimated using average parameters measured in other patients with similar disease state and condition profiles. Unfortunately, there is no good way to estimate the elimination characteristics of liver metabolized drugs using an endogenous marker of liver function in the same manner that serum creatinine and estimated creatinine clearance are used to esti- mate the elimination of agents that are renally eliminated. Because of this, a patient is categorized according to the disease states and conditions that are known to change drug clearance, and the clearance previously measured in these studies is used as an estimate of the current patient’s clearance. To produce the most conservative phenobarbital or primidone doses in patients with mul- tiple concurrent disease states or conditions that affect their respective pharmacokinetics, the disease state or condition with the smallest clearance should be used to compute doses. When oral therapy for either drug or intramuscular treatment with phenobarbital is required, both anticonvulsants have good bioavailability (assume F = 1), and once daily dosing for phenobarbital or multiple daily dosing for primidone provides a relatively smooth serum concentration/time curve that emulates an intravenous infusion. Because of this, a very simple pharmacokinetic equation that computes the average phenobarbital or primidone steady-state serum concentration (Css in μg/mL = mg/L) is widely used and allows maintenance dosage calculation: Css = [F(D/τ)] / Cl or D = (Css ⋅ Cl ⋅τ)/F, where F is the bioavailability fraction for the oral dosage form (F = 1 for both drugs), D is the dose of the anticonvulsant in mg, Cl is anticonvulsant clearance in L/h, and τ is the dosage interval in hours. When intravenous therapy with phenobarbital is required, a similar pharmacokinetic equation is widely used: Css = (D/τ) / Cl or D = Css ⋅ Cl ⋅τ, where D is the dose of phe- nobarbital in milligrams, and τ is the dosage interval in hours, Cl is phenobarbital clear- ance in liters per hour. Suggest an initial phenobarbital dosage regimen designed to achieve a steady-state con- centration equal to 20 μg/mL. Estimate clearance and volume of distribution according to disease states and con- ditions present in the patient. Once the correct clearance and volume of distribution estimates are identified for the patient, they can be converted into the phenobarbital half-life (t1/2) and elimination rate constant (k) estimates using the following equations: t1/2 = (0. A steady-state trough phenobarbital serum concentration should be measured after steady state is attained in 3–5 half-lives. Since the patient is expected to have a half-life equal to 122 hours, the phenobarbital steady-state concentration could be obtained any time after 4 weeks of dosing (5 half-lives = 5 ⋅ 122 h = 610 h or 25 d). Phenobarbital serum con- centrations should also be measured if the patient experiences an exacerbation of their epilepsy, or if the patient develops potential signs or symptoms of phenobarbital toxicity. Suggest an initial phenobarbital dosage regimen designed to achieve a steady-state concentration equal to 20 μg/mL. Estimate clearance and volume of distribution according to disease states and con- ditions present in the patient. Once the correct clearance and volume of distribution estimates are identified for the patient, they can be converted into the phenobarbital half-life (t1/2) and elimination rate constant (k) estimates using the following equations: t1/2 = (0. A steady-state trough phenobarbital serum concentration should be measured after steady state is attained in 3–5 half-lives. Phenobarbital serum con- centrations should also be measured if the patient experiences an exacerbation of their epilepsy, or if the patient develops potential signs or symptoms of phenobarbital toxicity. Suggest an initial primidone dosage regimen designed to achieve a steady-state primidone concentration equal to 6 μg/mL. Estimate clearance and volume of distribution according to disease states and con- ditions present in the patient.
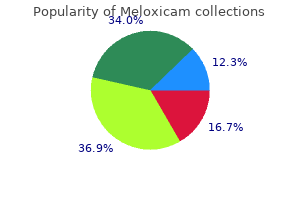
Pimozide hip joint arthritis pain location buy discount meloxicam 15mg, a dopamine receptor antagonist arthritis knee repair buy meloxicam with amex, may be helpful in patients as a first-line treatment or in those who are either unresponsive to or intolerant of the other agents mentioned arthritis treatment msm cheap meloxicam 15mg free shipping. Treatment is started at 1 mg/d, and the dosage is increased by 1 mg every 5 days; most patients require 7–16 mg/d. Adverse effects include extrapyramidal movement disorders, sedation, dryness of the mouth, blurred vision, and gastrointestinal disturbances. It is introduced at a dose of 2–3 mcg/kg/d, increasing after 2 weeks to 4 mcg/kg/d and then, if required, to 5 mcg/kg/d. The most common adverse effect is sedation; other adverse effects include reduced or excessive salivation and diarrhea. Both of these drugs may be particularly helpful for behavioral symptoms, such as impulse control disorders. Atypical antipsychotics, such as risperidone and aripiprazole, may be especially worthwhile in patients with significant behavioral problems. Injection of botulinum toxin A at the site of problematic tics is sometimes helpful when these are focal simple tics. Treatment of any associated attention deficit disorder (eg, with clonidine patch, guanfacine, pemoline, methylphenidate, or dextroamphetamine) or obsessive-compulsive disorder (with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or clomipramine) may be required. Deep brain stimulation is sometimes worthwhile in otherwise intractable cases but is best regarded as an investigational approach at this time. Drug-Induced Dyskinesias Levodopa or dopamine agonists produce diverse dyskinesias as a dose-related phenomenon in patients with Parkinson’s disease; dose reduction reverses them. Chorea may also develop in patients receiving phenytoin, carbamazepine, amphetamines, lithium, and oral contraceptives, and it resolves with discontinuance of the offending medication. Dystonia has resulted from administration of dopaminergic agents, lithium, serotonin reuptake inhibitors, carbamazepine, and metoclopramide; and postural tremor from theophylline, caffeine, lithium, valproic acid, thyroid hormone, tricyclic antidepressants, and isoproterenol. The pharmacologic basis of the acute dyskinesia or dystonia sometimes precipitated by the first few doses of a phenothiazine is not clear. In most instances, parenteral administration of an antimuscarinic drug such as benztropine (2 mg intravenously), diphenhydramine (50 mg intravenously), or biperiden (2–5 mg intravenously or intramuscularly) is helpful, whereas in other instances diazepam (10 mg intravenously) alleviates the abnormal movements. Tardive dyskinesia, a disorder characterized by a variety of abnormal movements, is a common complication of long- term neuroleptic or metoclopramide drug treatment (see Chapter 29). A reduction in dose of the offending medication, a dopamine receptor blocker, commonly worsens the dyskinesia, whereas an increase in dose may suppress it. The drugs most likely to provide immediate symptomatic benefit are those interfering with dopaminergic function, either by depletion (eg, reserpine, tetrabenazine) or receptor blockade (eg, phenothiazines, butyrophenones). Tardive dystonia is usually segmental or focal; generalized dystonia is less common and occurs in younger patients. Treatment is the same as for tardive dyskinesia, but anticholinergic drugs may also be helpful; focal dystonias may also respond to local injection of botulinum A toxin. Rabbit syndrome, another neuroleptic-induced disorder, is manifested by rhythmic vertical movements about the mouth; it may respond to anticholinergic drugs. Because the tardive syndromes that develop in adults are often irreversible and have no satisfactory treatment, care must be taken to reduce the likelihood of their occurrence. Antipsychotic medication should be prescribed only when necessary and should be withheld periodically to assess the need for continued treatment and to unmask incipient dyskinesia. Thioridazine, a phenothiazine with a piperidine side chain, is an effective antipsychotic agent that seems less likely than most to cause extrapyramidal reactions, perhaps because it has little effect on dopamine receptors in the striatal system. Finally, antimuscarinic drugs should not be prescribed routinely in patients receiving neuroleptics, because the combination may increase the likelihood of dyskinesia. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome, a rare complication of treatment with neuroleptics, is characterized by rigidity, fever, changes in mental status, and autonomic dysfunction (see Table 16–4). Symptoms typically develop over 1–3 days (rather than minutes to hours as in malignant hyperthermia) and may occur at any time during treatment. Treatment includes withdrawal of antipsychotic drugs, lithium, and anticholinergics; reduction of body temperature; and rehydration. Dantrolene, dopamine agonists, levodopa, or amantadine may be helpful, but there is a high mortality rate (up to 20%) with neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
Chemicals that inactivate Pilocarpine arthritis medication ulcers cheap 7.5 mg meloxicam amex, from a South American plant (Pilocarpus these esterases (anticholinesterases) are used in medicine spp arthritis in neck solutions purchase meloxicam no prescription. Arecoline is an alkaloid in the betel nut arthritis definition mayo clinic purchase meloxicam overnight, which is chewed extensively throughout India and South-East Asia. Presum- Physostigmine is an alkaloid, obtained from the seeds of ably the lime mix in the ‘chews’ provides the necessary al- the West African Calabar bean (spp. It is present in small amounts in the fungus Amanita muscaria (fly agaric), named after its capacity to kill Neostigmine (t½2 h) is a synthetic reversible anticholin- thedomesticfly(Muscadomestica);muscarinewassonamed esterase whose actions are more prominent on the neuro- because it was thought to be the insecticidal principle, but it muscular junction and the alimentary tract than on the is relatively non-toxic to flies (orally administered). The antimuscarinic components may explain stigmine is effective orally, and by injection (usually subcu- why the dried fungus was used previously to treat excessive taneous). Happily, poisoning by Amanita muscaria is seldom powerful action that is slower in onset and slightly longer serious, but species of Inocybe contain substantially larger in duration, and perhaps with fewer visceral effects. They were apparently prepared to Edrophonium is structurally related to neostigmine but put up with the autonomic actions to escape briefly from its action is brief and autonomic effects are minimal except reality – so much so that when the fungus was scarce in win- at high doses. The drug is used to diagnose myasthenia ter they were even prepared to drink their own urine to pro- gravis and to differentiate a myasthenic crisis (weakness long the experience. Sometimes, in generous mood, they due to inadequate anticholinesterase treatment or severe would even offer their urine to others as a treat. Myasthenic Anticholinesterases weakness is substantially improved by edrophonium whereas cholinergic weakness is aggravated but the effect At cholinergic nerve endings and in erythrocytes there is a is transient; the action of 3 mg i. The practice had the advantage methonium, procaine (and cocaine) and bambuterol (a that the demonstration of guilt provided simultaneous punishment. It is used widely as a garden insecticide genitourinary system (involuntary micturition), the skin and, clinically, to kill head and body lice. Sensitive insects (sweating), the skeletal system (muscle weakness, twitch- lack cholinesterase-rich erythrocytes and succumb to the ing) and the nervous system (miosis, anxiety, headache, accumulation of acetylcholine in the synaptic junctions convulsions, respiratory failure). The anticholinesterase block, and to excessive bronchial secretions and constric- malathion is effective against scabies, head and crab lice. At autopsy, ileal intussus- A more recent use of anticholinesterase drugs has been to ceptions are commonly found. They are polyneuropathy, with sensory and motor impairment usu- all reversible inhibitors that are orally active and cross the ally of the lower limbs. As the most common circumstance of acci- of the carbamate type that reversibly inactivates cholines- dental poisoning is exposure to pesticide spray or spillage, terase only for a few hours. This contrasts markedly with contaminated clothing should be removed and the skin the very long-lived inhibition caused by inhibitors of the washed. Cases of acute poisoning exceeding 70 beats per minute indicate that its effect is are usually met outside therapeutic practice, e. Although called nerve ‘gas’, stimulating postganglionic nerve endings (excessive they are actually volatile liquids, which facilitates their secretion and vasodilatation), but has no effect on the use. Diagnosis depends on observing a substan- pesticides inactivate cholinesterase by irreversibly tial part of the list of actions below. Typical features of acute poisoning involve the gastroin- Substances that reactivate the enzyme hasten the testinal tract (salivation, vomiting, abdominal cramps, destruction of the accumulated acetylcholine and, diarrhoea, involuntary defaecation), the respiratory system unlike atropine, they have both antinicotinic and antimuscarinic effects. The principal agent is 7 pralidoxime, which should be given by slow intravenous In recent times, there have been major instances of use against populations by both military and terrorist bodies (in the field and in an injection (diluted) over 5–10 min, initially 30 mg/kg underground transport system). If significant reactivation anxiety over my symptoms, he replied ‘my dear child, occurs, muscle power improves within 30 min. In poisoning with irreversible agents, erythrocyte or myasthenia gravis and she was correctly diagnosed in plasma cholinesterase content should be measured if pos- 1927. It was delayed polyneuropathy is slow and is dependent on one of my better days, and I was lying on the sofa after tea... That mune basis and some 85% of patients have a raised titre of was my first meeting with neostigmine, and we have autoantibodies to the muscle acetylcholine receptor. These antibodies accelerate receptor Neostigmine was introduced in 1931 for its stimulant ef- turnover, shortening their typical lifetime in the skeletal fects on intestinal activity.
Additional information: