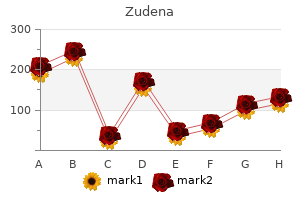
Zudena
"Purchase zudena 100mg with amex, erectile dysfunction premature ejaculation".
By: I. Ernesto, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Nova Southeastern University Dr. Kiran C. Patel College of Osteopathic Medicine
Note: Fractures of the bilateral pedicles and associated small paraspinal hematoma (arrows) causes for erectile dysfunction and its symptoms purchase 100 mg zudena with visa. C1 Fracture Description: Three primary types of fractures have been identified involving the C1 vertebrae: (1) the posterior arch fracture usually occurs at the junction of the posterior arch and the lateral mass; (2) the lateral mass fracture usually occurs unilaterally with the fracture line passing either through the articular surface or just anterior and posterior to the lateral mass on one side; and (3) the burst fracture (Jefferson fracture) is characterized by four fractures impotence bicycle seat cheap 100mg zudena with visa, two in the anterior arch and two in the posterior arch impotence of organic origin discount 100mg zudena mastercard. This fracture may present as a stable nondisplaced fracture with no encroachment on the spinal cord or as a displaced fracture with varying degrees of encroachment on the spinal cord. The degree of injury depends on the magnitude of the axial loading and whether the spine is in flexion, neutral, or an extension position. Epidemiology: Trauma to the spine occurs more commonly in the cervical region than in any other area of the spine. Signs and Symptoms: the patient may present with pain or a varying degree of paralysis. May demonstrate other related bony or soft tissue injuries to the upper cervical region. Treatment: Most fractures of the C1 vertebrae can be treated with immobilization (e. Cervical Facet Lock Description: A dislocation of the zygapophyseal or facet joint of the cervical spine. A facet lock (dislocation or subluxation) occurs when the inferior articulating process (facet) of the superior vertebra is locked in front of the superior articulating process (facet) of the inferior vertebra. The position of the head and neck at the time of impact and the direction of the force are key factors in this type of injury. Epidemiology: Unilateral facet injuries represent 6% to 10% of all cervical spine injuries. Bilateral facet dislocations are frequently associated with neurological deficits. Axial image shows normal relationship of the inferior and superior facets as the “hamburger on a bun” sign. Treatment: For unilateral facet dislocation, surgical treatment (open reduction) with internal fixation is more successful than closed reduction traction with a halo vest. Prognosis: Surgical treatment results in reduced treatment failure, reduced pain, and neurological deterioration as compared to nonsurgical treatment. Midline sagittal T2-weighted image (same patient as above) showing high signal of C2-C3 disk consistent with an acute injury of the disk (arrow). Vertebral Compression Fracture Description: Compression fractures of the lumbar spine occur as a result of a combination of flexion and axial loading (compression) of the vertebrae. Etiology: This fracture can occur as a result of trauma, metastatic disease to the spine, or osteoporosis. Epidemiology: Compression fractures are common in the aging and geriatric patients with osteoporosis. Signs and Symptoms: Patient presents with back pain and possible neurologic deficit. Treatment: These injuries are usually stable because the bony posterior elements and longitudinal ligaments are intact. Prognosis: Depends on the extent of the injury and status of the spinal canal and cord. Spinal Cord Hematoma Description: A spinal cord hematoma is a collection of blood in the spinal cord, most commonly due to trauma. Etiology: Most spinal cord hematomas occur as a result of trauma to the spinal cord, ligamentous structures, and/or bony vertebra. Other associated causes may include an acute herniated disk or hemorrhage from an arteriovenous malformation. Epidemiology: Trauma to the spinal column occurs at an incidence of approximately 2 to 5 per 100,000 population. Less frequent causes include falls, diving accidents, and sports and recreational injuries.
Longitudinal color Doppler image of the proximal patella tendon demonstrating severe tendinosis with marked hyperemia erectile dysfunction jet lag zudena 100 mg for sale. Other pathologic processes may mimic prepatellar bursitis and judicious use of medical imaging including ultrasound erectile dysfunction morning wood buy generic zudena 100mg on-line, magnetic resonance imaging erectile dysfunction treatment with homeopathy purchase 100 mg zudena with mastercard, plain radiography, and computed tomography may help clarify the diagnosis (Figs. Given that bursitis is usually the result of either trauma or abnormal function of the affected joint, one should assume that additional pathology other than the bursitis being treated is present. Sagittal proton density (A) and fat-suppressed T2-weighted (B) magnetic resonance images through the knee show an ovoid mass of fat signal intensity within the Hoffa fat pad (arrows). The fatty nature of this intra-articular mass confirms the diagnosis of synovial lipoma. A: Bilateral weight-bearing radiograph of the knees demonstrating degenerative changes and a calcified mass inferolateral to each joint. B: Lateral view of the right knee with evidence of a calcified mass anterior to the proximal tibia. Axial T2-weighted magnetic resonance images of prepatellar bursitis (A) and superficial infrapatellar bursitis (B). Periarticular lesions detected on magnetic resonance imaging: prevalence in knees with and without symptoms. The deep infrapatellar bursa lies between the anterior subcutaneous tissues of the knee and the anterior surface of the patellar tendon (Fig. The bursa serves to cushion and facilitate sliding of the skin and subcutaneous tissues of the anterior inferior portion of the knee over the tibia. The deep infrapatellar bursa is held in place by patellar tendon which is an extension of the common tendon of the quadriceps tendon (Fig. Both the quadriceps tendon and its expansions as well as the patellar tendon and the deep infrapatellar bursa are subject to the development of inflammation caused by overuse, misuse, or direct trauma. The quadriceps tendon is made up of fibers from the four muscles that comprise the quadriceps muscle: the vastus lateralis, the vastus intermedius, the vastus medialis, and the rectus femoris (Fig. The tendons of these muscles converge and unite to form a single, exceedingly strong tendon. The patella functions as a sesamoid bone within the quadriceps tendon, with fibers of the tendon expanding around the patella and forming the medial and lateral patella retinacula, which help strengthen the knee joint. These fibers are called expansions and are subject to strain; the tendon proper is subject to the development of tendinitis. The deep infrapatellar and prepatellar bursae also may concurrently become inflamed with dysfunction of the quadriceps tendon. The deep infrapatellar bursa is held in place by patellar tendon which is an extension of the common tendon of the quadriceps tendon. The quadriceps tendon is made up of fibers from the four muscles that comprise the quadriceps muscle: the vastus lateralis, the vastus intermedius, the vastus medialis, and the rectus femoris. The bursa serves to cushion and facilitate sliding of the patellar tendon over the tibia. The bursa is subject to inflammation from a variety of causes with acute trauma to the knee and repetitive microtrauma being the most common. Acute injuries to the bursa can occur from direct blunt trauma to the anterior knee from falls onto the knee as well as from overuse injuries including running on uneven or soft surfaces or 937 jobs that require kneeling or crawling on the knees like carpet laying and scrubbing floors. If the inflammation of the bursa is not treated and the condition becomes chronic, calcification of the bursa with further functional disability may occur (Fig. Gout and other crystal arthropathies may also precipitate acute deep infrapatellar bursitis as may bacterial, tubercular, or fungal infections. Lateral radiograph of the right knee showing an osseous mass attached to the tibial tubercle. The mass extends to the inferior aspect of the patella and is surrounded by several ossified fragments. Infrapatellar bursal osteochondromatosis associated with unresolved Osgood-Schlatter disease. Physical examination of the patient suffering from deep infrapatellar bursitis will reveal point tenderness over the anterior knee.
However erectile dysfunction utah purchase 100mg zudena with mastercard, the use of a seton Preoperative Preparation prior to implantation was unnecessary if there was no acute inflammatory process impotence hypnosis purchase 100 mg zudena with amex. Some surgeons experienced in using the plug have prepared the bowel as for a major colon resection erectile dysfunction zinc purchase zudena in india, with laxatives and Preparing the Plug antibiotics. Allowing immersion for >5 min risks stool was preferable to solid for prevention of extrusion of fragmentation of the plug. When the use of a small-volume preoperative nonhydrated plug is extremely painful. It was accepted that there was Managing the Recessed Internal Opening no evidence base for this consideration. Therefore, in the If there is epithelialization of the internal opening (dimpled absence of data, the Panel concluded that bowel preparation or recessed), limited mobilization of the mucosal edges and⁄or the use of a small-volume enema should be left to the with debridement prior to suture placement should be individual surgeon’s personal preference. Passing the Plug the use of a suture or ligature was recommended to pull the narrow end of the plug from the internal opening through the Intraoperative Management track to the external opening until the plug is snug. Anaesthetic Trimming the Plug Any excess plug should be trimmed at the level of the inter- This was deemed to be a matter of the patient’s or surgeon’s nal opening (the wide end) and sutured with 2-0 long-term, preference. Positioning the Patient There was no consensus, however, as to whether the plug should be buried under the mucosa. The excess external plug This was regarded as a matter of the surgeon’s preference. The the critical element, however, was to ensure adequate visu- external opening may be enlarged if necessary to facilitate alization of the internal opening to place the suture drainage. Postoperative Care Surgical Technique the Panel had a stimulating discussion on various postopera- Identifying the Internal and External Openings tive management alternatives. However, in the absence of the plug cannot be inserted unless there is clear delineation evidence-based data, opinions revolved around what seemed of the primary and secondary openings. Irrigation of the reasonable and appropriate with more emphasis on the “art” track with saline or peroxide was recommended. Activity: No strenuous activity, exercise, or heavy lifting tion of the track and to facilitate insertion of the plug. Abstinence from sexual intercourse for 2 Panel unanimously affirmed that debridement, curettage, or weeks. Outcome D e fi ning Failure Early extrusion of the plug is either a technical error [the track being too large, the plug pulled too tightly, faulty fixa- tion (i. The Panel unanimously agreed that the over- whelming majority of fistulas which heal do so within Fig. The tie is then whether the operation should be considered a failure rests affixed to the fistula plug so that it will be pulled through the internal orifice out the external. Alex Ky Conclusions nonantigenic because it is degraded via a combination of the anal fistula plug was felt to be a reasonable alternative hydrolytic and enzymatic pathways. Members of the Panel were copolymer indicate that the bioabsorption process should be asked to state what they felt to be a reasonable rate of success complete within 6 months [11]. The device consists of a and concluded that 50–60 % should be considered accept- disk 16 mm in diameter, attached to six tubes, each 9 cm in able. The size of the plug can be tailored by changing the concluded that patient selection, avoidance of local infec- number and length of the tubes so that it occupies the fistula tion, and meticulous technique were required. Besides the tract until the bioabsorbable nature of the material allows consideration of cost it was felt that the patient would not be the body to fill the defect with native tissue [12]. In com- adversely affected by insertion of the fistula plug because all parison to the Surgisis plug, the disk was devised to decrease other management options were still available. The plug is depicted in nized, however, that even in patients with apparent healing Fig. Finally it was unanimously agreed that the procedure should be undertaken only by trained surgeons familiar with anorec- tal anatomy and experienced in conventional anal fistula sur- Preparation gery and in the management of its complications. Prepare the patient and surgical site using standard tech- niques appropriate for anal fistula repair. Gore Bio-A Plug Remove the device from its sterile packaging using aseptic technique. Using sharp sterile scissors, trim the disk diameter to a the Gore Bio-A is a synthetic plug as compared to Surgisis, size appropriate for the defect allowing for adequate fixa- which is a biologic plug.