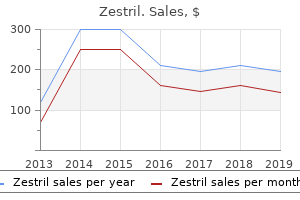
Zestril
"Purchase genuine zestril online, blood pressure medication kidney pain".
By: T. Rozhov, M.S., Ph.D.
Co-Director, Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine
Specifically arteria ophthalmica superior cheap 2.5mg zestril overnight delivery, measures of absolute risk or the probability of disease are preferred to measures such as relative risk blood pressure variations zestril 5 mg amex. The difference in absolute risk between interventions depends on the number of events in each group blood pressure danger zone chart purchase zestril toronto, such that the difference (absolute risk reduction) is smaller when there are fewer events. In contrast, the difference in relative risk is fairly constant between groups with different baseline risk for the event, such that the difference (relative risk reduction) is similar across these groups. Relative risk reduction is often more impressive than absolute risk reduction. Another useful measure is the number needed to treat (or harm). The number needed to treat is the number of patients who would need be treated with an intervention for 1 additional patient to benefit (experience a positive outcome or avoid a negative outcome). The absolute risk reduction is used to calculate the number needed to treat. Long-acting opioid analgesics 7 of 74 Final Update 6 Report Drug Effectiveness Review Project Systematic reviews weigh the quality of the evidence, allowing a greater contribution from studies that meet high methodological standards and, thereby, reducing the likelihood of biased results. In general, for questions about the relative benefit of a drug, the results of well- executed randomized controlled trials are considered better evidence than results of cohort, case- control, and cross-sectional studies. In turn, these studies provide better evidence than uncontrolled trials and case series. For questions about tolerability and harms, observational study designs may provide important information that is not available from controlled trials. Within the hierarchy of observational studies, well-conducted cohort designs are preferred for assessing a common outcome. Case-control studies are preferred only when the outcome measure is rare and the study is well conducted. Systematic reviews pay particular attention to whether results of efficacy studies can be generalized to broader applications. Efficacy studies provide the best information about how a drug performs in a controlled setting. These studies attempt to tightly control potential confounding factors and bias; however, for this reason the results of efficacy studies may not be applicable to many, and sometimes to most, patients seen in everyday practice. Most efficacy studies use strict eligibility criteria that may exclude patients based on their age, sex, adherence to treatment, or severity of illness. For many drug classes, including the antipsychotics, unstable or severely impaired patients are often excluded from trials. In addition, efficacy studies frequently exclude patients who have comorbid disease, meaning disease other than the one under study. Efficacy studies may also use dosing regimens and follow-up protocols that are impractical in typical practice settings. These studies often restrict options that are of value in actual practice, such as combination therapies and switching to other drugs. Efficacy studies also often examine the short-term effects of drugs that in practice are used for much longer periods. Finally, efficacy studies tend to assess effects by using objective measures that do not capture all of the benefits and harms of a drug or do not reflect the outcomes that are most important to patients and their families. Systematic reviews highlight studies that reflect actual clinical effectiveness in unselected patients and community practice settings. Effectiveness studies conducted in primary care or office-based settings use less stringent eligibility criteria, more often assess health outcomes, and have longer follow-up periods than most efficacy studies. The results of effectiveness studies are more applicable to the “average” patient than results from the highly selected populations in efficacy studies. Examples of effectiveness outcomes include quality of life, frequency or duration of hospitalizations, social function, and the ability to work. These outcomes are more important to patients, family, and care providers than surrogate or intermediate measures, such as scores based on psychometric scales.
Efficacy of a new 7-day transdermal sequential estradiol/levonorgestrel patch in women arteria vertebral purchase zestril 10mg visa. Efficacy and safety of low mrf-008 hypertension buy zestril 2.5mg otc, standard heart attack the alias radio remix demi lovato heart attack remixes 20 cheap 10 mg zestril with mastercard, and high dosages of an estradiol transdermal system (Esclim) compared with placebo on vasomotor symptoms in highly symptomatic menopausal patients. Hormone therapy Page 64 of 110 Final Report Update 3 Drug Effectiveness Review Project 76. Quality of life of postmenopausal women on a regimen of transdermal estradiol therapy: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Efficacy and tolerability of a novel estradiol vaginal ring for relief of menopausal symptoms. Effects of ultra-low-dose transdermal estradiol on cognition and health-related quality of life. Women’s Health Initiative Study Group, Anderson G, Cummings S, et al. Design of the Women’s Health Initiative Clinical Trial and Observational Study. Stefanick ML, Cochrane BB, Hsia J, Barad DH, Liu JH, Johnson SR. Jirapinyo M, Theppisai U, Manonai J, Suchartwatnachai C, Jorgensen LN. Effect of combined oral estrogen/progestogen preparation (Kliogest) on bone mineral density, plasma lipids and postmenopausal symptoms in HRT-naive Thai women. Hormone replacement therapy, sleep quality and psychological wellbeing. Effects of estrogen plus progestin on health- related quality of life. Polo-Kantola P, Erkkola R, Helenius H, Irjala K, Polo O. When does estrogen replacement therapy improve sleep quality? Efficacy of estradiol for the treatment of depressive disorders in perimenopausal women: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Morrison MF, Kallan MJ, Ten Have T, Katz I, Tweedy K, Battistini M. Lack of efficacy of estradiol for depression in postmenopausal women: a randomized, controlled trial. Khoo SK, Coglan M, Battistutta D, Tippett V, Raphael B. Hormonal treatment and psychological function during the menopausal transition: an evaluation of the effects of conjugated estrogens/cyclic medroxyprogesterone acetate. Estrogen improves psychological function in asymptomatic postmenopausal women. Quality-of-life and depressive symptoms in postmenopausal women after receiving hormone therapy: results from the Heart and Estrogen/Progestin Replacement Study (HERS) trial. Hormone therapy Page 65 of 110 Final Report Update 3 Drug Effectiveness Review Project 92. A comparative study of safety and efficacy of continuous low dose oestradiol released from a vaginal ring compared with conjugated equine oestrogen vaginal cream in the treatment of postmenopausal urogenital atrophy. Bachmann G, Notelovitz M, Nachtigall L, Birgerson L. A comparative study of a low- dose estradiol vaginal ring and conjugated estrogen cream for postmenopausal urogenital atrophy. Rioux JE, Devlin C, Gelfand MM, Steinberg WM, Hepburn DS. Nathorst-Boos J, Wiklund I, Mattsson LA, Sandin K, von Schoultz B. Is sexual life influenced by transdermal estrogen therapy? A double blind placebo controlled study in postmenopausal women. Safety and efficacy of a continuous once-a-week 17beta- estradiol/levonorgestrel transdermal system and its effects on vasomotor symptoms and endometrial safety in postmenopausal women: the results of two multicenter, double- blind, randomized, controlled trials.
Combination Therapy: The use of two or more therapies and especially drugs to treat a disease or condition hypertension ranges order generic zestril on-line. Confidence interval: The range of values calculated from the data such that there is a level of confidence hypertension stage 2 discount zestril 2.5mg with amex, or certainty can high blood pressure medication cause joint pain purchase zestril 2.5 mg without a prescription, that it contains the true value. The 95% confidence interval is generally used in Drug Effectiveness Review Project reports. If the report were hypothetically repeated on a collection of 100 random samples of studies, the resulting 95% confidence intervals would include the true population value 95% of the time. Confounder: A factor that is associated with both an intervention and an outcome of interest. Controlled clinical trial: A clinical trial that includes a control group but no or inadequate methods of randomization. Control group: In a research study, the group of people who do not receive the treatment being tested. The control group might receive a placebo, a different treatment for the disease, or no treatment at all. Convenience sample: A group of individuals being studied because they are conveniently accessible in some way. Convenience samples may or may not be representative of a population that would normally be receiving an intervention. Crossover trial: A type of clinical trial comparing two or more interventions in which the participants, upon completion of the course of one treatment, are switched to another. Direct analysis: The practice of using data from head-to-head trials to draw conclusions about the comparative effectiveness of drugs within a class or group. Results of direct analysis are the preferred source of data in Drug Effectiveness Review Project reports. Dosage form: The physical form of a dose of medication, such as a capsule, injection, or liquid. The route of administration is dependent on the dosage form of a given drug. Various dosage forms may exist for the same compound, since different medical conditions may warrant different routes of administration. Dose-response relationship: The relationship between the quantity of treatment given and its effect on outcome. In meta-analysis, dose-response relationships can be investigated using meta- regression. Double-blind: The process of preventing those involved in a trial from knowing to which comparison group a particular participant belongs. While double-blind is a frequently used term Targeted immune modulators 143 of 195 Final Update 3 Report Drug Effectiveness Review Project in trials, its meaning can vary to include blinding of patients, caregivers, investigators, or other study staff. Double-dummy: The use of two placebos in a trial that match the active interventions when they vary in appearance or method of administrations (for example, when an oral agent is compared with an injectable agent). Effectiveness: The extent to which a specific intervention used under ordinary circumstances does what it is intended to do. Effectiveness outcomes: Outcomes that are generally important to patients and caregivers, such as quality of life, responder rates, number and length of hospitalizations, and ability to work. Data on effectiveness outcomes usually comes from longer-term studies of a “real-world” population. Effect size/estimate of effect: The amount of change in a condition or symptom because of a treatment (compared to not receiving the treatment). It is commonly expressed as a risk ratio (relative risk), odds ratio, or difference in risk. Efficacy: The extent to which an intervention produces a beneficial result under ideal conditions in a selected and controlled population. Equivalence level: The amount which an outcome from two treatments can differ but still be considered equivalent, as in an equivalence trial, or the amount which an outcome from treatment A can be worse than that of treatment B but still be considered noninferior, as in a noninferiority trial. Equivalence trial: A trial designed to determine whether the response to two or more treatments differs by an amount that is clinically unimportant. This lack of clinical importance is usually demonstrated by showing that the true treatment difference is likely to lie between a lower and an upper equivalence level of clinically acceptable differences.
Note: advise the patient NOT to manipulate or express fluid from the nipple as long as possible be- Cysts may cause pain heart attack questions purchase zestril in india, alarm the patient or may fore the surgery blood pressure 60 over 30 purchase zestril online. It is essential to find the correct hide more serious underlying pathology blood pressure normal low order zestril 2.5mg on line. Usually duct by expressing the fluid immediately before in- they are solitary, 30% of patients experience jecting the dye into the duct. A cyst with a smooth lining is easily seen on ultrasound. Cysts may be drained with a Phyllodes tumor syringe (use minimum 14G to assure aspiration of the sometimes viscous fluid). In cases of repeated This is a tumor with benign, borderline and malig- filling, a surgical removal of the lining is needed. The tumor grows from the stromal Fibrotic changes may lead to multiple small cells of the breast; 70% of cases are benign, mostly nodules (adenosis) as well. The tumor presents as a firm, Histologic confirmation may be necessary to rule palpable mass and may grow very fast, even within out a malignant lesion (age group is similar to breast weeks. Wide excision of the lesion with clear negative margins is indicated to avoid Milk duct papilloma recurrence which is more frequent than in fibro- This is a proliferation of the epithelium of a mam- adenoma (Figure 11). It may occur isolated or in the presence indicated (even in malignant forms). In cases of 311 GYNECOLOGY FOR LESS-RESOURCED LOCATIONS (a) out drainage to the nipple may swell and become painful during lactation. An extra nipple or nipple and areola are seen in up to 5% of female patients (often in the axilla, along the breast or the submammary fold). In cases of persistent pain surgical removal may be indicated. Poland’s syndrome (in female or male) is a rare complex malformation due to missing develop- ment of the pectoral muscle. Usually areola and nipple are present and the mammary gland is miss- ing. The hand may also be involved with brachy- dactyly (short fingers). Micromastia There are several reasons for bilateral hypoplasia of the breasts. Of course the size of breasts may vary (b) considerably between individuals and may just rep- resent a normal variation. Keep in mind that some syndromes cause hypoplastic development of the breasts such as Turner syndrome, adrenogenital syndrome or other forms of intersexuality. Also patients with anorexia nervosa or malnutrition may present with micromastia. Macromastia During puberty as well as pregnancy excessive Figure 10 (a) Identification of the secreting duct. No removal of skin or nipple is ulceration due to problems with hygiene. Remember that a patient complaining of breast symptoms may simply be pregnant. So rule out pregnancy in a patient malignancy, mastectomy should be offered to avoid complaining of swollen and painful breasts. Due to the huge size of the mass, closure of the wound after the opera- tion may be a problem. Be aware that a skin graft CONCLUSIONS may be necessary. Take all Mammary Paget’s disease changes of the breast seriously and have in mind it could be breast cancer. When performing surgery beware when operating Congenital abnormalities in female and in male on the lesion – include larger or smaller margins Any part of the breast may be located aberrantly in according to the findings and do not remove the the embryonic mammary line (axilla down to in- whole breast tissue. Additional mammary gland tissue monitoring, care and enough patience for healing may appear especially in the axilla. Such tissue with- – otherwise a large abscess may form easily. Courtesy of Erik Erichsen, Ethiopia 313 GYNECOLOGY FOR LESS-RESOURCED LOCATIONS Note: the breast is not only essential for breast- 3. Risk factors for feeding but also part of the women’s identity!