Artane
"Purchase 2 mg artane overnight delivery, chronic pain treatment guidelines".
By: Z. Barrack, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Vice Chair, Albert Einstein College of Medicine
Disinfectants are used to kill or eliminate microorganisms and/or inactivate virus on inanimate objects and surfaces (medical devices texas pain treatment center frisco tx buy 2mg artane mastercard, instruments pain treatment in osteoporosis order artane pills in toronto, equipment knee pain treatment uk 2 mg artane free shipping, walls, floors). Certain products are used both as an antiseptic and as a disinfectant (see specific information for each product). Selection Recommended products 1) Core list No single product can meet all the needs of a medical facility with respect to cleaning, disinfection and antisepsis. However, use of a limited selection of products allows greater familiarity by users with the products in question and facilitates stock management: – ordinary soap; – a detergent and, if available, a detergent-disinfectant for instruments and a detergent- disinfectant for floors and surfaces; – a disinfectant: chlorine-releasing compound (e. Alcohol acts faster than polyvidone iodine, but its duration of action is shorter. Application to mucous membranes or broken skin is contra-indicated, however, alcohol may be used on broken skin in the event of accidental exposure to blood. For example, for antiseptic hand rub, depending on the product specifications: • Bactericidal effect may be achieved with a single application of 30 seconds duration, or 2 consecutive applications of 30 seconds each, or a single application of 60 seconds duration. Antiseptics and disinfectants Thus, when purchasing locally, it is important to verify the quality of the product and specific instructions for use (number of applications, duration of application, and volume to be used per application). For surgical activity, ensure that the product is suitable for use as a surgical hand rub. Precautions should be taken during storage and use to avoid contact with a heat source (flame, electrocautery, etc. Given the possible interactions between different groups of antiseptics, antiseptic cleansing and antisepsis should only be carried out using products from the same class. Instructions for glutaraldehyde use must be followed scrupulously: 1) two preliminary washes of the equipment through immersion in a detergent-disinfectant solution for instruments, followed each time by rinsing; 2) complete immersion of the equipment in a 2% glutataldehyde solution for 20 minutes; 3) thorough final rinsing, with filtered water (or sterile water for endoscopes introduced into a sterile cavity) to eliminate any residue; 4) thorough drying with a sterile towel; 5) sterile wrapping and use within 24 hours. Glutaraldehyde solution is irritating to skin and mucous membranes, and releases toxic vapours. Personnel exposed to glutaraldehyde should take precautions to protect skin and eyes and avoid inhalation of vapours (risk of nausea, headache, breathing disorders, rhinitis, eye irritation, dermatitis). Precautions should be taken during storage and use to avoid contact with a heat source. Non-recommended products – Hydrogen peroxide (3% or 10 volumes) has limited efficacy as antiseptic agent but can be useful to clean contaminated wounds. Updated: February 2017 Antiseptics and disinfectants Preparation and use of antiseptic solutions Preparation Aqueous solutions of many antiseptics can be contaminated by pathogens (especially Pseudomonas aeruginosa) during handling. To avoid this, the following precautions must be taken: – Prepare all aqueous antiseptic solutions with clean water that has been boiled for a few minutes and cooled. Every medical facility should define a clear policy concerning the renewal of antiseptic solutions. Use – Do not use antiseptic solutions belonging to different classes for the same procedure: incompatibilities between different compounds exist. No evidence exists that antiseptics reduce the risk of transmission, however, their use – after thorough cleaning – is not contraindicated. If an antiseptic is used despite this recommendation, it must be allowed to dry before vaccine injection. Preparation and use of disinfectant solutions The effectiveness of disinfection can be impaired by error in preparation (concentration, temperature), failure to follow recommended contact times, or deterioration of the product due to poor storages conditions. Personnel carrying out disinfection should wear protective clothing when preparing or using disinfectant solutions: gown, rubber apron, gloves with long cuffs, goggles and mask. Preparation Solutions should be prepared with clean water (chlorine solutions should be prepared with cold water only, in non-metal containers). Antiseptics and disinfectants – Solution for disinfecting floors and surfaces: prepare just before use, and discard any unused solution. The solution may be used for a maximum of 24 hours; if visibly soiled, discard and replace with fresh soaking solution before 24 hours are up. Disinfection of floors and surfaces – Apply detergent-disinfectant intended for floors and surfacesa, without rinsing. Follow manufacturer’s instructions for dilution and specific preparation procedures. Or – After cleaning with a detergent (cleaning product without an antimicrobial agent) and rinsing with water, apply a 0.
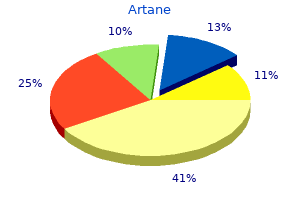
Syndromes
- Head tilting
- You may get nitroglycerin and morphine to help reduce chest pain.
- Difficulty breathing
- Arthritis caused by ankle surgery in the past
- Pain in the flank (side of the abdomen) or abdomen, which may extend to the groin or down the leg
- Urinary tract infection - adults
- They are easy to use.
- Blood in your stools or your stools appear black or tarry
When donor concentration is used in place of Ct pain syndrome treatment purchase artane line, apparent Km and Jmax values are obtained laser treatment for dogs back pain discount artane 2mg on line. It has recently been noted that since substrates must first partition or cross the membrane to access the binding site pain treatment centers of illinois new lenox buy genuine artane, accurate assessing of P-gp kinetics can be difficult (207). P-gp-Mediated Efflux Activity on the Cellular Level Within the cell, P-gp can be expressed in several organelles and as such can influence the cellular distribution of its substrates. Studies with tumor cells have shown P-gp expression on the cell surface, in cytoplasmic vesicles, in Golgi apparatus, and in the nuclear envelope (208,209). Within vesicles and in Golgi apparatus, P-gp acts to sequester compounds as the transport is directed within the vesicle. At the nuclear membrane, P-gp acts to restrict access of substrates to the nucleus by directing transport in a cytoplasmic direction. This subcellular localization of P-gp can be an important consideration for P-gp substrates with intracellular targets (208). The actions of P-gp located on the cell surface that act to restrict substrate access and to enhance elimination via efflux directed from cytoplasm to extracellular milieu are the most widely studied and understood. These experiments can roughly be classified into two categories—studies performed in the P-gp-deficient mouse model as pioneered by Schinkel et al. The following is a brief review of some of the important findings of these studies that have clearly shown how P-gp efflux activity can influence each aspect of drug disposition. Absorption All orally administered drugs must pass through the gastrointestinal tract to reach the blood and thus pass the barrier formed by the enterocytes in the intestine. For years, low first-pass bioavailability of a drug was attributed mainly to clearance via hepatic metabolism and biliary clearance or incomplete absorption in the intestine due to poor solubility or intrinsic permeability properties. Although these are important factors in determining the overall oral bioavailability of certain 376 Troutman et al. During absorption, P-gp-mediated efflux activity can potentially attenuate the overall bioavailability of its substrates by multiple mechanisms. Additionally, P-gp efflux during intestinal absorption may enhance intestinal metabolic elimination, thus indirectly reducing the amount of compound able to reach the bloodstream (details of how P-gp can affect intestinal metabolism are discussed below) (16). In the liver, P-gp is expressed in the canalicular membrane of the hepatocyte and can potentially enhance first-pass biliary excretion of the compound. The oral bioavailability of paclitaxel was 35% for the mdr1a(À/À) mice versus 11% for the wild-type mice. Similar studies have been performed with other P-gp sub- strates such as cyclosporin A and fexofenadine; an increased oral absorption of all these substrates was observed in the P-gp-deficient mice (212,235). The effects of P-gp-mediated efflux activity have been shown in studies aimed at elucidating the oral disposition of b-adrenoceptor antagonists. These findings were not compatible with the saturable first-pass effect attributable to metabolism. The tmax and mean absorption times of the orally administered P-gp substrate, talinolol, were sig- nificantly reduced with coadministration of verapamil. By using verapamil to alter the pharmacokinetic properties (specifically the intestinal absorption) of the b-adrenoceptor antagonist talinolol, it has been clearly shown in an intact model that the absorption of this drug is significantly affected by P-gp present in the intestine (226). Similarly, the nonlinear and limited bioavailability of celiprolol and pafenolol have been shown to be due to the actions of P-gp-mediated efflux activity in the intestine (5,236–238). Digoxin absorption is not influenced by first- pass metabolism and any changes to digoxin absorption are thought to be due to changes in the actions of P-gp. However, it is important to note that P-gp efflux activity does not always dictate these outcomes to a compound’s absorption profile. Absorption is a highly complex multifactorial process in which P-gp can play a part. The magnitude of the effect of P-gp efflux activity on a compound’s absorption profile ultimately depends on the P-gp activity in combination with other critical factors such as solubility, permeability, and metabolism. Distribution In some instances, P-gp can significantly affect the profile of drug distribution from systemic circulation into organs and tissues, most notably those that possess a specialized blood-tissue barrier such as the brain. Experiments with mdr1a(À/À) mice have shown how P-gp affects the distribution of its substrates into certain tissues (11,12,124,212–219). A few examples are shown below to demonstrate the role played by P-gp in the tissue distribution of drugs. Some of the most informative results came from a study involving altered distribution of P-gp substrates in mdr1a(À/À) mice.