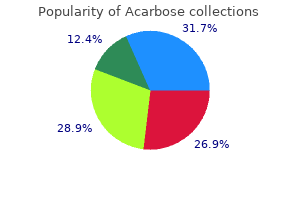
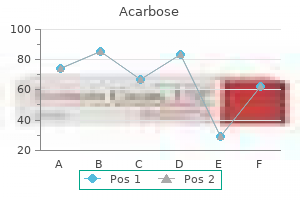
Acarbose
"Buy acarbose 50mg without a prescription, diabetes insipidus johns hopkins".
By: M. Copper, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Co-Director, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
Most of the middle sec- tion of the original fap is removed to allow the posterior wall of the fap and mucosal edge of the mucosal fap to be approximated diabetes type 2 drugs generic 25 mg acarbose fast delivery. The posterosuperior region of lacrimal and nasal mucosa is difcult to approximate because the middle turbinate holds the nasal mucosal fap away from the sidewall diabetes type 2 eating plan purchase 50 mg acarbose amex. In this region the agger nasi cell is opened and the mucosa from this cell approximated to this region of the lacrimal mucosa metabolic disease spine buy discount acarbose 25 mg. This results in a U-shaped fap and the surgeon should aim to achieve approximation of lac- rimal and nasal mucosa superiorly, posteriorly, and infe- riorly. This mucosal fap can be difcult to fashion with standard through-biting Blakesley forceps so the pediatric Fig. Approximating the lacrimal and nasal mucosa should result in a frst intention healing rather than a sec- posteriorly as possible through the sac wall (Fig. This ondary intention healing and should reduce the formation results in the largest possible anterior fap. The tip of the spear of granulation tissue and scarring and therefore lessen the knife is pushed into the tented sac wall just underneath the potential risk of closure of the sac and failure of the sur- region of the probe and the sac wall is opened using a rotating gery (Fig. Do not place the entire blade of the spear Next the tightness of the common canaliculus is evalu- knife into the sac but rather cut with the anterior two-thirds ated by placing a Bowman’s canalicular probe through the of the blade. If the common cana- lower releasing incisions in the anterior fap so that the fap liculus holds the probe tightly then lacrimal tubes should can be rolled out on the lateral nasal wall (Fig. If the gripping of incisions in the posterior fap and this fap is also rolled out the probe is equivocal then tubes are placed in patients with (Fig. For placement of tubes the puncta are dilated and To determine the width of the mucosal faps, the amount silastic lacrimal intubation tubes (O’Donoghue tubes) are of raw bone above and below the sac is estimated. Cadaveric dissection demonstrating the to ensure the largest possible anterior fap. Otolaryngol Clin N Am incision (C) posteriorly to allow for the largest anterior lacrimal fap. This allows mucosal apposition between the posterior raw bone above and below the opened lacrimal sac (block arrows). A spacer of loop of tubing is pulled in the medial canthus of the eye so silastic tubing is slid over the tubes and used to push the that the tubes are not tight (Fig. The silastic tubing is cut and the Gelfoam/MeroGel gently lifted of the faps and the posi- tion of the faps checked before it is replaced (Fig. This aids in clearing any residual blood clots and keeping the nasal cavity moist and clear of secretions. The patient is placed on broad-spectrum antibiotics for 5 days and antibiotic eye drops are used for 3 weeks. If O’Donoghue tubes were placed, they are removed in the clinic after 4 weeks and the patency of the nasolacrimal system checked by placing a drop of fuorescein in the conjunctiva and en- doscopically monitoring the fow of fuorescein from the conjunctiva to the nose. It is rare to see any granulations but if they are present they should be removed. Once fuorescein tomatic improvement, a complete absence of symptoms, or has been placed in the conjunctiva it should be visualized im- as an anatomically patent nasolacrimal system after surgery. The lac- suggest a common canaliculus problem but had otherwise rimal sac should be marsupialized and well healed forming normal canaliculi were included. Care is taken to ensure that tubes are not positioned too tight, making eye opening difcult. Of the 11 patients considered failures, six had an anatomically patent nasolacrimal system with a free fow of fuorescein from the conjunctiva to the nose (such as demonstrated in Fig. However, symp- tomatic patients are still classifed as failures even if the surgery was technically successful. In the anatomically obstructed group the success rate was 95% whereas in the functional group it was 81%. This functional group still had a 95% ana- tomical patency but a few patients with a patent system still had symptoms and were therefore classifed as failures. If success is defned as complete absence of symptoms with anatomical patency, functional obstruction of the lacrimal system does not have as good a prognosis as anatomical ob- struction and this should be kept in mind when consenting patients with functional obstruction. Results and Technique Modifcations in Revision group were under the age of 14 years.
Haemorrhage under the periosteum occurs • Rib fractures diabetes medications weight gain purchase acarbose 50mg visa, particularly axillary and posterior ribs easily in children managing diabetes during pregnancy order on line acarbose. The elevated periosteum lays down new • Metaphyseal fractures • Metaphyseal sclerosis bone diabetes symptoms runny nose buy discount acarbose on-line, which may be so extensive that it envelops the shaft, • Epiphyseal separation forming periosteal reactions. The fractures are recognized sites such as the inferior iliac spine from avul- caused by squeezing the baby and are thus usually seen in sion of the rectus femoris muscle or the ischium from avul- the axillary and posterior portions of the ribs. Contrast is therefore only used as part of skeletal surveys in suspected non-accidental routinely to evaluate vessels and extra-axial lesions or to injury or myeloma (Fig. However, to enable mation on the venous sinuses of the brain such as when good differentiation of grey and white matter, a slice thick- looking for thrombosis. The window settings are selected that can quantify the passage of contrast through the brain for brain tissue or bone, depending on the structure being to evaluate the presence and extent of infarction and ischae- assessed (see Fig. Contrast the ventricular system and subarachnoid space surround- enhancement of a brain lesion is therefore a consequence ing the brain. Multiple well-defned lytic lesions of various sizes are seen in all areas of the skull vault. Calcifcation is normally seen in the pineal gland and choroid plexus particularly in the lateral ventricles. The supratentorial regions are usually well shown, but details of the posterior fossa may be obscured by arte- fact from the surrounding bone. Abnormal head computed tomography When an abnormality is seen, it is important to decide whether it has an intra-axial or extra-axial location as the pathologies and therefore the differential diagnosis are very different. Intra-axial lesions can involve the white and grey matter structures of the brain parenchyma, while extra-axial lesions may involve the meninges, extracerebral spaces and skull vault. Specifc diagnoses are suggested by combining the clinical features with information about multiplicity, size, position and density of the lesion. Shift VertA of midline structures, such as the septum pellucidum, the third ventricle or the pineal gland away from a lesion indi- (i) cates a signifcant mass effect (Fig. Note how the oedema extends through the white matter but spares the overlying grey matter cortex. Both are associated with mass effect causing distortion of the lateral ventricles. Therefore, the anatomy is not limited (free) and does not produce any signal Brain 433 t * (a) (b) Fig. The lateral ventricles including the temporal horns (arrows) are dilated but the fourth ventricle (*) is normal in size. The hydrocephalus was due to a tumour (t) obstructing the aqueduct, which connects the third and fourth ventricles. Each sequence has to be acquired separately so the fusion within a cystic mass is also relatively specifc for pus overall scan time is much longer, during which the patient within a pyogenic abscess. Any therefore fow more rapidly in the direction of the axon intracranial ferrous metal present such as aneurysm clips bundle. An advance in diffusion imaging uses this feature or cochlear implants are absolute contraindications. The technique may be useful in understanding appear white) on T1-weighted images (see Box 15. Neurosonography It is relatively simple to scan the heads of neonates using ultrasound to obtain images of the ventricular system and brain (Fig. Scanning is done through the open fon- tanelle where there is no bone to impede the transmission of the ultrasonic waves. No sedation is required and the procedure is readily carried out even on intensive care units. Neurosonography has proved particularly useful in detecting intracranial haemorrhage, which premature babies are more prone to (Fig. It has also been used to demonstrate the presence of congenital abnormalities of the brain. When the fontanelle closes it is still possible to perform Doppler studies through the thin pterygon region of the skull to assess the fow of blood through the major intracranial arteries such as in intracranial stenosis. Courtesy of Dr Maddigan, St George’s Hospital, Of all brain tumours, approximately one-third are gliomas, London.
They receive lemniscal fbers Clinical and their collaterals diabetic diet kidney disease order acarbose 25mg on line, and these nuclei send axons Connection Clinical Two tuning fork tests may be used Connection to determine the types of deaf- ness blood glucose 90 purchase discount acarbose. The Weber tuning fork test is performed Conduction deafness results from by placing the stem of a vibrating tuning fork any interference with the passage at the middle of the forehead and asking the of sound waves through the external or mid- patient in which ear the tone is heard blood glucose procedure discount acarbose 50mg free shipping. Bone conduction patient with normal hearing, the tone is per- (transmission of sound waves through the cra- ceived equally in both ears. Therefore, conduc- unilateral nerve deafness hears the tone in the tion deafness is never complete or total. Sensorineural deafness primarily results from The patient with a unilateral conduction deaf- damage to the hair cells of the spiral organ, ness hears the tone louder in the affected ear. A The defect or damage is in the portion of the vibrating tuning fork is held near the patient’s auditory mechanism common to both air and auricle (air conduction) until it can no longer be bone conduction, and therefore, hearing fail- heard. The degree of fork is placed in contact with the mastoid pro- hearing loss is, of course, related to the amount cess (bone conduction). The spiral organ (of Corti) M me e n Cochlear duct di i a s Endolymph l c Cochlear m u s nerve Medulla Restiform body Scala tympani Bipolar primary Spiral Inner Outer auditory ganglion Dendrites hair hair neuron of spiral cells cells ganglion Supporting Basilar cells cells membrane Figure 12-4 Schematic diagram showing auditory paths. Chapter 12 The Auditory System: Deafness 167 13 14 11 Medial geniculate nucleus 12 2 7 1 15 Rostral midbrain / Posterior thalamus Brachium of Commissure of inferior colliculus inferior colliculus Inferior colliculus 2 10 9 7 16 1 Caudal midbrain 8 6 Lateral lemniscus Superior olivary nucleus 5 1. Decussation of superior 1 cerebellar peduncle Rostral medulla Figure 12-5 Transverse sections showing locations and relations of auditory pathways. Where in the auditory system does a superior olivary and trapezoid nuclei, as well as unilateral lesion produce total deafness in the adjacent reticular formation, terminates on the ipsilateral ear? As an acoustic neurinoma on the tory feedback system provides a mechanism for vestibular nerve in the internal acoustic regulating selective attention to certain sounds. Contrast conduction deafness and neural Hearing loss may be treated with deafness. Conduction deafness must result from The implants consist of stimulating electrodes damage to the: implanted in the auditory cortex, cochlear a. A patient with the inability to recognize hair cells in the spiral organ can beneft from the source of sounds may be expected to a cochlear implant. An external microphone have damage to which of the following picks up environmental sounds, which are nuclei? Using tuning forks, an cochlear nerve transmit action potential sig- examiner can inexpensively determine nals into the brain where they are recognized the type of deafness and laterality. The “hearing” through a cochlear When the vibrating tuning fork is placed implant is different from normal hearing and at the middle of the forehead, the patient requires the implanted patients to relearn how does not perceive the tone equally in the to translate the novel sounds into conversation. When the vibrating tuning fork is held next to the Chapter Review ears, it is heard much louder and longer on the left than on the right. When the Questions tuning fork is placed against the mastoid process on the right side, the sound is 12-1. Frequency (tone) and intensity (loudness) right side of an auditory stimulus is primarily d. Similar irrigation in a second comatose patient results in one eye turning up and out and the other eye turning down and in. In other words, the ves- Equilibrium depends upon input from three tibular system is intimately involved in motor sources: visual, proprioceptive, and vestibular. Equilibrium can be maintained by any two All vestibular activity is refex in nature and of these inputs, but not by only one. In cases of exces- readily demonstrated in a person whose proprio- sive vestibular stimulation or when an imbalance ceptive paths in the spinal cord have degenerated, exists between input from the right and left sides, commonly due to pernicious anemia. The cortical area associated with case, when the person closes the eyes or is in a vertigo is in the postcentral gyrus at the base of dark room, equilibrium will be lost because of the the intraparietal sulcus. Clinical The vestibular system has strong connections Connection with the cerebellum and with autonomic centers in the reticular formation as occur in motion sick- When a person with the loss of ness. In addition, strong commissural connections awareness of the position of the between the right and left vestibular nuclei exist lower limbs stands with the feet close together and play a key role in the compensatory mecha- and closes the eyes, swaying and falling occurs. The maculae are The receptors that respond to linear acceleration oriented at right angles to each other, with that or position of the head, as well as the receptors of the utricle being almost in the horizontal plane that respond to rapid rotation of the head, are and that of the saccule in almost the sagittal plane. Linear acceleration or changes in position of the The vestibular parts of the bony labyrinth consist head in any direction stimulate a macula on each of the vestibule and semicircular canals.
Competitive Sports Given the high-risk nature of this population diabetes prevention campaign in malaysia buy cheap acarbose on line, restriction from any competitive sport is probably warranted diabetes signs of low sugar acarbose 25 mg on line. Special circumstances may occur when participation in low static and dynamic sports may be considered on an individual basis for Class 1 patients diabetes type 1 amputation purchase discount acarbose on-line. There are, however, no significant data that would allow accurate assessment of risk for an individual patient. Heart Transplantation Exercise capacity as measured by both aerobic capacity and musculoskeletal strength is significantly decreased in the pediatric population following heart transplantation. These values are not significantly different from those reported in the adult population. The reasons for this finding appear to be due to both central and peripheral factors combining to impair aerobic capacity. This may be due to systolic impairment but more importantly to diastolic dysfunction with high cardiac filling pressures. Abnormalities of autonomic innervation and function also impact on cardiac output during exercise. This significantly decreases chronotropic reserve and blunts the time course of the chronotropic response. There is some evidence for reinnervation and improved chronotropy late after transplant in some patients or as a response to cardiac training (discussed below). In addition to the cardiac effects, autonomic tone is abnormal in the peripheral vasculature. Limitations of the peripheral exercising musculature are likely at least as important as central mechanisms in limiting aerobic capacity. Following heart transplant, skeletal muscle mass is often reduced by 20% of normal. This may reflect the marked deconditioning in these patients that occurs prior to transplantation but may also be the result of immunosuppressant therapy. These changes result in an impaired ability of the exercising muscle to extract oxygen. Muscle strength is significantly impaired, especially in the early transplant period. Use of ongoing immunosuppressant medications may continue to exacerbate the problem of demineralization. Serial studies of exercise performance following pediatric heart transplant are limited. The reason for these discrepant findings are unclear but are probably the combined improvement of systolic and especially diastolic function in the immediate posttransplant period as well as the longer-term improvement in musculoskeletal conditioning, even in the absence of formal rehabilitation. In addition, improved chronotropy suggests at least some patients benefit from autonomic reinnervation of the donor heart. There are no significant data on the risks and benefits of exercise training in pediatric heart transplant recipients. Studies in adults consistently show significant improvement in maximal aerobic capacity. There is also some evidence from small studies that suggest that high-intensity interval training is more effective in this population than prolonged moderate intensity training (187,188,189,190,191,192). Principle for Recreational Activities and Exercise Training in Children After Heart Transplantation without Coronary Artery Disease F. Exercise aims at correct technique and running, cycling, running breathing pattern to avoid the Valsalva maneuver. Safety and feasibility of inpatient exercise training in pediatric heart failure: a preliminary report. They should be evaluated for physical activity by physicians and healthcare providers who have specialized knowledge in this area. Assessment of systolic and diastolic function by echocardiography and cardiac catheterization is routine in this population and should be a part of any preparticipation evaluation. As the period of time from transplantation lengthens, the risk for development of graft dysfunction and, most importantly, coronary graft vasculopathy increases. Routine exercise testing, myocardial perfusion imaging, and even selective coronary angiography are essential parts of screening to assure safe participation in physical activity. Unlike many congenital cardiac conditions, following heart transplantation, noncardiac medical issues may be just as important as cardiac functioning in determining the ability to perform certain activities.