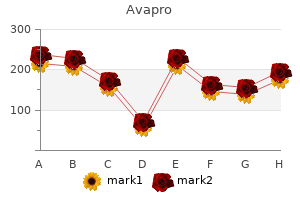
Avapro
"Buy 300mg avapro amex, diabetes diet on a budget".
By: Z. Dargoth, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Co-Director, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center School of Medicine
It is part of parental and professional responsibility to speak up for children diabetes definition fasting blood glucose cheap 300 mg avapro, but to do so at the cost of excluding the child’s viewpoint would essentially isolate the child further xenotransplantation diabetes type 1 purchase avapro 150 mg without a prescription. SUPPORT SERVICES AND BEING EMPOWERED / 113 In the following case example diabetes mellitus food diet order 300 mg avapro otc, the experience of Rachel is compounded following a medical intervention which directs attention from her disabled sister, Susan, to herself. The sequence of events raises issues about possible causation which ultimately reflect on the difficulties which Rachel has to learn to handle. The case of Rachel and Susan (high negative association) Rachel, aged 14, has a younger sister Susan, aged 12, who has profound physical and intellectual disabilities. Susan attends a special school,requires one-to-one attention at all times and spends most of her time during the day in a purpose-built wheelchair. Susan is unable to feed herself and is fed via a tube directly into her stomach and, to add to her difficulties,she suffers from frequent epileptic fits. Rachel, a bright girl with a lively personality, attends a secondary school and helps with the care of Susan when at home. Rachel spoke only of caring for Susan; there was no expression equivalent to ‘playtime with Susan’, an indication that Rachel was more conscious of ‘a sense of duty to care’ (my expression) than simply enjoying the company of her sister. At the time of interview, Rachel had recovered from minor surgery to remove a lump from her neck, but some days after the operation she had experienced an ‘epileptic fit’ (as explained to her) which lasted about ten minutes. Rachel was taken to hospital and stayed for a period including overnight observation. She returned home only to find, some weeks later, that a similar thing happened again. The doctor indicated on the second occasion that the attack was likely to be of ‘psychological origins’ and not a true fit. Rachel was sent home and has had subsequent fits and experienced going to hospital on a regular basis as a consequence. Rachel has been prescribed medication to help control the fits,although an optimum balance appears yet to be determined and the fits continue on a regular basis. Comment The medical view appears to favour ‘psychological’ rather than a ‘physio- logical’ explanation for Rachel’s fits. Rachel indicates that she feels she is being blamed for something she cannot control. Certainly, something 114 / BROTHERS AND SISTERS OF CHILDREN WITH DISABILITIES changed after Rachel had minor surgery and unfortunately the medical reaction, as reported, would locate ‘blame’ as her problem. If the psycho- logical explanation is accepted and the ‘fit’ is viewed as a reaction to stress or trauma, perhaps her difficulties are not a ‘medical’ condition in a psy- chological sense. This would clearly be a form of disability by association, arising from the perception that emulating disability increases the attention gained. However, whatever the causation of Rachel’s fits, and whether or not there is a medical acknowledgement that these are physio- logical in origins, the need for medication seems to offer some progress forward. Indeed such a need might enable Rachel to gain control of her ‘psychological’ difficulty. Perhaps there is an undetected physiological causation, but wherever the true explanation lies, Rachel is experiencing difficulties and needs help. As a sibling of a severely disabled sister Rachel might be viewed as someone seeking attention if the psychological explanation is accepted, and according to her behavioural indication her reactions could be considered as an expression of anger towards herself, linking to the concept of a negative overreaction to being the sibling of a severely disabled sister. The consequences of such a reaction can only be tested by enabling Rachel to gain the attention she needs in some other way: possibly by substituting her ‘bad’ experience with a more positively constructed one. Essentially Rachel needs more time for herself and more attention at home, and the latter should not always be directed through Susan. The probability is that there is some element of both the psychological and physiological in Rachel’s condition, and whether or not the fits are caused by some physiological dysfunction, perhaps as an unexpected consequence of surgery, the social element of the case, nevertheless, needs dealing with. Perhaps one-to-one attention, or involvement with a sibling group would help. Rachel needs to have her own identity reaffirmed as an individual in her own right, and to achieve this she may need professional assistance, irrespective of whether her fits are a result of surgery or a cry for help. SUPPORT SERVICES AND BEING EMPOWERED / 115 A need for assessment I am concerned, also, following research into family support (Burke and Cigno 1996) that family attitudes towards a son or daughter with disabili- ties might result in a family becoming isolated from a community, which might otherwise support it.
Diseases
- CDG syndrome type 3
- Ophthalmophobia
- Benign autosomal dominant myopathy
- CAHMR syndrome
- Schwartz Newark syndrome
- Lumbar malsegmentation short stature
- Panic disorder
This patient is likely to have a large deficit in total body potassium diabetes insipidus in dogs treatment cost cheap avapro 300 mg mastercard, and with hydration and insulin treatment diabetes alert dogs uk purchase avapro once a day, his serum potassium level will decrease diabetes clinical definition purchase avapro without prescription. Failure to adequately replace potassium can have severe consequences in patients with DKA, and potassium should be started immediately unless urine output is compromised or hyperkalemia exists. Administration of bicarbonate is not generally required in most cases of DKA and is generally reserved for treatment of severe acidosis (pH < 7. Studies have indicated that the use of bicarbonate does not affect the course of most cases of DKA, and there is some theoretical rationale for not using bicar- bonate unless clearly necessary. A 49-year-old man was referred from a walk-in clinic when he was discovered to have a blood glucose level of 246 mg/dl during evaluation of an acute GI syndrome. Subsequently, a diagnosis of diabetes was confirmed by a finding of fasting blood glucose values of 190 mg/dl and 176 mg/dl, measured when the patient was not ill. He has not received medical treatment or been evaluated for many years but reports being in generally good health. Perform 24-hour urine collection, obtain an estimate of his creati- nine clearance, and measure total protein excretion B. Measure the albumin-creatinine ratio on a spot urine sample C. Defer specific assessment because he has just been diagnosed, and diabetic nephropathy is unlikely to have developed D. Measure serum BUN and creatinine concentrations E. Perform renal ultrasound Key Concept/Objective: To know that urinary albumin excretion is the most sensitive means of detecting early diabetic nephropathy An abnormally high rate of albumin excretion is the earliest manifestation of diabetic nephropathy, and microalbuminuria can be detected well before changes in creatinine clearance and pathologic proteinuria occur. Microalbuminuria is predictive of the pro- gression of renal disease in most cases, and its occurrence marks the point in the course of nephropathy at which treatment is most efficacious. Therefore, all patients who are diagnosed with diabetes should undergo screening for renal albumin excretion. For patients with type 1 diabetes, formal evaluation can be deferred for several years because the time of disease onset is generally clear, and abnormalities in renal function do not occur during the first 5 years after onset. Patients with type 2 diabetes should be screened at the time of diagnosis because the time of onset of type 2 diabetes is often hard to discern, and asymptomatic hyperglycemia may have been present for several years. Screening for microalbuminuria can be done with a 24-hour urine collection, an overnight collection, a 4-hour timed collection, or a spot collection with determination of albumin-creatinine ratio. All these measures require a specific assay for albumin because standard clinical laboratory measurements of urinary protein are not sensitive enough to detect microalbuminuria. Diabetic nephropathy is usually quite advanced before changes in the BUN and serum creatinine levels occur. Although one of the ear- liest renal manifestations of diabetes is transient kidney enlargement, renal ultrasound is not useful for screening for diabetic nephropathy. A 52-year-old woman presents to the emergency department after experiencing 4 days of worsening men- tal status. Physical examination shows a somnolent, obese woman with dry mucous membranes. Results of laboratory studies are as follows: sodium concentration, 128 mEq/L; potassium concentration, 4. Which of the following would be the most appropriate intervention in the care of this patient? Demeclocycline Key Concept/Objective: To be able to recognize hyperglycemic hyponatremia Hyperglycemia lowers the plasma sodium concentration; in the absence of insulin, glu- cose is an effective osmole that attracts water from cells and thereby dilutes extracellu- lar sodium. Therefore, the blood glucose level should always be examined when a low plasma sodium concentration is being evaluated. The plasma sodium concentration falls by approximately 3 mEq for every 200 mg/dl (10 mmol) increase in blood glucose and will increase by this amount when hyperglycemia is corrected with insulin. To eval- uate hyponatremia in the presence of hyperglycemia, the serum sodium concentration must be "corrected" for the osmotic effect of glucose. In this patient, the corrected sodi- um concentration is within normal limits, and the sodium value will normalize once the high glucose level is treated. Hypertonic fluid, fluid restriction, loop diuretics, and demeclocycline can all be used in the management of hyponatremia, depending on the etiology of the problem. A 60-year-old man comes to your clinic for follow-up. His medications include levothyroxine and albuterol.
HAM characteristically leads to a deterioration of cognitive function 7 INFECTIOUS DISEASE 97 Key Concept/Objective: To understand the various clinical manifestations of HTLV-I infection HTLV-I only infrequently becomes established as a latent infection with expression of viral gene products diabetes type 2 explained simply discount avapro amex. The virus thus has a very low level of disease penetrance diabetes test yourself order avapro 300 mg free shipping. One manifestation of HTLV-I infection is adult T cell leukemia (ATL) diabetes type 1 kosthold cheap avapro 300 mg with mastercard. Four clinical types have been described: acute, lymphomatous, chronic, and smoldering. Acute ATL is characterized by a short clinical prodrome with an average of 2 weeks between the onset of symptoms and diagnosis. The clinical picture is characterized by rapidly progressive skin lesions, pulmonary infiltrates, and diarrhea. Patients with acute ATL have abnormal circulating lymphocytes with little lymphadenopathy. Lymphomatous ATL, the second most common type, accounting for 20% of cases, presents as lym- phadenopathy in the absence of abnormal circulating cells. Both acute ATL and lym- phomatous ATL are associated with hypercalcemia, not hypocalcemia. The other major manifestation of HTLV-I infection is HAM. At onset, symptoms include weakness or stiffness in one or both legs, back pain, and urinary incontinence. On examination, patients characteristically have hyperreflexia, ankle clonus, extensor plantar responses, and spastic paraparesis. A patient presents to you in clinic and states that he recently donated blood for the first time. He was informed by the blood bank that he may have HIV infection and was advised to seek medical care. After a thorough interview, you decide that he does not have risk factors for HIV. Which of the following is true regarding the serologic tests for diagnosing HIV infection? The blood supply in the United States is screened only for HIV-1 infection, because HIV-2 infection has not been reported in the United States B. The positive predictive value of a positive enzyme immunoassay (EIA) for HIV infection is the same in all patients tested C. Patients with positive EIA results and indeterminate results on Western blot assay can be retested in a year for definitive results E. Viral RNA detection is a more sensitive test for acute HIV infection than is detection of p24 antigenemia Key Concept/Objective: To understand various features of the tests used to diagnose acute and chronic HIV infection HIV-1 infection is far more common in the United States than is HIV-2 infection. However, cases of HIV-2 have been reported in the United States, generally in patients who were born in, had traveled to, or had a sex partner from western Africa. Thus, both HIV-1 and HIV-2 pose a danger to blood recipients. The positive predictive value of a positive result on EIA depends on the seroprevalence of HIV-1 antibody in the popula- tion from which the individual is being tested. Thus, in a patient with no risk factors, the positive predictive value is lower, necessitating a confirmatory test: the Western blot assay. The current generation of EIAs have shortened the estimated antibody-negative window period of primary infection to approximately 1 month or less. The results of Western blot assay are indeterminate in 4% to 20% of patients whose serum samples are repeatedly reactive on HIV-1 EIA. Many of these patients have recently undergone sero- conversion and should be followed very closely with repeat serologic testing to confirm or eliminate the diagnosis of HIV infection. Viral RNA detection is a more sensitive and specific way to diagnose acute HIV infection than is p24 antigenemia testing. A patient with HIV infection who is receiving retroviral therapy presents to you for the first time after being relocated by his employer. He has had HIV infection for 12 years; his first viral load was 100,000 copies/ml of plasma. He currently has a CD4+ T cell count of 400 cells/µl and a viral load of 10,000 copies/ml.