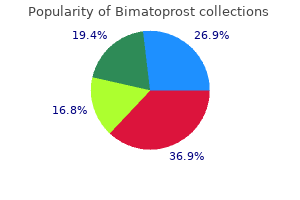
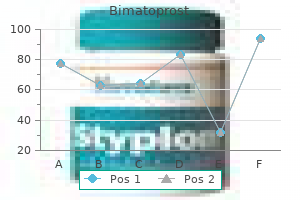
Bimatoprost
"Purchase bimatoprost toronto, symptoms 9dpo".
By: O. Altus, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Assistant Professor, University of Massachusetts Medical School
It has been produced in response to the need for valid medications that cause tinnitus buy cheap bimatoprost line, reliable and timely information on the prevalence medications mitral valve prolapse trusted bimatoprost 3 ml, trends medicine shoppe locations purchase bimatoprost pills in toronto, and patterns of drug use related problems. This information is needed for planning, implementing and evaluating, effective prevention, treatment, policy response and other interventions for substance use related problems. Since the 1980s there have been major changes in trends and patterns of drug use including: global increases in the production and use of drugs; new forms of old drugs (eg. These challenges are being met by scientific advances in drug abuse epidemiology, including: improved techniques to assess the extent of drug related behaviours and problems; and the introduction and development of methods which aim to understand drug using behaviours as much as measure them. This Guide seeks to provide technical guidance to countries and communities in all aspects of drug abuse epidemiology in order to address emerging and changing problems associated with drug use. The Guide provides practical guidance on internationally comparable, yet locally appropriate and culturally adaptable measures and methods. The Guide is designed to be suitable for countries and communities at all levels of health development, including those with limited resources and experience in drug abuse epidemiology. The document may, however, be freely reviewed, abstracted, reproduced or translated, in part or in whole, but not for sale or for use in conjunction with commercial purposes. The views expressed in documents by named authors are solely the responsibility of those authors. Donoghoe World Health Organization, Programme on Substance Abuse, Geneva, Switzerland. Maggie Jean-Francois Ministère de la Solidarité, de la Santé et de la Protection sociale, Paris, France. Maria Elena Medina-Mora Head, Division of Epidemiology and Social Sciences, Mexican Institute of Psychiatry, Mexico. Smart Head, Social Epidemiology, Social Evaluation and Research Addiction Research Foundation Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Some of the original text from these publications (which are listed below) has been included in the Guide. Arif Formerly Division of Mental Health, World Health Organization Geneva, Switzerland. Hughes Formerly Division of Mental Health, World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. Varma Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India. We gratefully acknowledge the substantial contribution of the following Centres and investigators to the project. University Mental Health Research Institute Eginition Hospital – Athens, Greece Dr Meni Malliori Dr V. Kontea National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences – Bangalore, India Dr C. Chandra Shekar Dr Prathima Murthy National Centre for Psychiatric and Addiction Studies – Cairo, Egypt Dr Alsayed Alkott National Drug Research Centre Universiti Sains Malaysia Pulau Pinang, Malaysia Prof. Galvan University of Zimbabwe Medical School Department of Psychiatry – Harare, Zimbabwe Prof. Butau Many other people contributed to the field assessment, participated in focus groups and contributed to the field assessment. Background Whilst alcohol, tobacco and other drugs are used in most countries of the world, the extent, patterns and consequences of use differ from country to country and from time to time. The effective prevention of health problems and other consequences of substance use requires information on the prevalence, characteristics and patterns of use, together with information on the problems associated with that use. These publications reviewed drug epidemiology methods in general and the use of these methods in some specific populations. They described how these methods can be used to collect information necessary for the planning, implementation and evaluation of prevention and treatment programmes. Until the publication of these guides, there had been no international agreement from a public health perspective on the type of drug use data that should be collected by countries nor had there been any systematic exchange of information about drug abuse reporting systems utilised in different countries. It was hoped that if the guidelines proposed were widely adopted, it would help to improve the international comparability and scientific quality of the epidemiological data generated. Since the publication of the guidelines in the early 1980s, there have been important changes in trends and patterns of drug use, which present new challenges to public health practitioners and program planners.
It reflects failure to receive adequate nutrition over a long period of time and is also affected by recurrent and chronic illness treatment 12mm kidney stone order bimatoprost 3ml with mastercard. Therefore wasting is acute malnutrition – a result of inadequate food intake or a recent episode of illness causing loss of weight and onset of malnutrition symptoms 4 dpo generic 3 ml bimatoprost amex. This is a composite indicator which takes into account both chronic and acute malnutrition treatment ulcerative colitis purchase bimatoprost 3ml overnight delivery. Causes include inadequate maternal food intake during pregnancy, short maternal stature and infection such as malaria. Cigarette smoking on the part of the mother also is associated with low birth weight. Most common medical complications in severely malnourished children include generalized oedema, hypothermia, hypoglycaemia, dehydration, anaemia, septicemia/infections and cardiac failure. Treat complications eg dehydration, shock, anemia, infections, hypothermia, hypoglycemia and electrolyte imbalance. In some cases obesity occurs secondary to other disorders or conditions such as hypothyroidism, Cushing’s disease and others. In this regard men with over 24 percent body fat and women with over 35 percent body fat are considered obese. Desirable amounts are 8 to 24 percent body fat for men and 21 to 35 percent for women. Reduction of haemoglobin impairs oxygen transport to the tissues – the basis of the clinical features of anaemia. Four major groups are distinguished: Haemorrhagic anaemia develops due to various forms of bleeding (trauma, excessive menses, bleeding associated with pregnancy and birth giving, and parasitic infestations such as hookworms and scistosomiasis). Bone marrow depression can be caused by diseases (autoimmune, viral infection), radiation and chemotherapy and intake of some drugs (anti-inflammatory, antibiotics). Nutritional anaemias are o Iron deficiency anaemia o Folic acid deficiency anaemia o Vitamin B12 deficiency anaemia Anaemia affects all population groups but children aged below five years and pregnant women are the most vulnerable. Detection of anaemia is by determining the concentration Hb and the cut-off points at sea level are as follows: Table 4: Population group Hb levels indicating anaemia (g/dl) Children 6 to 59 months Below 11. Iron in foods of animal origin (haem iron) is more easily absorbed compared with iron in foods of plant origin (which is mostly nonhaem iron). Vitamin C enhances absorption of iron while tea and coffee inhibits iron absorption. Iron Deficiency the main function of iron is transport of oxygen at various sites in the body. Thus iron is a component of haemoglobin and myglobin (protein molecule in the muscle which carries oxygen for muscle metabolism). Iron is a component of cytochromes (involved in cell respiration); component of xanthine oxidase (involved in catabolism of purines which make nucleic acids). Iron is a component of aconitase (involved in the Krebb’s Cycle) and many other enzymes such as peroxidase and catalase. While Hb concentration is used to define anaemia, it does not define the body’s iron status. Depletion of iron stores: the body’s storage pool (deposits in the liver, spleen and bone marrow) diminishes due to insufficient dietary intake. Iron deficiency erythropoiesis: storage levels substantially reduced, inadequate iron is available in the bone marrow for the synthesis of Hb. Iron deficiency anaemia: last and most severe stage of iron deficiency – iron stores are insufficient to maintain Hb synthesis. Also when food is boiled in water iron is leached and is lost if the water is discarded. The hormones have profound influence on energy metabolism, protein synthesis, growth and development. They also play part in the conversion of carotene to Vitamin A and synthesis of cholesterol. This, in turn, affects brain development, physical growth and functioning of muscles, heart, liver and kidneys. Goitre is an enlarged thyroid gland – a result of thyroid over-activity as it strives to capture sufficient iodine from the blood.
It occurs mostly the last week before menstruation (premenstrual phase) resolving or markedly improving at menstruation Risk factors Hormone changes over a normal menstrual cycle ( excesses or defciencies of estrogen or progesterone) Side efects caused by the progestogen component of cyclical Hormonal Replacement Terapy Excessive Serotonin and β-endorphins secretion Exaggerated end-organ response to the normal cyclical changes in ovarian hormones medications you should not take before surgery buy generic bimatoprost 3ml on line. Hormonal therapy • Progesterone supplements (suppositories medications on backorder purchase generic bimatoprost online, pessaries 10 medications doctors wont take buy bimatoprost 3ml otc, injections, oral micronized) Ș Duphaston 10mg tabs P. O Dose: 20mg Once daily 11th to 25th day of the menstrual cycle Ș Utrogetan 100mg tabs P. O Dose: 200mg Once daily 16th to 25th day of the menstrual cycle Ș Lutenyl 5mg tabs P. A normal menstrual period lasts 2-7 days and a normal cycle lasts between 21 and 35 days. O Dose: 20mg Once daily 11th to 25th day of the menstrual cycle Ș Utrogetan 100mg tabs P. Breast Cancer Defnition This is a malignant growth that begins in the tissue of the breast in which abnormal cells grow in an uncontrolled way. This is the most common and the second killer in women afer cervical cancer in the world, but can also appear in men. Endometrium cancer Defnition: Endometrium cancer is a growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus, it usually occurs in postmenopausal women (age peak: 40 to 55 years). Ovarian cancer Defnition: Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death of among all gyneacologic cancer worldwide. More than 90% of ovarian cancers are epithelial origin from the surface (coelomic) epithelium. Causes Age Primary ovarian failure Radiation and drugs Surgery Sheehan syndrome Signs and Symptoms “Hot fushes “(i. Cause Bacterial infections (polymicrobial) Signs and symptoms Asymptomatic Unpleasant fshy smelling vaginal discharges External genital irritation Dysuria. Recomandations Avoid alcohol during treatment with oral metronidazole and for 24 hours thereafer, due to possible disulfram-type reaction. Trichomonal vaginitis Defnition: Trichomonal vaginitis is an infammation of vagina and vulva. Signs and symptoms Dysuria Foul-smelling, frothy vaginal discharge that is most noticeable several days afer a menstrual period. Recommendations Advise sexual abstention until symptoms improve and partner(s) treated Avoid alcohol during treatment with oral metronidazole and for 24 hours thereafer, due to possible disulfram-type reaction. Vulvo-vaginal candidiasis Defnition: Vulvo-vaginal candidiasis is a fungal infammation of the vagina and vulva. Causes Fungus (candida albicans and non-albicans) Signs and symptoms Pruritis vulvae, Whitish curd-like vaginal discharge Vulval irritation Dyspareunia Dysuria. Subfertility, causes, treatment and aoutcomes, Best pract Res clin obstet gynae col,2003,17(2):169-185 3. American academy of family physicians, advanced life support in obstetrics, 2006, Chapter J: Post partum Hemmorhage. American College of Obstetrician and Gynecologists Commitee on Gynecologic Practice. Australian protocols/infections on pregnancy Toxo plasmosis in pregnancy (2004) 12. Matthé P M Burger, professor of gynaecology, Management of stage 1 endometrial carcinoma Postoperative radio therapy is not justifed in women with medium risk disease 14. A Randomised trial of two vacuum extraction technics Obstet Gynecol 1997; 89:758-762 15. Transvaginal sonographic ovarian fndings in a random sample of women 25-40 years old. Corey L,et All,Once-daily Valaciclovir to reduce the risk of transmission of Genital Herpes. Homko, Danforth’s obstetrics and gynecology, 9th edition, chapter 15, Diabetes Melitis and pregnancy (2003) 32. Quantitative bacteriology of amniotic fuid from patient with clinical intramniotic infection at term.
In general medications prescribed for adhd quality 3ml bimatoprost, a confidence interval uses these Clearly atlas genius - symptoms bimatoprost 3 ml, it is also preferable that these sample means be concepts to create reasonable bounds for the population very similar to each other treatment 8mm kidney stone order generic bimatoprost on line, so that any one of them is mean, based on information from a sample. They are easy likely to be close to the true value of the population to prepare and relatively easy to understand. The standard deviation for this long list of sample means, a measure of how similar these sample means Calculating a confidence interval are to each other, is called the eerrrroorr ofof ththee To construct a confidence interval, a lower bound and an memeaann. Note that the long list of sample means is not actually needed in order to estimate this standard error, upper bound are calculated. For the sample of weights, as it can be calculated from a single sample standard with n = 10 and x = 67. Note that the shorter the interval the better, and that a larger sample will likely produce a shorter interval. In fact, in this case, it is exactly in the middle of the interval; whereas the population mean, while likely to be included, is certainly not guaranteed to be within this interval. Interpreting a confidence interval from the t distribution with n-1 = 9 degrees of freedom. It is conceivable that there could be a long list of random However, if the sample size is above n = 30, then the samples taken from a population and that a confidence number 2. For very large samples, the interval could be calculated based on the information number will be 1. The result would be a long list of able in most standard statistics texts and online statistics confidence intervals and the expectation is that, if this resources. Unfortunately, for a specific sample one does not know if the including those from regression analyses and for odds raconfidence interval obtained from the study sample is tios, among many others. Basic biostatistics: concepts and tools 71 Interpreting measures outside the confidence interval When interpreting confidence intervals, one needs to know what to do with measures that fall outside of the interval. One would expect that 95% of such confidence intervals would in fact contain the population mean. We can use a confidence interval to test a hypothesis, namely, the hypothesis that μ = 80. In this case, the hypothesis was tested and rejected based on the lower and upper limits of the confidence interval. In general, confidence intervals can be used in this way to test hypotheses; however, there is a more formal approach described in Box 4. Hypothesis tests, p-values, statistical power Hypothesis-testing is relatively straightforward. We need to make a careful statement of the statistical hypothesis to be tested, the p-value associated with this test and the statistical power the test has for “detecting” a difference of a specified magnitude. The p-value In the above situation, the null hypothesis was rejected because the observed outcome was deemed to be too unlikely or rare under the assumption that the null hypothesis was true. The cut point for rarity in this circumstance was set when the ˞-level was set at ˞ = 0. A more precise measure of the rarity of this observed outcome, again under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true, can be obtained readily. This area is called the p-value and it represents the likelihood that a value for the mean of a random sample from this population, would be as far away as 67. That is, the observed outcome is so rare that it is difficult to believe that μ = 80 kg. Statistical power In the description of the two-sample t-test below, there is reference to the null hypothesis: 72 Chapter 4 H 0, H 1 22 ≠ which examines the differences between the means of two populations. If these are two populations of body weights, then, in this context, clearly, the larger the difference between the two population means, the easier it will be to reject this null hypothesis using the sample means. In order to set up a statistical test for this question, we select two options for comparison: • the null hypothesis: H0: μ = 80 kg andg • the alternative: H : μ ≠ 80 kg. If H11 is selected, the usual statement is that the null hypothesis H0 has been rejected. Note that the alternative is expressed as H1: μ ≠ 80 kg rather than eitherg μ > 80 or0 μ < 80. This implies that a two-tailed test is to be done rather than a one-tailed test as would be the case if either of the other two alternatives were used.